filmov
tv
Particle Physics (6 of 41) The Nuclear Strong Force

Показать описание
In this video I will explain the nuclear strong force.
Next video in the Particle Physics series can be seen at:
Particle Physics (6 of 41) The Nuclear Strong Force
Particle Physics (22 of 41) What is a Photon? 6. Gravitational Redshift
Particle Physics (15 of 41) Elementary Particles: How Are Baryons Made From Quarks?
Particle Physics (14 of 41) Elementary Particles: What Is A Quark? (Part 2)
Particle Physics (7 of 41) The Electromagnetic Force
Particle Physics (16 of 41) Elementary Particles: How Are Mesons Made From Quarks?
Particle Physics (23 of 41) What is a Photon? 7. Cosmic Microwave Background
Particle Physics (41 of 41) What is a Photon? 25. Atmospheric Water Vapor Absorption
Particle Physics (13 of 41) Elementary Particles: What Is A Quark? (Part 1)
Particle Physics (4 of 41) The Pion: What Is It?
Particle Physics (9 of 41) The Gravitational Force
Particle Physics (36 of 41) What is a Photon? 20. The Electric Field
Particle Physics (17 of 41) What is a Photon?
Particle Physics (5 of 41) The 4 Fundamental Forces of Nature
Particle Physics (1 of 41) The Atom: 'What Is It?'
Particle Physics (8 of 41) The Weak Force
Particle Physics (38 of 41) What is a Photon? 22. UV Rays - How Do We Get Sunburns?
Discover the Wonders of Physics org! #facts #space #astronomy #mystery
ALL of AQA Particle Physics in 42 minutes | A Level Physics Revision
Particle Physics (34 of 41) What is a Photon? 18. Amplitude vs Intensity - How 'Big' is a ...
Particle Physics (25 of 41) What is a Photon? 9. Compton Scattering
Gravity in Particle Physics
Particle Physics (24 of 41) What is a Photon? 8. How Are X-Rays Produced?
JEE Aspirants ka Sach 💔 #JEE #JEEMain #Shorts
Комментарии
 0:05:50
0:05:50
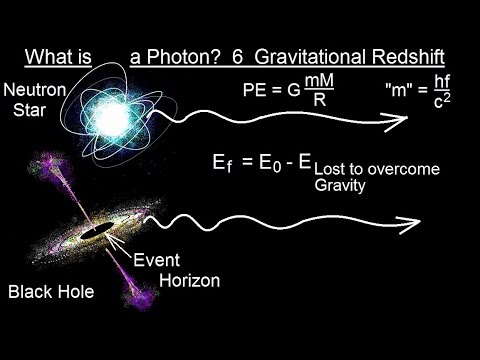 0:05:07
0:05:07
 0:06:27
0:06:27
 0:06:51
0:06:51
 0:10:34
0:10:34
 0:04:03
0:04:03
 0:06:01
0:06:01
 0:03:31
0:03:31
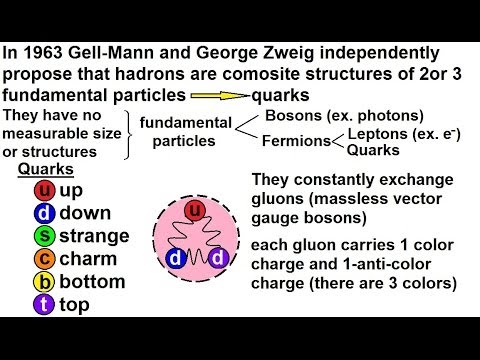 0:09:22
0:09:22
 0:09:41
0:09:41
 0:08:02
0:08:02
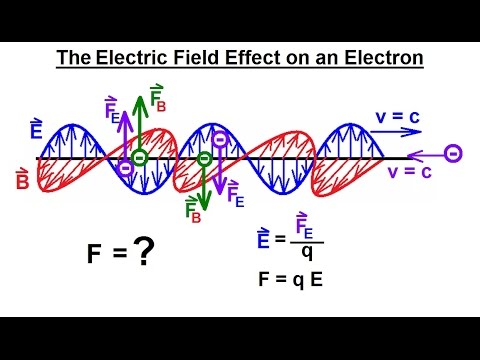 0:06:44
0:06:44
 0:13:15
0:13:15
 0:05:08
0:05:08
 0:05:28
0:05:28
 0:05:16
0:05:16
 0:07:45
0:07:45
 0:00:41
0:00:41
 0:42:41
0:42:41
 0:09:47
0:09:47
 0:12:52
0:12:52
 0:13:45
0:13:45
 0:07:47
0:07:47
 0:00:12
0:00:12