filmov
tv
Visual Group Theory, Lecture 6.1: Fields and their extensions

Показать описание
Visual Group Theory, Lecture 6.1: Fiends and their extensions
This series of lectures is about Galois theory, which was invented by a French mathematician who tragically died in a dual at the age of 20. He invented the concept of a group to prove that there was no formula for solving degree-5 polynomials. Galois theory involves an algebraic object called a field, which is a set F endowed with two binary operations, addition and multiplication with the standard distributive law. Formally, this means that (F,+) and (F-{0},*) must both be abelian groups. Common examples of fields include the rationals, reals, complex numbers, and Z_p for prime p. In this lecture, we examine what happens when we begin with the rational numbers, and the "throw in" roots of polynomials to generate bigger fields called "extensions".
This series of lectures is about Galois theory, which was invented by a French mathematician who tragically died in a dual at the age of 20. He invented the concept of a group to prove that there was no formula for solving degree-5 polynomials. Galois theory involves an algebraic object called a field, which is a set F endowed with two binary operations, addition and multiplication with the standard distributive law. Formally, this means that (F,+) and (F-{0},*) must both be abelian groups. Common examples of fields include the rationals, reals, complex numbers, and Z_p for prime p. In this lecture, we examine what happens when we begin with the rational numbers, and the "throw in" roots of polynomials to generate bigger fields called "extensions".
Visual Group Theory, Lecture 6.1: Fields and their extensions
Visual Group Theory, Lecture 6.5: Galois group actions and normal field extensions
Visual Group Theory, Lecture 6.6: The fundamental theorem of Galois theory
Group Theory, lecture 2.4: Conjugation in the symmetric group
Visual Group Theory, Lecture 4.6: Automorphisms
Group Theory in Physics 6-A: Galois Theory -1 (in Persian)
Visual Group Theory, Lecture 1.1: What is a group?
Visual Group Theory: Lecture 7.5: Euclidean domains and algebraic integers
Visual Group Theory, Lecture 2.1: Cyclic and abelian groups
Visual Group Theory, Lecture 6.7: Ruler and compass constructions
Visual Group Theory, Lecture 6.2: Field automorphisms
Visual Group Theory, Lecture 3.1: Subgroups
How to Answer Any Question on a Test
Lecture 5.2 and 6.1 - Group Theory Applied to Condensed Matter Physics
Visual Group Theory, Lecture 2.4: Cayley's theorem
Group theory, abstraction, and the 196,883-dimensional monster
Visual Group Theory, Lecture 6.4: Galois groups
Visual Group Theory, Lecture 3.7: Conjugacy classes
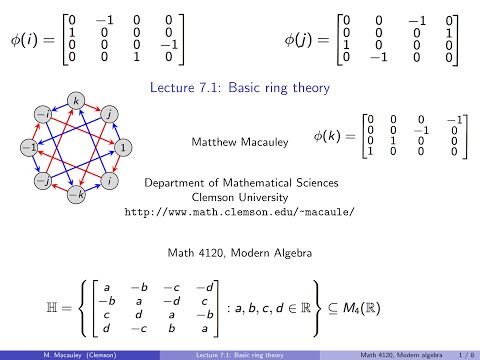
Visual Group Theory, Lecture 7.1: Basic ring theory
Group theory 6: normal subgroups and quotient groups
Group Theory Lecture 5.5 Automorphisms of Permutation Groups
Visual Group Theory, Lecture 5.7: Finite simple groups
The First Isomorphism Theorem for Groups (Algebra 1: Lecture 6 Video 1)
Group Theory in Physics 6-B: Galois Theory -1
Комментарии
 0:26:34
0:26:34
 0:26:28
0:26:28
 0:31:29
0:31:29
 0:30:47
0:30:47
 0:24:34
0:24:34
 1:05:32
1:05:32
 0:16:15
0:16:15
 0:30:09
0:30:09
 0:30:45
0:30:45
 0:22:46
0:22:46
 0:35:41
0:35:41
 0:13:43
0:13:43
 0:00:27
0:00:27
 1:09:59
1:09:59
 0:11:00
0:11:00
 0:21:58
0:21:58
 0:34:13
0:34:13
 0:39:19
0:39:19
 0:32:36
0:32:36
 0:24:48
0:24:48
 0:19:37
0:19:37
 0:36:34
0:36:34
 0:12:06
0:12:06
 1:03:59
1:03:59