filmov
tv
Quarks simplified

Показать описание
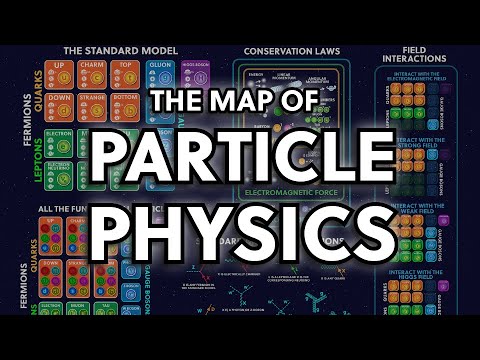
Quarks are fundamental particles that are a fundamental building block of matter. They are elementary particles and one of the basic constituents of protons and neutrons, which are the building blocks of atomic nuclei. The science of quarks involves the study of their properties, interactions, and their role in the fundamental forces and structure of matter. Here are some key points about the science of quarks:
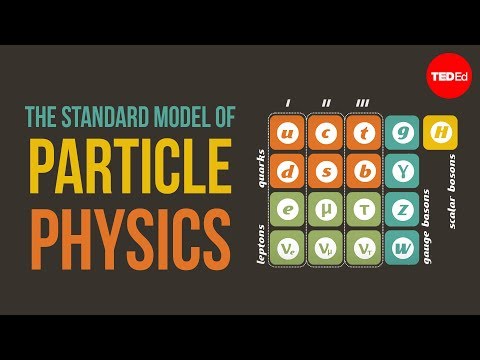
1. Quark Theory: Quark theory, also known as quantum chromodynamics (QCD), is the branch of physics that describes the behavior of quarks and the strong nuclear force that binds them together. Quarks are postulated to be elementary particles, meaning they cannot be broken down into smaller components. According to the theory, quarks come in six different flavors: up, down, charm, strange, top, and bottom.
2. Quantum Chromodynamics (QCD): Quantum chromodynamics is the theory that describes the strong nuclear force, which is responsible for holding quarks together to form protons, neutrons, and other particles called hadrons. QCD explains how quarks interact through the exchange of particles called gluons, which carry the strong force. The theory predicts the properties and behavior of quarks and their interactions within the framework of quantum mechanics.
3. Quark Confinement: One of the remarkable features of quarks is that they are never observed in isolation. This phenomenon is known as quark confinement. Due to the strong nuclear force, quarks are always bound together to form composite particles called hadrons. This means that quarks are only observed in combinations of two or three quarks, such as protons and neutrons, which are composed of three quarks each.
4. Quark Structure of Matter: Quarks are fundamental in understanding the structure of matter. Protons and neutrons, which are baryons, are composed of three quarks. The up and down quarks are the primary constituents of these particles. Quarks also exist in mesons, which are composed of a quark and an antiquark. The interactions between quarks and the strong nuclear force determine the stability and properties of these composite particles.
5. Experimental Evidence: The science of quarks is supported by extensive experimental evidence. High-energy particle accelerators, such as the Large Hadron Collider (LHC), have been crucial in studying the properties and interactions of quarks. Experiments have confirmed the existence of quarks, observed their different flavors, and measured their charges and masses. These experiments have provided strong validation for the theory of quarks and quantum chromodynamics.
#sciencefacts #quarks #science #physics #particlephysics #qcd #hardron #scienceshorts #homeschool #physicsfacts
1. Quark Theory: Quark theory, also known as quantum chromodynamics (QCD), is the branch of physics that describes the behavior of quarks and the strong nuclear force that binds them together. Quarks are postulated to be elementary particles, meaning they cannot be broken down into smaller components. According to the theory, quarks come in six different flavors: up, down, charm, strange, top, and bottom.
2. Quantum Chromodynamics (QCD): Quantum chromodynamics is the theory that describes the strong nuclear force, which is responsible for holding quarks together to form protons, neutrons, and other particles called hadrons. QCD explains how quarks interact through the exchange of particles called gluons, which carry the strong force. The theory predicts the properties and behavior of quarks and their interactions within the framework of quantum mechanics.
3. Quark Confinement: One of the remarkable features of quarks is that they are never observed in isolation. This phenomenon is known as quark confinement. Due to the strong nuclear force, quarks are always bound together to form composite particles called hadrons. This means that quarks are only observed in combinations of two or three quarks, such as protons and neutrons, which are composed of three quarks each.
4. Quark Structure of Matter: Quarks are fundamental in understanding the structure of matter. Protons and neutrons, which are baryons, are composed of three quarks. The up and down quarks are the primary constituents of these particles. Quarks also exist in mesons, which are composed of a quark and an antiquark. The interactions between quarks and the strong nuclear force determine the stability and properties of these composite particles.
5. Experimental Evidence: The science of quarks is supported by extensive experimental evidence. High-energy particle accelerators, such as the Large Hadron Collider (LHC), have been crucial in studying the properties and interactions of quarks. Experiments have confirmed the existence of quarks, observed their different flavors, and measured their charges and masses. These experiments have provided strong validation for the theory of quarks and quantum chromodynamics.
#sciencefacts #quarks #science #physics #particlephysics #qcd #hardron #scienceshorts #homeschool #physicsfacts
Комментарии





![[Quarks] Explained in](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/CC7eIxN0cAU/hqdefault.jpg)