filmov
tv
PID Controller Explained

Показать описание
▶ You can read the full post here
⌚Timestamps:
00:00 - Intro
00:49 - Examples
02:21 - PID Controller
03:28 - PLC vs. stand-alone PID controller
03:59 - PID controller parameters
05:29 - Controller tuning
06:20 - Controller tuning methods
=============================
In this video, we’re going to talk about the PID Controller and its transformation from a single station device to what it has evolved into today. We’re going to explain why PID Controllers are used in industrial processes.
We’ll illustrate how Controller settings affect different processes under control. We’ll also provide an overview of Controller Tuning.
Let’s start with a discussion about home temperature control.
If the room temperature is below the setpoint, the furnace is turned ON. When the room temperature increases above the setpoint, the furnace turns OFF.
This type of control is referred to as ON/OFF or Bang-Bang Control. The temperature is not exactly held at the setpoint of 70°F, but cycles above and below the setpoint.
ON/OFF control may be ok for your house, but it is not ok for industrial processes or motion control. Let’s look at an example of tank level control to explain why.
The Valve fills the tank as the pump drains it. If the valve is operated with ON/OFF control, the water will fluctuate around the 50% setpoint. For our purpose, let’s say the fluctuation is ±10%. In most industrial applications, this fluctuation around the setpoint is not acceptable.
What if it’s possible to throttle the valve and place it in any position between ON and OFF?
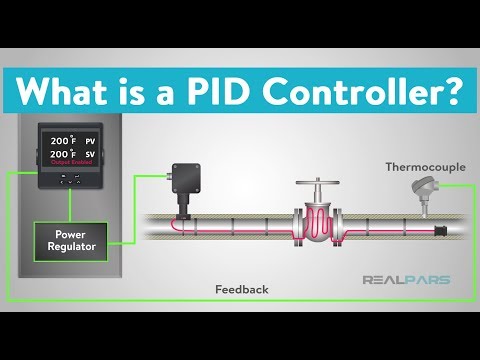
Let’s look at how a PID Controller fits into a feedback control loop. The Controller is responsible for ensuring that the Process remains as close to the desired value as possible regardless of various disruptions.
The controller compares the Transmitter Process Variable (PV) signal, and the Setpoint.
Let’s refer to the difference between the Process Variable and the Setpoint as the Error signal.
Based on that comparison, the controller produces an output signal to operate the Final Control Element. This PID Controller output is capable of operating the Final Control Element over its entire 100% range.
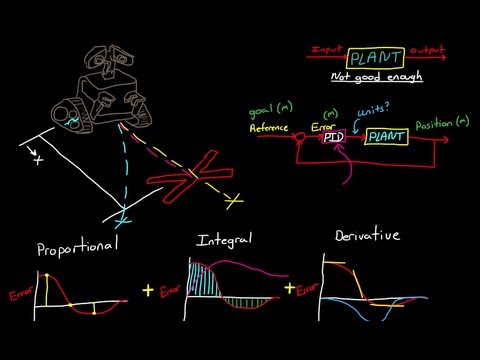
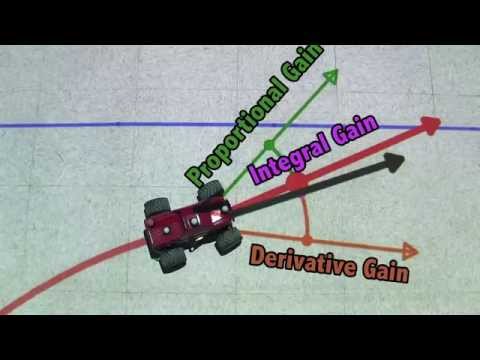
The PID controller determines how much and how quickly correction is applied by using varying amounts of Proportional, Integral, and Derivative action. Each block contributes a unique signal that is added together to create the controller output signal.
- The proportional block creates an output signal proportional to the magnitude of the Error Signal.
Unfortunately, the closer you get to the setpoint, the less it pushes. Eventually, the process just runs continuously close to the setpoint, but not quite there.
- The integral block creates an output proportional to the duration and magnitude of the Error Signal. The longer the error and the greater the amount, the larger the integral output.
As long as an Error exists, Integral action will continue.
- The derivative block creates an output signal proportional to the rate of change of the error signal. The faster the error changes, the larger the derivative output.
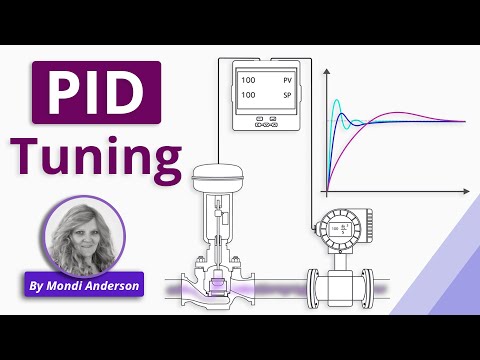
Derivative control looks ahead to see what the error will be in the future and contributes to the controller output accordingly. That brings us to a term called Controller Tuning.
There are many different manual methods for tuning a controller that involves observing the process response after inflicting controller setpoint changes.
One method involves increasing the amount of setpoint change and repeating the procedure until the process enters a state of steady-state oscillation.
Most process controllers, PLC, and DCS loop controllers sold today have Autotuning capability.
The PID controller learns how the process responds to a change in setpoint, and suggested PID settings.
=============================
=============================
Missed our most recent videos? Watch them here:
=============================
=============================
=============================
#RealPars #PID #IndustrialAutomation
Комментарии
 0:09:25
0:09:25
 0:05:39
0:05:39
 0:07:44
0:07:44
 0:22:19
0:22:19
 0:11:42
0:11:42
 0:49:18
0:49:18
 0:13:07
0:13:07
 0:27:11
0:27:11
 0:04:51
0:04:51
 0:08:43
0:08:43
 0:14:13
0:14:13
 0:08:10
0:08:10
 0:13:10
0:13:10
 0:07:08
0:07:08
 0:13:13
0:13:13
 0:02:58
0:02:58
 0:09:56
0:09:56
 0:07:33
0:07:33
 0:03:53
0:03:53
 0:10:33
0:10:33
 0:04:41
0:04:41
 0:10:44
0:10:44
 0:16:15
0:16:15
 0:08:10
0:08:10