filmov
tv
Forces between Molecules | A Level Chemistry | OCR, AQA, Edexcel

Показать описание
Our A-Level Chemistry Experts are here to help you ace A-Level Chemistry!
This week we are revising Forces between Molecules
A-Level Chemistry can be tough but fortunately we’ve made this tutorial to help you score the A* you need for questions on everything to do with Forces between Molecules.
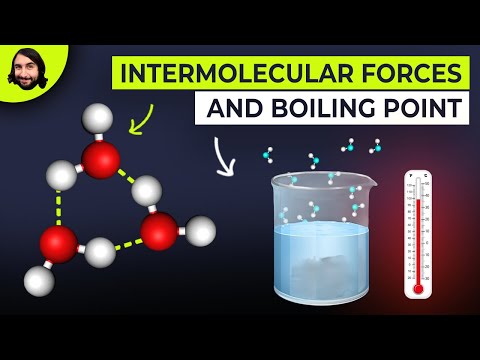
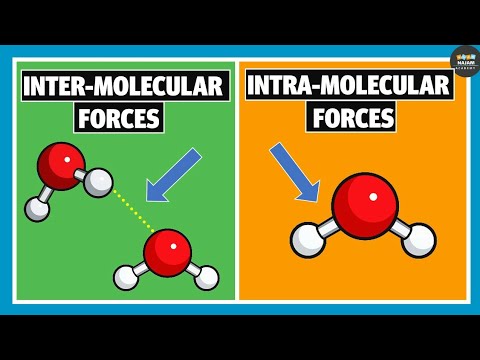
An intermolecular force is the force that arises from the interaction between molecules. Intermolecular attractions are not nearly as strong as the intramolecular attractions that hold compounds together (covalent or ionic bonds).
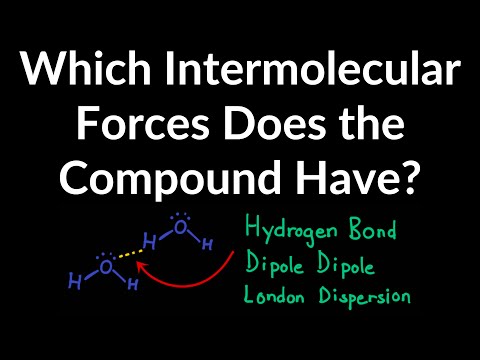
There are three main types of intermolecular force:
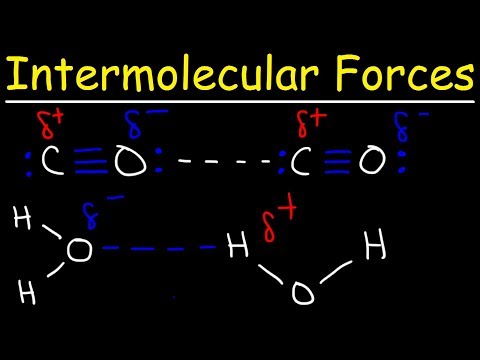
Permanent dipole-dipole forces
Induced dipole-dipole forces – Also known as van der Waals, dispersion or London forces.
Hydrogen bonding
Permanent dipole-dipole forces are the weak intermolecular forces of attraction that arise between permanently polar molecules. These forces are between the delta positive end of one polar bond with the delta negative end of another polar bond.
The more polar the molecules, the stronger the force of attraction between them.
If you charge a rod with a cloth by rubbing it and then place it next to water, the liquid will be attracted to the rod. This is because water is a polar liquid made up of polar molecules. The charges on the rod will attract the oppositely charged ions in water. For example if the rod is charged with negative charge, it will attract the delta positive charges of water.
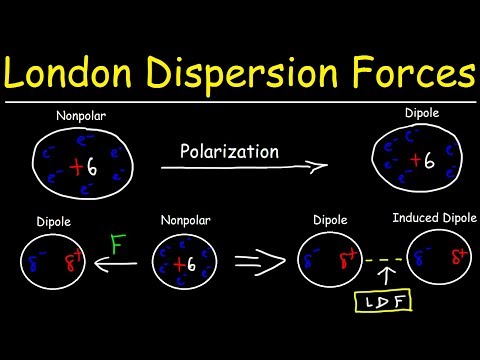
Induced dipole-dipole forces are weak intermolecular forces of attraction present between all atoms and all molecules that exist – whether polar or non-polar – as a result of the present of electrons in the molecule and the formation of temporary dipoles. They are the weakest type of intermolecular force.
When two atoms comes towards each other, the electron clouds of these atoms repel each other.
This causes a sudden displacement of electrons in one atom to one side causing the atom to have a temporary dipole: a transient asymmetry of charge distribution around an atom.
Once a temporary dipole is formed, it induces temporary dipoles in neighbouring atoms and molecules in a domino like effect. The two temporary dipoles are attracted towards each other by induced dipole- dipole forces also known as London or Van der Waals forces.
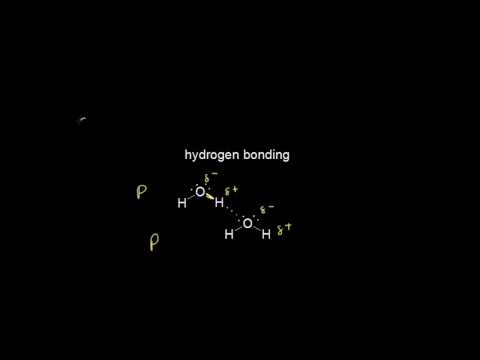
Hydrogen bonds are a special type of permanent dipole-dipole forces that only form when hydrogen forms a covalent bond with a very electronegative element: either nitrogen, oxygen or fluorine. They are the strongest type of intermolecular force.
As nitrogen, oxygen and fluorine are more electronegative hydrogen, they attract the electron pair in the covalent bond with hydrogen towards themselves. This forms a polar bond – hydrogen is δ+, and the other atom is δ-.
#ALevelChemistry #ALevelBiology #Biology #Chemistry #StudyMind
 0:10:54
0:10:54
 0:05:19
0:05:19
 0:05:37
0:05:37
 0:10:40
0:10:40
 0:08:07
0:08:07
 0:06:53
0:06:53
 0:07:01
0:07:01
 0:04:46
0:04:46
 0:08:05
0:08:05
 0:05:20
0:05:20
 0:11:36
0:11:36
 0:35:58
0:35:58
 0:21:25
0:21:25
 0:47:35
0:47:35
 0:04:25
0:04:25
 0:11:17
0:11:17
 0:04:23
0:04:23
 0:21:14
0:21:14
 0:10:38
0:10:38
 0:05:20
0:05:20
 0:08:36
0:08:36
 0:11:41
0:11:41
 0:03:08
0:03:08
 0:32:50
0:32:50