filmov
tv
What Are Catalysts? | Reactions | Chemistry | DICE-21

Показать описание
Catalyst and types of catalyst #catalyst #types of catalyst #chemistry
0000 Intro of DICE-21
00:05 on this lecture / what is catalysis what is Catalyst ?
00:45 What is Catalysis and types of Catalysis ?
02:42 Homogeneous Catalysis
03:37 Heterogeneous Catalysis
06:49 What is Catalyst ?
08:02 Positive Catalyst
09:03 Negative Catalyst
11:45 Induced Catalyst
14:20 Auto Catalyst
23:42 Q&A
==========================================
Catalysis is the phenomenon in which the rate of any reaction is altered (accelerated or retarded) by the presence of a substance,
which itself remains unchanged chemically in the reaction. The substance which alters the rate of the reaction is called catalyst.
On the basis of phases involved catalysis are of two types:
• homogenous catalysis
• heterogeneous catalysis
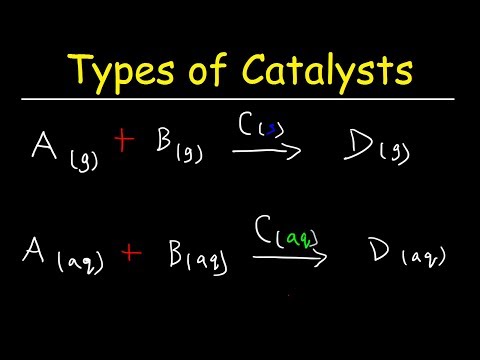
Homogenous Catalysis
When the reactants and catalysts are in the same physical state i.e. catalyst is in the same phase as the reactant is called homogenous catalysis.
For Example
Lead Chamber Process:
2SO2(g) + O2(g) →┴NO2 2SO3(g)
Inversion of Cane Sugar:
H2SO4(aq) C12H22O11 + H2O → C6H12O6 + C6H12O6 (Cane sugar) (Glucose) (Fructose)
Heterogenous Catalysis
A catalytic process in which the catalyst and the reactants are in different phases is called heterogeneous catalysis.
This process is also known as surface catalysis or contact catalysis.
For Example
• Decomposition of H2O2:
Pt(s) 2H2O2(l) → 2H2O(l) + O2(g)
• Haber's Process:
Fe(s) N2(g) + 3H2(g) → 2NH3(g)
What is a Catalyst?
Catalyst is a substance which alters the rate of chemical reaction (may increase or decrease the rate) without being consumed itself during the course of reaction.
Based on behavior, catalysts can be classified into four types:
• Positive catalyst
• Negative catalyst
• Induced catalyst
• Auto catalyst
Positive Catalyst
The substance which increases the rate of reaction is known as positive catalyst.
It acts by decreasing the activation energy for reaction. The phenomenon is known as positive catalysis
. Examples:
•V2O5 used in contact process:
V2O5 2SO2 + O2 → 2SO3
•Decomposition of H2O2 in the presence of Platinum.
Pt(s) 2H2O2(l) → 2H2O(l) + O2(g)
Negative catalyst
The substance which decreases the rate of reaction is known as negative catalyst.
It acts by increasing the activation energy for reaction. These are also known as inhibitor or retarder. The phenomenon is known as negative catalysis.
Negative catalysts work by providing an alternate path to the reaction having a higher activation energy than the uncatalyzed reaction. So that lesser molecules will have sufficient energy to cross the barrier and the reaction will be slower.
Example: • Decomposition of hydrogen peroxide(H2O2) decreases in the presence glycerin.
2H2O2 →┴(glycerin/H3PO4) 2H2O + O2
Induced catalyst:
When one reactant influences the rate of other reaction which doesn't occur under ordinary conditions is known as induced catalyst.
Or we can say, when a chemical reaction increases the rate of another chemical reaction, it is called induced catalysis.
Example:
Sodium arenite solution is not oxidized by air. but when air is passed through a mixture of the solution of sodium arsenite and sodium sulphite, simultaneous oxidation of both takes place. Thus the oxidation of sodium arsenite is induced by oxidation of sodium sulphite.
Na3AsO3 →┴(Air ) No reaction
Auto catalyst
In certain reactions, one of the product formed acts as a catalyst for the reaction is known as auto catalyst and the phenomenon is known as auto catalysis.
Example:
In the oxidation of oxalic acid(C2H2O4) by potassium permanganate(KMnO4),
Mn2+ ion formed from MnSO4 act as catalyst and increases the rate of reaction.
Here the concentration of CA in the beginning is maximum(CAo), means the (C0-CA) term will be minimum. Then as the reaction proceeds the rate of increase of (C0-CA) is more than the rate of decrease of CA.
So graph increases. Then there will be a time, when rate of increase of (C0-CA) is equal to rate of decrease of CA.
Now rate reaches maximum. After this rate of decrease of CA is more than the rate of increase of (C0- CA). That's why graph will now decrease.
Initially, when the rate is low, conversion will also be low. Then there comes a time when rate is maximum and that's why conversion will also be high. Then again when rate is low, conversion will also be low.
Q&A
1.What is Catalysis
?
2.What is catalyst explain and classified their types?
jee,jee tips,jee tips and tricks,jee tips by toppers,jee topper tips,iit jee topper tips,jee mains topper tips,jee strategy,jee strategy 2021,jee preparation strategy,jee 2021 preparation strategy,jee mains preparation strategy,iit jee preparation strategy,vedantu jee strategy 2021,jee topper interview,jee topper interview 2021,jee 2021,jee main 2021,jee main,can you do it,vedantu jee,ap sir,ap
0000 Intro of DICE-21
00:05 on this lecture / what is catalysis what is Catalyst ?
