filmov
tv
Hyperuricemia: Understanding Its Signs, Effects & Management Essentials

Показать описание
Medical Centric Recommended : (Affiliate Links)
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Hyperuricemia, a condition characterized by high levels of uric acid in the blood, can be a silent harbinger of various health issues, including gout, kidney stones, and renal failure. Understanding its symptoms, seeking effective treatment, and implementing strategic management can significantly mitigate its impacts. This comprehensive guide delves into the essentials of hyperuricemia, offering insights and strategies for those affected.
Understanding Hyperuricemia
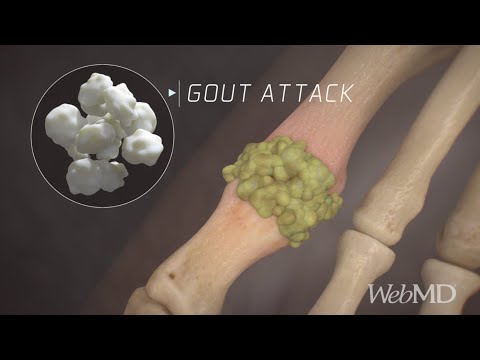
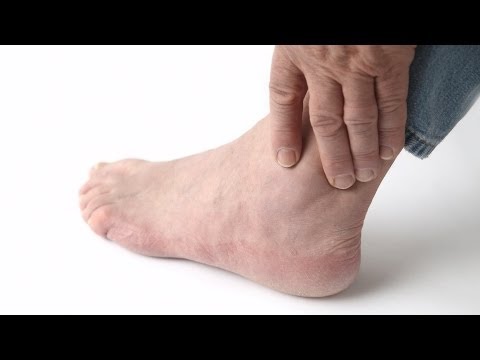
Hyperuricemia occurs when the body produces more uric acid than it can excrete or when it is unable to efficiently eliminate uric acid. While uric acid is a normal waste product found in the blood, excessive amounts can crystallize and deposit in joints, kidneys, and other tissues, leading to painful conditions like gout.
Symptoms to Watch For
Initially, hyperuricemia may not present any symptoms. However, as uric acid levels rise, symptoms can emerge, including:
Joint Pain and Swelling: The first signs often appear in the big toe but can affect other joints.
Kidney Stones: Uric acid crystals can accumulate in the kidneys, leading to stones.
Fatigue and High Blood Pressure: Elevated uric acid levels can indirectly contribute to these conditions.
Treatment Options
Treatment for hyperuricemia aims to reduce uric acid levels in the blood and manage symptoms. Options include:
Medications: Drugs like allopurinol and febuxostat help lower uric acid production, while probenecid aids in increasing uric acid excretion.
Pain Relief: For acute gout attacks, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), colchicine, or corticosteroids can be prescribed to alleviate pain and inflammation.
Management Strategies
Managing hyperuricemia involves lifestyle adjustments alongside medical treatment. Here are key strategies:
Dietary Changes: Reduce intake of purine-rich foods (e.g., red meat, seafood) and sugary beverages. Embrace a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and low-fat dairy products.
Hydration: Increase water intake to help flush uric acid from the body.
Limit Alcohol: Alcohol, especially beer, can increase uric acid levels.
Weight Management: Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight can reduce uric acid levels and alleviate stress on joints.
Exercise Regularly: Regular physical activity can help control weight and improve overall health, indirectly affecting uric acid levels.
Monitoring and Regular Check-Ups
Regular monitoring of uric acid levels is crucial for those diagnosed with hyperuricemia. Frequent check-ups allow healthcare providers to adjust treatment plans as necessary, ensuring optimal management of the condition.
Conclusion
Hyperuricemia, while challenging, can be managed effectively with the right combination of medical treatment, lifestyle changes, and regular monitoring. Recognizing the symptoms early and adopting a proactive approach to treatment and management can help mitigate the risks associated with elevated uric acid levels, leading to a healthier, more comfortable life.
Remember, if you suspect you have hyperuricemia or are experiencing symptoms associated with high uric acid levels, consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and tailored treatment plan.
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Hyperuricemia, a condition characterized by high levels of uric acid in the blood, can be a silent harbinger of various health issues, including gout, kidney stones, and renal failure. Understanding its symptoms, seeking effective treatment, and implementing strategic management can significantly mitigate its impacts. This comprehensive guide delves into the essentials of hyperuricemia, offering insights and strategies for those affected.
Understanding Hyperuricemia
Hyperuricemia occurs when the body produces more uric acid than it can excrete or when it is unable to efficiently eliminate uric acid. While uric acid is a normal waste product found in the blood, excessive amounts can crystallize and deposit in joints, kidneys, and other tissues, leading to painful conditions like gout.
Symptoms to Watch For
Initially, hyperuricemia may not present any symptoms. However, as uric acid levels rise, symptoms can emerge, including:
Joint Pain and Swelling: The first signs often appear in the big toe but can affect other joints.
Kidney Stones: Uric acid crystals can accumulate in the kidneys, leading to stones.
Fatigue and High Blood Pressure: Elevated uric acid levels can indirectly contribute to these conditions.
Treatment Options
Treatment for hyperuricemia aims to reduce uric acid levels in the blood and manage symptoms. Options include:
Medications: Drugs like allopurinol and febuxostat help lower uric acid production, while probenecid aids in increasing uric acid excretion.
Pain Relief: For acute gout attacks, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), colchicine, or corticosteroids can be prescribed to alleviate pain and inflammation.
Management Strategies
Managing hyperuricemia involves lifestyle adjustments alongside medical treatment. Here are key strategies:
Dietary Changes: Reduce intake of purine-rich foods (e.g., red meat, seafood) and sugary beverages. Embrace a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and low-fat dairy products.
Hydration: Increase water intake to help flush uric acid from the body.
Limit Alcohol: Alcohol, especially beer, can increase uric acid levels.
Weight Management: Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight can reduce uric acid levels and alleviate stress on joints.
Exercise Regularly: Regular physical activity can help control weight and improve overall health, indirectly affecting uric acid levels.
Monitoring and Regular Check-Ups
Regular monitoring of uric acid levels is crucial for those diagnosed with hyperuricemia. Frequent check-ups allow healthcare providers to adjust treatment plans as necessary, ensuring optimal management of the condition.
Conclusion
Hyperuricemia, while challenging, can be managed effectively with the right combination of medical treatment, lifestyle changes, and regular monitoring. Recognizing the symptoms early and adopting a proactive approach to treatment and management can help mitigate the risks associated with elevated uric acid levels, leading to a healthier, more comfortable life.
Remember, if you suspect you have hyperuricemia or are experiencing symptoms associated with high uric acid levels, consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and tailored treatment plan.
Комментарии
 0:03:56
0:03:56
 0:05:14
0:05:14
 0:06:12
0:06:12
 0:01:34
0:01:34
 0:01:28
0:01:28
 0:11:33
0:11:33
 0:08:15
0:08:15
 0:04:35
0:04:35
 0:49:09
0:49:09
 0:58:29
0:58:29
 0:11:07
0:11:07
 0:09:55
0:09:55
 0:04:34
0:04:34
 0:09:23
0:09:23
 0:04:08
0:04:08
 0:02:20
0:02:20
 0:06:13
0:06:13
 0:07:19
0:07:19
 0:02:12
0:02:12
 0:03:36
0:03:36
 0:10:29
0:10:29
 0:05:27
0:05:27
 0:04:16
0:04:16
 0:00:45
0:00:45