filmov
tv
Prove sin x + sin 3x + sin 5x + sin 7x = 4 cos x cos 2x sin 4x

Показать описание
In this video, we will learn to prove the equation sin x + sin 3x + sin 5x + sin 7x = 4 cos x cos 2x sin 4x.
The link of the video explaining, the proof of the identity sin A + sin B = 2 sin((A+B)/2) cos((A-B)/2) has been given below
Other topics of this video are:
Class XI miscellaneous exercise problem 5
NCERT Class XI miscellaneous exercise problem 5
I, Ravi Ranjan Kumar Singh, have produced this video. All credits of this video belong to me.
The link of the video explaining, the proof of the identity sin A + sin B = 2 sin((A+B)/2) cos((A-B)/2) has been given below
Other topics of this video are:
Class XI miscellaneous exercise problem 5
NCERT Class XI miscellaneous exercise problem 5
I, Ravi Ranjan Kumar Singh, have produced this video. All credits of this video belong to me.
Visualizing the derivative of sin(x)
The geometric interpretation of sin x = x - x³/3! + x⁵/5! -...
Proof of the derivative of sin(x) | Derivatives introduction | AP Calculus AB | Khan Academy
The most important limit in Calculus // Geometric Proof & Applications
Limit of sin(x)/x as x approaches 0 | Derivative rules | AP Calculus AB | Khan Academy
Does sin¯¹(sin x) = x?
Trigonometry Identities: sin(-x) = - sin(x) and cos(-x) = cos(x)
Proof sin2x=2sinxcosx
Unit 1 Pure Mathematics Trigonometry 5
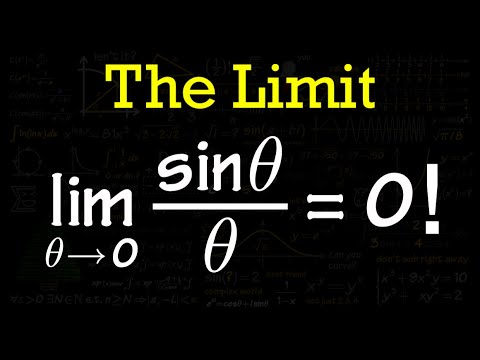
The Limit (do not use L'Hospital rule)
Proof of angle addition formula for sine | Trigonometry | Khan Academy
Trigonometric Identity: sin(π-x) = sin(x)
Finding the Derivative of x⋅sin(x) #Shorts #calculus #math #maths #mathematics #education #learn
❖ Taylor / Maclaurin Series for Sin (x) ❖
Derivative of sin(x) and cos(x), PROOF
A-Level Maths G1-16 Differentiation: Differentiate sin(x) from First Principles
Limit of sin(x)/x as x goes to Infinity (Squeeze Theorem) | Calculus 1 Exercises
Visual Calculus: Derivative of sin(θ) is cos(θ)
Limit of sin(x)/x as x approaches 0 (Proof) | Derivative rules | Science Valhalla
Proof: Derivative of Sin is Cos (Version 2)
PreCalculus - Trigonometry: Trig Identities (32 of 57) Proof Half Angle Formula: sin(x/2)
Proof of Compound Angle Identity sin(x+y)
Derivative of sin(x) from First Principles
sinx+sin2x+sin3x+...+sin nx || Sum of sine series when angles are in AP || Proof by C+iS Method
Комментарии
 0:00:59
0:00:59
 0:22:02
0:22:02
 0:05:52
0:05:52
 0:11:54
0:11:54
 0:09:16
0:09:16
 0:07:34
0:07:34
 0:03:47
0:03:47
 0:02:03
0:02:03
 1:27:09
1:27:09
 0:12:08
0:12:08
 0:08:26
0:08:26
 0:08:27
0:08:27
 0:00:39
0:00:39
 0:05:51
0:05:51
 0:09:18
0:09:18
 0:04:53
0:04:53
 0:03:59
0:03:59
 0:03:08
0:03:08
 0:02:22
0:02:22
 0:09:39
0:09:39
 0:02:04
0:02:04
 0:11:24
0:11:24
 0:09:39
0:09:39
 0:09:08
0:09:08