filmov
tv
VECTOR example grad(div F) at point (2,-1,0) (PART-4)

Показать описание
In this video explaining VECTOR example grad(div F).
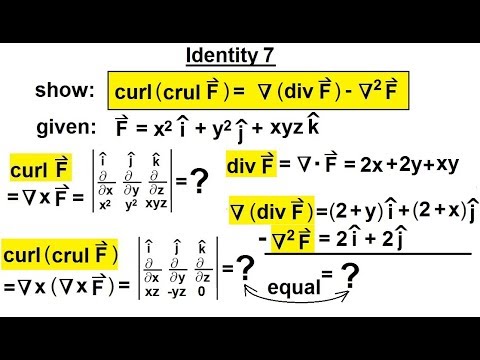
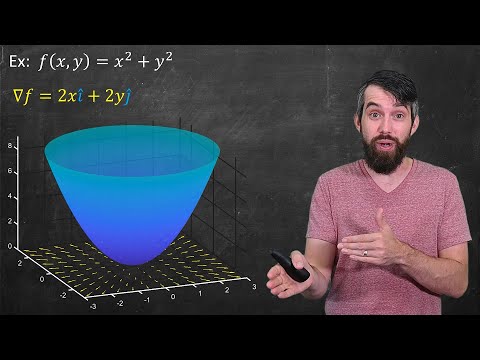
Note that the gradient of a scalar field is a vector field that points in the direction of the steepest increase of the scalar field and its magnitude represents the rate of change of the scalar field in that direction. In this case the gradient ∇f at any point (x y z) gives the direction of maximum increase of the scalar field f and its magnitude represents the rate of change of f in that direction.
#vector #scalarvector
18MAT21 MODULE 1:Vector Calculus
18MAT21 MODULE 2:Differential Equation higher order
18MAT21 MODULE 3: Partial differential equations
18MAT21 MODULE 4: Infiinite series & Power series solution
18MAT21 MODULE 5: Numerical methods
18MAT11 Module1: Differential Calculus1
18MAT11 Module2: differential Calculus2
18MAT11 Module4: Ordinary differential equations
Linear Algebra: 18MAT11 MODULE 5
LAPLACE TRANSFORM : 18MAT31
Fourier Transforms Z-transform : 18MAT31 & 17MAT31
Fourier Series: 18MAT31 & 17MAT31
Calculus of Variation & Numerical Methods 18MAT31
Numerical Methods ODE's: 18MAT31 & 17MAT41
Joint Probability & Sampling Theory: 18MAT41 & 17MAT41
Probability Distributions: 18MAT41 & 17MAT41
Calculus of Complex Functions: 18MAT41 & 17MAT41
Curve fitting & Statistical Method 18MAT41 17MAT31
Note that the gradient of a scalar field is a vector field that points in the direction of the steepest increase of the scalar field and its magnitude represents the rate of change of the scalar field in that direction. In this case the gradient ∇f at any point (x y z) gives the direction of maximum increase of the scalar field f and its magnitude represents the rate of change of f in that direction.
#vector #scalarvector
18MAT21 MODULE 1:Vector Calculus
18MAT21 MODULE 2:Differential Equation higher order
18MAT21 MODULE 3: Partial differential equations
18MAT21 MODULE 4: Infiinite series & Power series solution
18MAT21 MODULE 5: Numerical methods
18MAT11 Module1: Differential Calculus1
18MAT11 Module2: differential Calculus2
18MAT11 Module4: Ordinary differential equations
Linear Algebra: 18MAT11 MODULE 5
LAPLACE TRANSFORM : 18MAT31
Fourier Transforms Z-transform : 18MAT31 & 17MAT31
Fourier Series: 18MAT31 & 17MAT31
Calculus of Variation & Numerical Methods 18MAT31
Numerical Methods ODE's: 18MAT31 & 17MAT41
Joint Probability & Sampling Theory: 18MAT41 & 17MAT41
Probability Distributions: 18MAT41 & 17MAT41
Calculus of Complex Functions: 18MAT41 & 17MAT41
Curve fitting & Statistical Method 18MAT41 17MAT31
Комментарии
 0:05:02
0:05:02
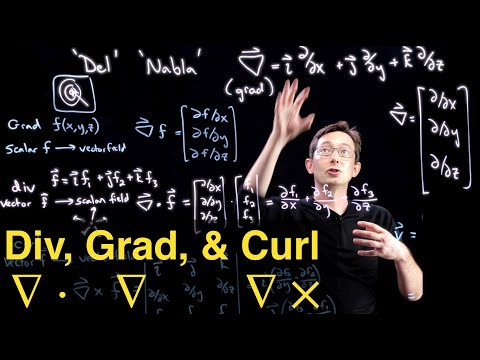 0:13:02
0:13:02
 0:06:27
0:06:27
 0:15:36
0:15:36
 0:10:25
0:10:25
 0:02:14
0:02:14
 0:02:18
0:02:18
 0:15:42
0:15:42
 1:20:39
1:20:39
 0:08:09
0:08:09
 0:28:09
0:28:09
 0:12:52
0:12:52
 0:07:47
0:07:47
 0:06:44
0:06:44
 0:20:57
0:20:57
 0:15:04
0:15:04
 0:06:28
0:06:28
 0:09:00
0:09:00
 0:04:51
0:04:51
 0:00:15
0:00:15
 0:00:12
0:00:12
 0:16:27
0:16:27
 0:53:13
0:53:13
 0:12:59
0:12:59