filmov
tv
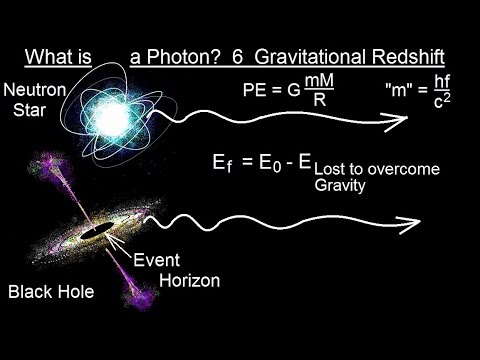
Particle Physics (22 of 41) What is a Photon? 6. Gravitational Redshift

Показать описание
In this video I will explain how photon is affected by gravity can lose or gain energy.
Next video in the Particle Physics series can be seen at:
Particle Physics (22 of 41) What is a Photon? 6. Gravitational Redshift
Particle Physics (23 of 41) What is a Photon? 7. Cosmic Microwave Background
Particle Physics (38 of 41) What is a Photon? 22. UV Rays - How Do We Get Sunburns?
Particle Physics (34 of 41) What is a Photon? 18. Amplitude vs Intensity - How 'Big' is a ...
Particle Physics (20 of 41) What is a Photon? 4. Pair Production
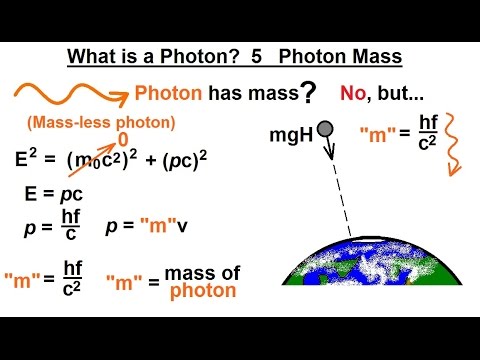
Particle Physics (21 of 41) What is a Photon? 5. Photon Mass (or No Mass)
Particle Physics (41 of 41) What is a Photon? 25. Atmospheric Water Vapor Absorption
Particle Physics (40 of 41) What is a Photon? 24. Atmospheric CO2 Atmosphere
Particle Physics (17 of 41) What is a Photon?
Particle Physics (1 of 41) The Atom: 'What Is It?'
Particle Physics (25 of 41) What is a Photon? 9. Compton Scattering
Particle Physics (33 of 41) What is a Photon? 17. Mie Scattering - Radio Waves vs Sunlight
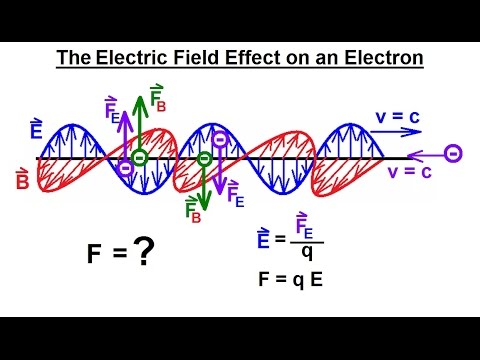
Particle Physics (36 of 41) What is a Photon? 20. The Electric Field
Particle Physics (16 of 41) Elementary Particles: How Are Mesons Made From Quarks?
Particle Physics (2 of 41) The Structure of Atoms
Particle Physics (27 of 41) What is a Photon? 11. Volume (Density) of Photons
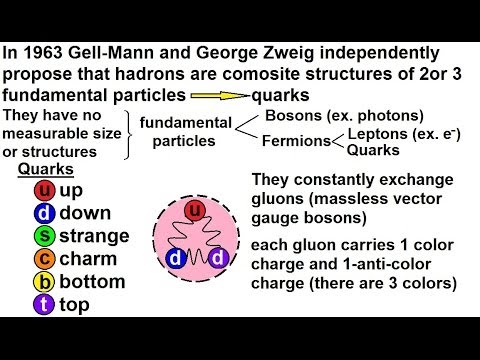
Particle Physics (13 of 41) Elementary Particles: What Is A Quark? (Part 1)
Particle Physics (14 of 41) Elementary Particles: What Is A Quark? (Part 2)
Particle Physics (32 of 41) What is a Photon? 16. Mie Scattering - Radio Waves Quantized as Photons?
Particle Physics (19 of 41) What is a Photon? 3. The Photoelectric Effect (Einstein's Nobel Pri...
Particle Physics (39 of 41) What is a Photon? 23. How Does a Microwave Oven Heat Food?
Particle Physics (6 of 41) The Nuclear Strong Force
Particle Physics (3 of 41) Quantum Mechanics and Special Relativity
Particle Physics (24 of 41) What is a Photon? 8. How Are X-Rays Produced?
Комментарии
 0:05:07
0:05:07
 0:06:01
0:06:01
 0:07:45
0:07:45
 0:09:47
0:09:47
 0:06:02
0:06:02
 0:05:30
0:05:30
 0:03:31
0:03:31
 0:09:08
0:09:08
 0:13:15
0:13:15
 0:05:28
0:05:28
 0:12:52
0:12:52
 0:10:19
0:10:19
 0:06:44
0:06:44
 0:04:03
0:04:03
 0:06:53
0:06:53
 0:09:58
0:09:58
 0:09:22
0:09:22
 0:06:51
0:06:51
 0:12:01
0:12:01
 0:05:07
0:05:07
 0:03:34
0:03:34
 0:05:50
0:05:50
 0:06:08
0:06:08
 0:07:47
0:07:47