filmov
tv
Degenerative diseases causing chronic low back pain

Показать описание
This is a short survey of degenerative diseases that can cause chronic low pain
ADDITIONAL TAGS:
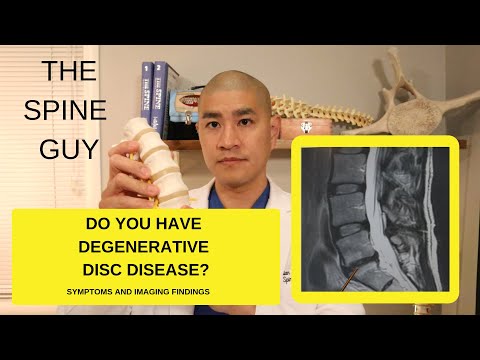
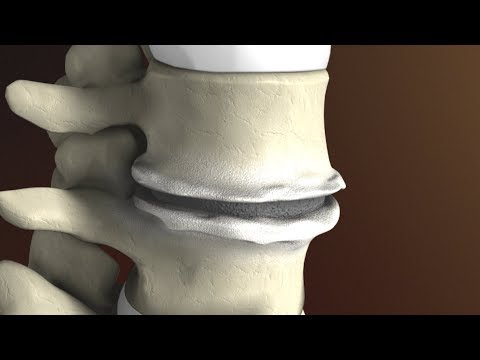
Discogenic disease (Degenerative disc disease)
Etiology: catabolic activity and/or mechanical disruption (trauma)
Pathophys: compress nerve root; release inflammatory mediators → axial + uni/bilateral radicular symptoms → +/- decreased sensation, strength, reflexes
Rule out cauda equina (saddle anesthesia, urinary/bowel incontinence
Tests: straight leg raise; slump test
Facet arthropathy:
Arthritic disease of zygapophyseal joints (Z-joints), which articulate btwn vertebral bodies
Sx: non radiating axial back pain +/- referred pain to flank or thigh
Provoked by facet loading (lumbar extension and rotation to affected side)
Sacroiliac joint dysfunction:
SIJ are synovial-fibrous joints that transmit force from spine to pelvis to lower extremities
Sx: low back pain, usually worse on one side
Can be caused by arthritis, spondyloarthropathy, pregnancy
Tests: hip flexion/abduction/external rotation (FABER); pelvis compression; posterior superior iliac spine (PSIS) palpation; Gaenslen test
Spinal stenosis:
Pathophys: degenerative disease → progressive narrowing of spinal canal (+/- subarticular recesses and neural foramina) → impinge on spinal cord +/- nerve root → inflam, pain, dysfunction
Sx: neurogenic claudication +/- lower extrem weakness with lumbar extension, relieved with flexion (shopping cart sign)
Muscle sprain:
Often paraspinal muscle, often following injury/exercise
Painful, reproducible spasticity on palpation
Also consider: spondylolisthesis, spondylolysis, myelopathy, osteomyelitis, malignancy
ADDITIONAL TAGS:
Discogenic disease (Degenerative disc disease)
Etiology: catabolic activity and/or mechanical disruption (trauma)
Pathophys: compress nerve root; release inflammatory mediators → axial + uni/bilateral radicular symptoms → +/- decreased sensation, strength, reflexes
Rule out cauda equina (saddle anesthesia, urinary/bowel incontinence
Tests: straight leg raise; slump test
Facet arthropathy:
Arthritic disease of zygapophyseal joints (Z-joints), which articulate btwn vertebral bodies
Sx: non radiating axial back pain +/- referred pain to flank or thigh
Provoked by facet loading (lumbar extension and rotation to affected side)
Sacroiliac joint dysfunction:
SIJ are synovial-fibrous joints that transmit force from spine to pelvis to lower extremities
Sx: low back pain, usually worse on one side
Can be caused by arthritis, spondyloarthropathy, pregnancy
Tests: hip flexion/abduction/external rotation (FABER); pelvis compression; posterior superior iliac spine (PSIS) palpation; Gaenslen test
Spinal stenosis:
Pathophys: degenerative disease → progressive narrowing of spinal canal (+/- subarticular recesses and neural foramina) → impinge on spinal cord +/- nerve root → inflam, pain, dysfunction
Sx: neurogenic claudication +/- lower extrem weakness with lumbar extension, relieved with flexion (shopping cart sign)
Muscle sprain:
Often paraspinal muscle, often following injury/exercise
Painful, reproducible spasticity on palpation
Also consider: spondylolisthesis, spondylolysis, myelopathy, osteomyelitis, malignancy
 0:05:44
0:05:44
 0:21:39
0:21:39
 0:01:16
0:01:16
 0:05:59
0:05:59
 0:06:09
0:06:09
 0:11:21
0:11:21
 0:01:45
0:01:45
 0:05:02
0:05:02
 0:10:23
0:10:23
 0:03:21
0:03:21
 0:05:00
0:05:00
 0:03:25
0:03:25
 0:03:52
0:03:52
 0:01:00
0:01:00
 0:01:40
0:01:40
 0:00:35
0:00:35
 0:06:32
0:06:32
 0:00:40
0:00:40
 0:48:16
0:48:16
 0:08:13
0:08:13
 0:04:53
0:04:53
 0:00:49
0:00:49
 0:01:16
0:01:16
 0:00:32
0:00:32