filmov
tv
Sound and the Ear - GCSE Physics

Показать описание
This video introduces the concept of sound and the ear and all you need to know for GCSE. The limit of human hearing is between 20 and 20,000 Hz. 1 Hz is one cycle per second. The speed of sound in air is around 330 m/s at atmospheric pressure and in liquids and solids the speed of sound is much greater.
Sound waves are mechanical and longitudinal. A mechanical wave means that it involves oscillating particles which means that mechanical waves cannot travel in a vacuum. A longitudinal wave means that the particles oscillate parallel to the direction of the wave.
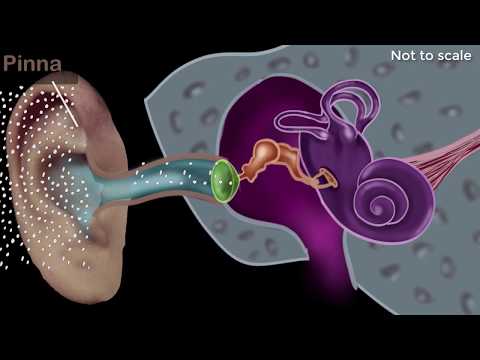
Within the ear, the sound waves vibrate the ear drum. The ear drum then vibrates three very small bones within the ear that transfers these oscillations to the auditory nerve. The auditory nerve sends these oscillations as electrical signals to the brain where they can be processed.
Thanks for watching,
Lewis
Relevant for GCSE Physics 9-1 in the following exam boards:
AQA (including Trilogy) (Physics Higher only)
Edexcel (Physics Higher only)
CCEA
OCR A (Physics Higher only)
OCR B (Physics Higher only)
_____________________________________
MY PHYSICS WEBSITES
Find even more videos organised by exam board and topic at:
GCSE Physics Online
A Level Physics Online
MY YOUTUBE CHANNEL
Your support in watching this video has been invaluable! To contribute towards the free videos on YouTube, make a small donation at:
FOLLOW ME
#waves #gcsephysics #physicsonline
Sound waves are mechanical and longitudinal. A mechanical wave means that it involves oscillating particles which means that mechanical waves cannot travel in a vacuum. A longitudinal wave means that the particles oscillate parallel to the direction of the wave.
Within the ear, the sound waves vibrate the ear drum. The ear drum then vibrates three very small bones within the ear that transfers these oscillations to the auditory nerve. The auditory nerve sends these oscillations as electrical signals to the brain where they can be processed.
Thanks for watching,
Lewis
Relevant for GCSE Physics 9-1 in the following exam boards:
AQA (including Trilogy) (Physics Higher only)
Edexcel (Physics Higher only)
CCEA
OCR A (Physics Higher only)
OCR B (Physics Higher only)
_____________________________________
MY PHYSICS WEBSITES
Find even more videos organised by exam board and topic at:
GCSE Physics Online
A Level Physics Online
MY YOUTUBE CHANNEL
Your support in watching this video has been invaluable! To contribute towards the free videos on YouTube, make a small donation at:
FOLLOW ME
#waves #gcsephysics #physicsonline
Комментарии
 0:02:27
0:02:27
 0:07:36
0:07:36
 0:04:33
0:04:33
 0:05:39
0:05:39
 0:00:11
0:00:11
 0:05:17
0:05:17
 0:12:53
0:12:53
 0:00:28
0:00:28
 0:00:58
0:00:58
 0:00:37
0:00:37
 0:00:30
0:00:30
 0:00:10
0:00:10
 0:00:41
0:00:41
 0:00:25
0:00:25
 0:01:39
0:01:39
 0:04:52
0:04:52
 0:03:45
0:03:45
 0:00:47
0:00:47
 0:01:35
0:01:35
 0:00:39
0:00:39
 0:03:20
0:03:20
 0:01:31
0:01:31
 0:03:14
0:03:14
 0:00:28
0:00:28