filmov
tv
Crohn's Disease Nursing | Crohns Symptoms, Pathophysiology, Treatment, Diet NCLEX

Показать описание
Crohn's disease nursing review regarding diet, symptoms, pathophysiology, nursing interventions and treatment for NCLEX exam. Crohn's disease is a type of inflammatory bowel disease that causes inflammation and ulcers formation in the GI tract.
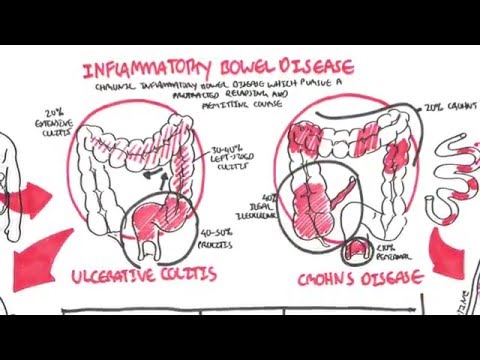
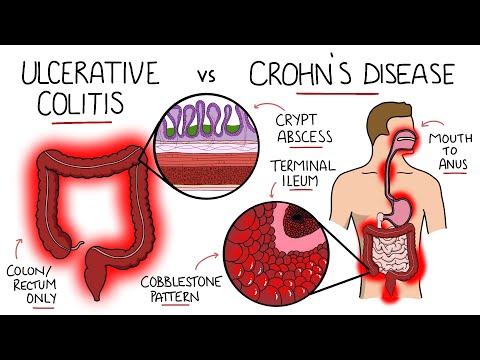
Crohn's can be found in both the small and large intestine; however, it seems to be most common in the terminal of the ileum and beginning of the colon.
Crohn's disease affects the whole bowel lining which is why its complications are unique when comparing crohn's disease vs ulcerative colitis. Crohn's disease complications include fistulas, fissures, abscesses, malnourishment, strictures which can lead to bowel obstructions, and other changes such as mouth ulcers, skin changes, gall and liver problems etc.
Crohn's disease symptoms include abdominal pain (which tends to be located in the right lower abdomen), ulcers in the mouth and GI lining, anal fissures, diarrhea which can contain pus, mucous, and blood, and undernourishment.
Crohn's disease tends to present in scattered patches throughout the GI tract where healthy areas will be noted next to diseased areas. This will give a cobble-stone appearance during a scope of the GI lining. This is different than ulcerative colitis which tends to start in the rectum and migrate in a continuous fashion through the large intestine without any skipped areas.
Nursing interventions for Crohn's Disease include: educating patient about this condition along with medication and diet regime and smoking cessation, monitoring nutrition status, assessing GI system by monitoring bowel sounds, bowel movements, monitoring administration of TPN (total parenteral nutrition) if ordered, providing ostomy education (if the patient has one).
Medications used to treat Crohn's includes: 5-Aminosalicylates, corticosteroids, Immunosuppression drugs, etc.
Popular Playlists:
Crohn's can be found in both the small and large intestine; however, it seems to be most common in the terminal of the ileum and beginning of the colon.
Crohn's disease affects the whole bowel lining which is why its complications are unique when comparing crohn's disease vs ulcerative colitis. Crohn's disease complications include fistulas, fissures, abscesses, malnourishment, strictures which can lead to bowel obstructions, and other changes such as mouth ulcers, skin changes, gall and liver problems etc.
Crohn's disease symptoms include abdominal pain (which tends to be located in the right lower abdomen), ulcers in the mouth and GI lining, anal fissures, diarrhea which can contain pus, mucous, and blood, and undernourishment.
Crohn's disease tends to present in scattered patches throughout the GI tract where healthy areas will be noted next to diseased areas. This will give a cobble-stone appearance during a scope of the GI lining. This is different than ulcerative colitis which tends to start in the rectum and migrate in a continuous fashion through the large intestine without any skipped areas.
Nursing interventions for Crohn's Disease include: educating patient about this condition along with medication and diet regime and smoking cessation, monitoring nutrition status, assessing GI system by monitoring bowel sounds, bowel movements, monitoring administration of TPN (total parenteral nutrition) if ordered, providing ostomy education (if the patient has one).
Medications used to treat Crohn's includes: 5-Aminosalicylates, corticosteroids, Immunosuppression drugs, etc.
Popular Playlists:
Комментарии
 0:25:48
0:25:48
 0:15:56
0:15:56
 0:11:40
0:11:40
 0:06:38
0:06:38
 0:08:59
0:08:59
 0:09:06
0:09:06
 0:26:33
0:26:33
 0:00:15
0:00:15
 0:08:08
0:08:08
 0:06:32
0:06:32
 0:23:47
0:23:47
 0:00:53
0:00:53
 0:01:33
0:01:33
 0:17:51
0:17:51
 1:06:30
1:06:30
 0:00:49
0:00:49
 0:01:09
0:01:09
 0:02:45
0:02:45
 0:07:50
0:07:50
 0:15:41
0:15:41
 0:02:05
0:02:05
 0:03:06
0:03:06
 0:18:39
0:18:39
 0:01:18
0:01:18