filmov
tv
A Nice Geometry Problem | Olympiad Mathematics | Important Geometry and Algebra Skills Explained

Показать описание
A Nice Geometry Problem | Olympiad Mathematics | Important Geometry and Algebra Skills Explained
Join this channel to get access to perks:
MEMBERS OF THIS CHANNEL
••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••
Mr. Gnome
ஆத்தங்கரை சண்முகம்
Εκπαιδευτήρια Καντά
AR Knowledge
堤修一
Sidnei Medeiros Vicente
Mark Ludington
Debashis Kesh
Arichai Vattanapat
Join this channel to get access to perks:
MEMBERS OF THIS CHANNEL
••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••
Mr. Gnome
ஆத்தங்கரை சண்முகம்
Εκπαιδευτήρια Καντά
AR Knowledge
堤修一
Sidnei Medeiros Vicente
Mark Ludington
Debashis Kesh
Arichai Vattanapat
Olympiad Mathematics | A Very Nice Geometry Problem
A Nice Geometry Problem | r=?
Math Olympiad | A Very Nice Geometry Problem
Olympiad Mathematics | A Very Nice Geometry Problem
A Very Nice Geometry Problem | Math Olympiad
Spain Math Olympiad | A Very Nice Geometry Problem
a nice geometry problem in the complex plane.
A nice geometry problem from New Zealand
China | Can You Solve this ? | Math Olympiad 👇
Evil Geometry Problem
A beautiful and challenging geometry construction
Angle Chasing Problem - Moscow 1952 | A Nice Geometry Challenge
A simple geometry problem with a nice generalization.
Challenging Math Olympiad Problem | Geometry Question | Mathematics | 2 Methods
A nice quick geometry problem.
Can You Find Angle X? | Geometry Challenge!
A nice geometry trick!
A beautiful geometry question. What is the ratio of sides?
A nice Iranian geometry problem
A nice geometry problem with complex numbers.
How to prepare your Geometry for the IMO and other math competitions
A quick geometry problem.
The hardest 'easy' geometry problem.
Fastest Geometry Summary
Комментарии
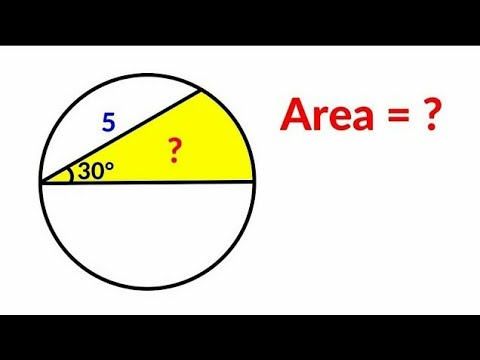 0:11:17
0:11:17
 0:04:41
0:04:41
 0:12:38
0:12:38
 0:11:21
0:11:21
 0:10:15
0:10:15
 0:11:52
0:11:52
 0:09:23
0:09:23
 0:06:36
0:06:36
 0:14:22
0:14:22
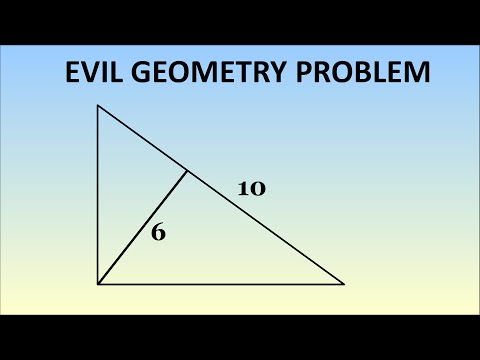 0:03:23
0:03:23
 0:04:49
0:04:49
 0:09:25
0:09:25
 0:13:11
0:13:11
 0:25:44
0:25:44
 0:04:58
0:04:58
 0:08:44
0:08:44
 0:12:30
0:12:30
 0:04:14
0:04:14
 0:05:34
0:05:34
 0:11:39
0:11:39
 0:05:42
0:05:42
 0:05:49
0:05:49
 0:16:40
0:16:40
 0:02:52
0:02:52