filmov
tv
Proof: Sequence 1/n Converges to 0 | Real Analysis Exercises

Показать описание
We will prove the sequence 1/n converges to 0. In other words, we're proving that the limit of 1/n as n approaches infinity is 0. We use the epsilon definition of a convergent sequence and the proof is straightforward, following the typical form of a convergent sequence proof and using the Archimedean Principle. #RealAnalysis
★DONATE★
Thanks to Robert Rennie, Barbara Sharrock, and Rolf Waefler for their generous support on Patreon!
Follow Wrath of Math on...
★DONATE★
Thanks to Robert Rennie, Barbara Sharrock, and Rolf Waefler for their generous support on Patreon!
Follow Wrath of Math on...
Proof: Sequence 1/n Converges to 0 | Real Analysis Exercises
Proof: Sequence (n+1)/n Converges to 1 | Real Analysis
Proof: Sequence 1/sqrt(n) Converges to 0 | Real Analysis
Proof: Sequence (3n+1)/(n+2) Converges to 3 | Real Analysis
Proof: Sequence (-1)^n Diverges | Real Analysis
Real Analysis Course #15 - Limit of 1/n Converges to 0
Definition of the Limit of a Sequence | Real Analysis
Proof: Sequence {sqrt(n+1)-sqrt(n)} Converges to 0 | Real Analysis Exercises
Proof that the Sequence (-1)^n Diverges using the Definition
Using Epsilon Limit Definition to Prove 1/n Converges to 0 [Real Analysis]
Sequence (-1)^n Converges or Diverges? Proof |Mad Teacher
Converging and Diverging Sequences Using Limits - Practice Problems
How to Write the epsilon,N-Proof: Sequence a_nb_n Converges to ab
Determining whether a sequence converges or diverges
How to Write epsilon, N-Proof: a_n/b_n Converges to a/b
Proving a sequence converges using the formal definition | Series | AP Calculus BC | Khan Academy
Prove that the Sequence {1/(2n)} Converges to Zero Using the Definition of Convergence
Proving a Sequence Converges with the Formal Definition Advanced Calculus
Proving Sequence Converges with Epsilon Limit Definition + Non-Converging Sequences [Real Analysis]
Proof: Limit Law for Sum of Convergent Sequences | Real Analysis
Proof: The Limit of a Sequence is Unique | Real Analysis
Sequence Converges iff Every Subsequences Converge to the Same Limit | Real Analysis
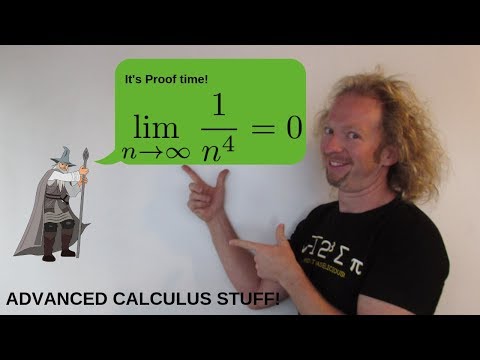
Proving a Sequence Converges Advanced Calculus Example with {(1/n^4)}
1/n! converges to zero by using formal definition
Комментарии
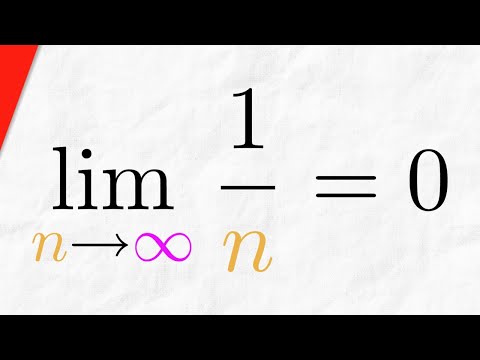 0:06:48
0:06:48
 0:06:43
0:06:43
 0:07:13
0:07:13
 0:06:53
0:06:53
 0:13:07
0:13:07
 0:04:22
0:04:22
 0:13:59
0:13:59
 0:11:06
0:11:06
 0:04:27
0:04:27
 0:09:06
0:09:06
 0:04:20
0:04:20
 0:30:13
0:30:13
 0:05:58
0:05:58
 0:05:39
0:05:39
 0:05:22
0:05:22
 0:05:30
0:05:30
 0:05:26
0:05:26
 0:07:57
0:07:57
 0:09:53
0:09:53
 0:07:56
0:07:56
 0:13:22
0:13:22
 0:08:54
0:08:54
 0:05:42
0:05:42
 0:05:15
0:05:15