filmov
tv
Prove (sin x - sin y)/(cos x + cos y) = tan((x - y)/2)

Показать описание
In this video, we will learn to prove the equation (sin x - sin y)/(cos x + cos y) = tan((x - y)/2).
The link of the video explaining, the proof of the identity sin A - sin B = 2 cos((A+B)/2) sin((A-B)/2) has been given below
The link of the video explaining, the proof of the identity cos A + cos B = 2 cos((A+B)/2) cos((A-B)/2) has been given below
Other topics of this video are:
Class XI exercise 3.3 problem 18
NCERT Class XI exercise 3.3 problem 18
I, Ravi Ranjan Kumar Singh, have produced this video. All credits of this video belong to me.
The link of the video explaining, the proof of the identity sin A - sin B = 2 cos((A+B)/2) sin((A-B)/2) has been given below
The link of the video explaining, the proof of the identity cos A + cos B = 2 cos((A+B)/2) cos((A-B)/2) has been given below
Other topics of this video are:
Class XI exercise 3.3 problem 18
NCERT Class XI exercise 3.3 problem 18
I, Ravi Ranjan Kumar Singh, have produced this video. All credits of this video belong to me.
Proof of the derivative of sin(x) | Derivatives introduction | AP Calculus AB | Khan Academy
The most important limit in Calculus // Geometric Proof & Applications
Proof of angle addition formula for sine | Trigonometry | Khan Academy
Does sin¯¹(sin x) = x?
The geometric interpretation of sin x = x - x³/3! + x⁵/5! -...
Derivative of sin(x) from First Principles
Visual Calculus: Derivative of sin(θ) is cos(θ)
Derivative of sin(x) and cos(x), PROOF
Trigonometric Functions | 1st PUC 11th CBSE | Mathematics | Part 4 of 10
Trigonometry Identities: sin(-x) = - sin(x) and cos(-x) = cos(x)
Trigonometric Identity: sin(π-x) = sin(x)
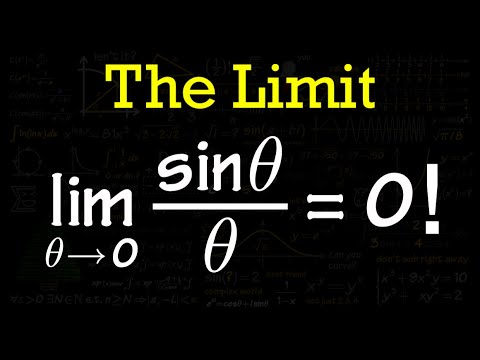
The Limit (do not use L'Hospital rule)
Limit of sin(x)/x as x approaches 0 | Derivative rules | AP Calculus AB | Khan Academy
PreCalculus - Trigonometry: Trig Identities (44 of 57) Prove sin(4x)/sinx=4cosxcos(2x)
Proof sin2x=2sinxcosx
Proof: Derivative of Sin is Cos (Version 2)
Limit of sin(x)/x as x goes to Infinity (Squeeze Theorem) | Calculus 1 Exercises
sinx+sin2x+sin3x+...+sin nx || Sum of sine series when angles are in AP || Proof by C+iS Method
Integral of sin(x)
sin(3x) in terms of sin(x)
❖ Taylor / Maclaurin Series for Sin (x) ❖
PreCalculus - Trigonometry: Trig Identities (32 of 57) Proof Half Angle Formula: sin(x/2)
A-Level Maths G1-16 Differentiation: Differentiate sin(x) from First Principles
Trigonometry Proof: cos (x + y) = cos x cos y – sin x sin y (https://youtu.be/b0o_dvFkYbU)
Комментарии
 0:05:52
0:05:52
 0:11:54
0:11:54
 0:08:26
0:08:26
 0:07:34
0:07:34
 0:22:02
0:22:02
 0:09:39
0:09:39
 0:03:08
0:03:08
 0:09:18
0:09:18
 0:20:13
0:20:13
 0:03:47
0:03:47
 0:08:27
0:08:27
 0:12:08
0:12:08
 0:09:16
0:09:16
 0:03:33
0:03:33
 0:02:03
0:02:03
 0:09:39
0:09:39
 0:03:59
0:03:59
 0:09:08
0:09:08
 0:00:23
0:00:23
 0:05:29
0:05:29
 0:05:51
0:05:51
 0:02:04
0:02:04
 0:04:53
0:04:53
 0:07:25
0:07:25