filmov
tv
Visual Group Theory, Lecture 6.6: The fundamental theorem of Galois theory
Показать описание
Visual Group Theory, Lecture 6.6: The fundamental theorem of Galois theory
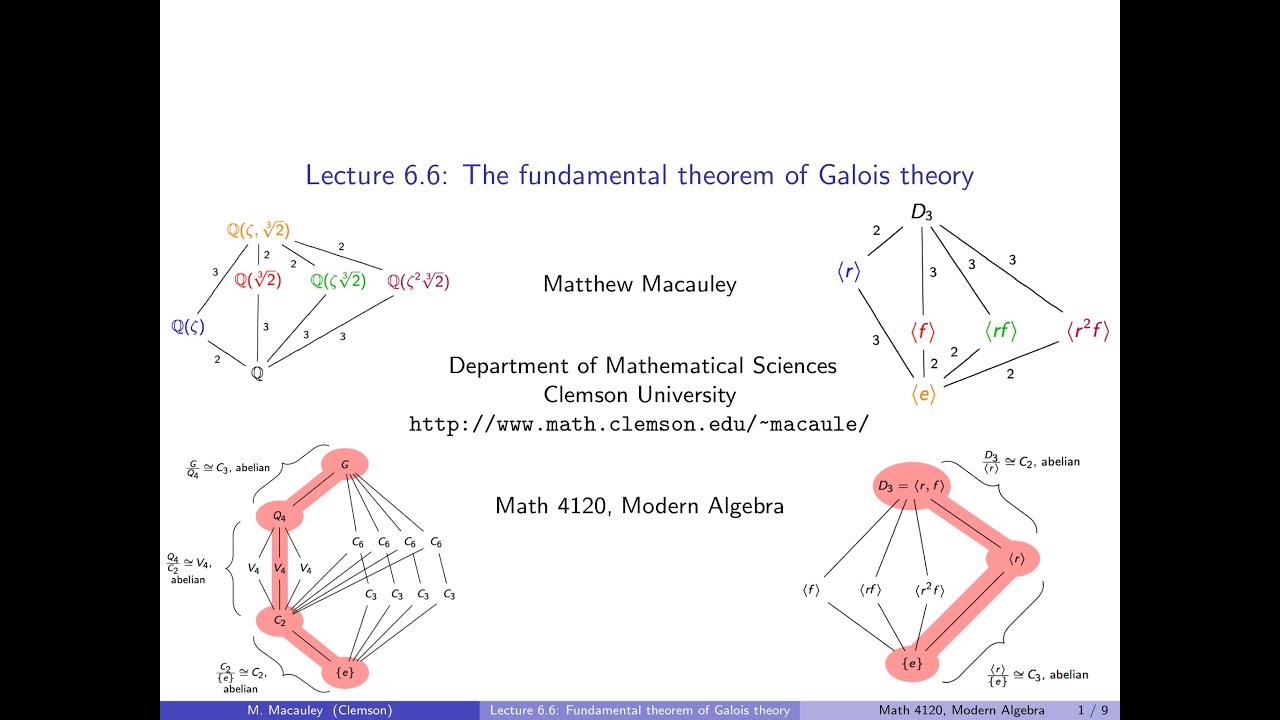
The fundamental theorem of Galois theory guarantees a remarkable correspondence between the subfield lattice of a polynomial and the subgroup lattice of its Galois group. After illustrating this with a detailed example, we define what it means for a group to be "solvable". Galois proved that a polynomial is solvable by radicals if and only if its Galois group is solvable. We conclude by finding a degree-5 polynomial f(x) whose Galois group acts on the roots by a 5-cycle and by a 2-cycle. Since these two elements generate the (unsolvable) symmetric group S_5, the roots of f(x) are unsolvable by radicals.
The fundamental theorem of Galois theory guarantees a remarkable correspondence between the subfield lattice of a polynomial and the subgroup lattice of its Galois group. After illustrating this with a detailed example, we define what it means for a group to be "solvable". Galois proved that a polynomial is solvable by radicals if and only if its Galois group is solvable. We conclude by finding a degree-5 polynomial f(x) whose Galois group acts on the roots by a 5-cycle and by a 2-cycle. Since these two elements generate the (unsolvable) symmetric group S_5, the roots of f(x) are unsolvable by radicals.
Visual Group Theory, Lecture 6.6: The fundamental theorem of Galois theory
Visual Group Theory: Lecture 7.5: Euclidean domains and algebraic integers
Visual Group Theory, Lecture 6.5: Galois group actions and normal field extensions
Visual Group Theory, Lecture 6.1: Fields and their extensions
Symmetric Groups (Abstract Algebra)
Lecture 6 Normal Extensions
Group theory 6: normal subgroups and quotient groups
Morphisms, rings, and fields | Group theory episode 6
Visual Group Theory, Lecture 4.6: Automorphisms
Visual Group Theory, Lecture 5.7: Finite simple groups
Group Theory, lecture 2.4: Conjugation in the symmetric group
Visual Group Theory, Lecture 2.1: Cyclic and abelian groups
Visual Group Theory, Lecture 5.3: Examples of group actions
Visual Group Theory, Lecture 6.4: Galois groups
Group Theory: Lecture 21/30 - Conjugacy Classes of the Alternating Group
Visual Group Theory, Lecture 2.3: Symmetric and alternating groups
The Group Theory Used to Solve the Hardest Differential Equation
Why study Lie theory? | Lie groups, algebras, brackets #1
Visual Group Theory, Lecture 6.2: Field automorphisms
Group Theory in Physics 6-A: Galois Theory -1 (in Persian)
Visual Group Theory, Lecture 6.7: Ruler and compass constructions
How small are atoms?
Visual Group Theory, Lecture 2.4: Cayley's theorem
Visual Group Theory, Lecture 3.2: Cosets
Комментарии
 0:31:29
0:31:29
 0:30:09
0:30:09
 0:26:28
0:26:28
 0:26:34
0:26:34
 0:05:30
0:05:30
 0:37:51
0:37:51
 0:24:48
0:24:48
 0:31:13
0:31:13
 0:24:34
0:24:34
 0:36:34
0:36:34
 0:30:47
0:30:47
 0:30:45
0:30:45
 0:44:05
0:44:05
 0:34:13
0:34:13
 0:35:57
0:35:57
 0:29:50
0:29:50
 0:01:00
0:01:00
 0:04:26
0:04:26
 0:35:41
0:35:41
 1:05:32
1:05:32
 0:22:46
0:22:46
 0:00:48
0:00:48
 0:11:00
0:11:00
 0:19:11
0:19:11