filmov
tv
How To Enable UEFI Bios Mode | Convert MBR Drives Format To GPT Using CMD

Показать описание
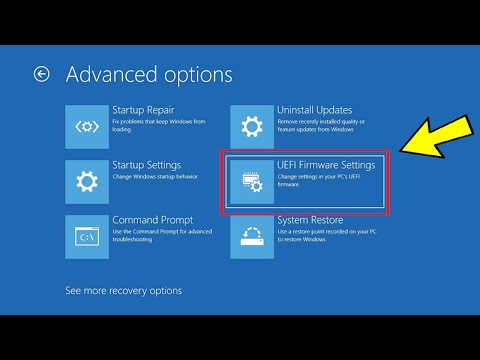
Legacy BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) and UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface) are two different firmware interfaces that are used to boot up the operating system and manage the hardware on a computer.
The main differences between Legacy BIOS and UEFI are:
Age: Legacy BIOS has been around since the 1980s, while UEFI was introduced in the late 1990s.
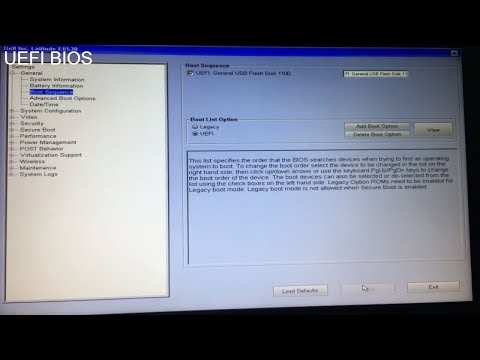
Booting: Legacy BIOS uses a Master Boot Record (MBR) partitioning scheme to boot up the operating system, while UEFI uses a GUID Partition Table (GPT) partitioning scheme.
Security: UEFI provides more secure boot process than legacy BIOS, which can be vulnerable to malware attacks.
Compatibility: Legacy BIOS is compatible with older hardware and operating systems, while UEFI requires more modern hardware and operating systems.
Features: UEFI supports features such as faster boot times, larger disk support, secure boot, and advanced power management, which are not supported by Legacy BIOS.
Overall, UEFI is considered the better option for modern computers because of its improved security features, faster boot times, and support for larger disk sizes. However, Legacy BIOS is still widely used on older hardware and is supported by older operating systems.
MBR (Master Boot Record) and GPT (GUID Partition Table) are two different partitioning schemes used to partition a hard drive. The main differences between MBR and GPT are:
1. Size: MBR supports up to 2 TB of hard drive space, while GPT can support up to 9.4 zettabytes (which is a lot more than the current maximum hard drive capacity).
2. Partitioning: MBR allows for a maximum of four primary partitions or three primary partitions and an extended partition, which can then be divided into logical partitions. GPT allows for up to 128 partitions.
3. Booting: MBR uses a boot loader to boot up the operating system, while GPT uses an EFI (Extensible Firmware Interface) system partition to boot up the OS.
4. Compatibility: MBR is supported by most older operating systems, while GPT is only supported by newer operating systems such as Windows 10, macOS, and Linux.
Overall, if you have a hard drive larger than 2 TB, you will need to use GPT partitioning. Otherwise, MBR will suffice.
DISCLAIMER: This Channel Does Not Promote Any illegal content, all contents provided by This Channel is meant for EDUCATIONAL purpose only. Copyright Disclaimer Under Section 107 of the Copyright Act 1976, allowance is made for "fair use" for purposes such as criticism, comment, news reporting, teaching, scholarship, and research.Fair use is a use permitted by copyright statute that might otherwise be infringing.Non-profit, educational or personal use tips the balance in favor of fair use.
Want to Promote Your Product ? Website ? or app ?
Sponsor My Video Now !
#gptdriveformat #mbrdriveformat #howtofix #legacybios #uefibios #microsoftwindows #mbrvsgpt #lagacyvsuefi #mudassirrehman
The main differences between Legacy BIOS and UEFI are:
Age: Legacy BIOS has been around since the 1980s, while UEFI was introduced in the late 1990s.
Booting: Legacy BIOS uses a Master Boot Record (MBR) partitioning scheme to boot up the operating system, while UEFI uses a GUID Partition Table (GPT) partitioning scheme.
Security: UEFI provides more secure boot process than legacy BIOS, which can be vulnerable to malware attacks.
Compatibility: Legacy BIOS is compatible with older hardware and operating systems, while UEFI requires more modern hardware and operating systems.
Features: UEFI supports features such as faster boot times, larger disk support, secure boot, and advanced power management, which are not supported by Legacy BIOS.
Overall, UEFI is considered the better option for modern computers because of its improved security features, faster boot times, and support for larger disk sizes. However, Legacy BIOS is still widely used on older hardware and is supported by older operating systems.
MBR (Master Boot Record) and GPT (GUID Partition Table) are two different partitioning schemes used to partition a hard drive. The main differences between MBR and GPT are:
1. Size: MBR supports up to 2 TB of hard drive space, while GPT can support up to 9.4 zettabytes (which is a lot more than the current maximum hard drive capacity).
2. Partitioning: MBR allows for a maximum of four primary partitions or three primary partitions and an extended partition, which can then be divided into logical partitions. GPT allows for up to 128 partitions.
3. Booting: MBR uses a boot loader to boot up the operating system, while GPT uses an EFI (Extensible Firmware Interface) system partition to boot up the OS.
4. Compatibility: MBR is supported by most older operating systems, while GPT is only supported by newer operating systems such as Windows 10, macOS, and Linux.
Overall, if you have a hard drive larger than 2 TB, you will need to use GPT partitioning. Otherwise, MBR will suffice.
DISCLAIMER: This Channel Does Not Promote Any illegal content, all contents provided by This Channel is meant for EDUCATIONAL purpose only. Copyright Disclaimer Under Section 107 of the Copyright Act 1976, allowance is made for "fair use" for purposes such as criticism, comment, news reporting, teaching, scholarship, and research.Fair use is a use permitted by copyright statute that might otherwise be infringing.Non-profit, educational or personal use tips the balance in favor of fair use.
Want to Promote Your Product ? Website ? or app ?
Sponsor My Video Now !
#gptdriveformat #mbrdriveformat #howtofix #legacybios #uefibios #microsoftwindows #mbrvsgpt #lagacyvsuefi #mudassirrehman
 0:05:44
0:05:44
 0:01:03
0:01:03
 0:00:23
0:00:23
 0:00:08
0:00:08
 0:00:48
0:00:48
 0:01:58
0:01:58
 0:03:26
0:03:26
 0:02:57
0:02:57
 0:04:58
0:04:58
 0:06:06
0:06:06
 0:06:21
0:06:21
 0:03:58
0:03:58
 0:01:03
0:01:03
 0:02:02
0:02:02
 0:18:47
0:18:47
 0:07:12
0:07:12
 0:01:21
0:01:21
 0:02:04
0:02:04
 0:04:27
0:04:27
 0:04:03
0:04:03
 0:00:58
0:00:58
 0:00:54
0:00:54
 0:02:03
0:02:03
 0:05:36
0:05:36