00:45 What is Catalysis and types of Catalysis ?
02:42 Homogeneous Catalysis
03:37 Heterogeneous Catalysis
06:49 What is Catalyst ?
08:02 Positive Catalyst
09:03 Negative Catalyst
11:45 Induced Catalyst
14:20 Auto Catalyst
23:42 Q&A
==========================================
Catalysis is the phenomenon in which the rate of any reaction is altered (accelerated or retarded) by the presence of a substance,
which itself remains unchanged chemically in the reaction. The substance which alters the rate of the reaction is called catalyst.
On the basis of phases involved catalysis are of two types:
• homogenous catalysis
• heterogeneous catalysis
Homogenous Catalysis
When the reactants and catalysts are in the same physical state i.e. catalyst is in the same phase as the reactant is called homogenous catalysis.
For Example
Lead Chamber Process:
2SO2(g) + O2(g) →┴NO2 2SO3(g)
Inversion of Cane Sugar:
H2SO4(aq) C12H22O11 + H2O → C6H12O6 + C6H12O6 (Cane sugar) (Glucose) (Fructose)
Heterogenous Catalysis
A catalytic process in which the catalyst and the reactants are in different phases is called heterogeneous catalysis.
This process is also known as surface catalysis or contact catalysis.
For Example
• Decomposition of H2O2:
Pt(s) 2H2O2(l) → 2H2O(l) + O2(g)
• Haber's Process:
Fe(s) N2(g) + 3H2(g) → 2NH3(g)
What is a Catalyst?
Catalyst is a substance which alters the rate of chemical reaction (may increase or decrease the rate) without being consumed itself during the course of reaction.
Based on behavior, catalysts can be classified into four types:
• Positive catalyst
• Negative catalyst
• Induced catalyst
• Auto catalyst
Positive Catalyst
The substance which increases the rate of reaction is known as positive catalyst.
It acts by decreasing the activation energy for reaction. The phenomenon is known as positive catalysis
. Examples:
•V2O5 used in contact process:
V2O5 2SO2 + O2 → 2SO3
•Decomposition of H2O2 in the presence of Platinum.
Pt(s) 2H2O2(l) → 2H2O(l) + O2(g)
Negative catalyst
The substance which decreases the rate of reaction is known as negative catalyst.
It acts by increasing the activation energy for reaction. These are also known as inhibitor or retarder. The phenomenon is known as negative catalysis.
Negative catalysts work by providing an alternate path to the reaction having a higher activation energy than the uncatalyzed reaction. So that lesser molecules will have sufficient energy to cross the barrier and the reaction will be slower.
Example: • Decomposition of hydrogen peroxide(H2O2) decreases in the presence glycerin.
2H2O2 →┴(glycerin/H3PO4) 2H2O + O2
Induced catalyst:
When one reactant influences the rate of other reaction which doesn't occur under ordinary conditions is known as induced catalyst.
Or we can say, when a chemical reaction increases the rate of another chemical reaction, it is called induced catalysis.
Example:
Sodium arenite solution is not oxidized by air. but when air is passed through a mixture of the solution of sodium arsenite and sodium sulphite, simultaneous oxidation of both takes place. Thus the oxidation of sodium arsenite is induced by oxidation of sodium sulphite.
Na3AsO3 →┴(Air ) No reaction
Auto catalyst
In certain reactions, one of the product formed acts as a catalyst for the reaction is known as auto catalyst and the phenomenon is known as auto catalysis.
Example:
In the oxidation of oxalic acid(C2H2O4) by potassium permanganate(KMnO4),
Mn2+ ion formed from MnSO4 act as catalyst and increases the rate of reaction.
Here the concentration of CA in the beginning is maximum(CAo), means the (C0-CA) term will be minimum. Then as the reaction proceeds the rate of increase of (C0-CA) is more than the rate of decrease of CA.
So graph increases. Then there will be a time, when rate of increase of (C0-CA) is equal to rate of decrease of CA.
Now rate reaches maximum. After this rate of decrease of CA is more than the rate of increase of (C0- CA). That's why graph will now decrease.
Initially, when the rate is low, conversion will also be low. Then there comes a time when rate is maximum and that's why conversion will also be high. Then again when rate is low, conversion will also be low.
Q&A
1.What is Catalysis
?
2.What is catalyst explain and classified their types?
jee,jee tips,jee tips and tricks,jee tips by toppers,jee topper tips,iit jee topper tips,jee mains topper tips,jee strategy,jee strategy 2021,jee preparation strategy,jee 2021 preparation strategy,jee mains preparation strategy,iit jee preparation strategy,vedantu jee strategy 2021,jee topper interview,jee topper interview 2021,jee 2021,jee main 2021,jee main,can you do it,vedantu jee,ap sir,ap
 0:03:34
0:03:34
 0:01:55
0:01:55
 0:05:23
0:05:23
 0:04:21
0:04:21
 0:01:34
0:01:34
 0:07:31
0:07:31
 0:05:03
0:05:03
 0:03:02
0:03:02
![[Chemistry] | The](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/FxGBLiWKwVA/hqdefault.jpg) 0:02:29
0:02:29
 0:09:00
0:09:00
 0:01:24
0:01:24
 0:02:36
0:02:36
 0:02:40
0:02:40
 0:02:52
0:02:52
 0:05:15
0:05:15
 0:07:30
0:07:30
 0:03:14
0:03:14
 0:01:00
0:01:00
 0:27:01
0:27:01
 0:02:15
0:02:15
 0:05:21
0:05:21
 0:16:33
0:16:33
 0:05:52
0:05:52
 0:09:08
0:09:08