filmov
tv
Russia Ukraine in Data

Показать описание
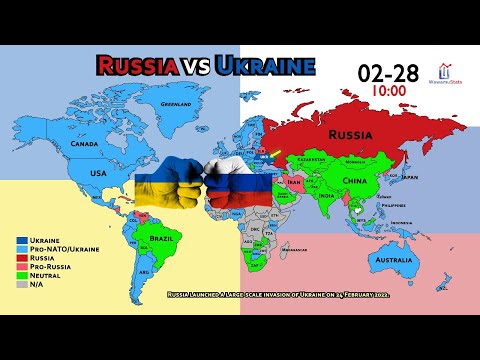
The Ukraine-Russia conflict, which began in 2014 and escalated in 2022, has its roots in historical, political, and territorial disputes. Ukraine's independence after the Soviet Union's collapse in 1991 left unresolved tensions, particularly over Crimea and the eastern regions of Donetsk and Luhansk. Russia's annexation of Crimea in 2014 and its support for separatist movements in eastern Ukraine were met with international condemnation, leading to sanctions and a protracted war that destabilized the region.
The full-scale invasion of Ukraine by Russia in February 2022 marked a dramatic escalation. Moscow justified the invasion with claims of protecting ethnic Russians and countering NATO's expansion, while Kyiv and the West denounced it as a blatant violation of international law. The conflict has devastated Ukrainian cities, displaced millions, and resulted in significant civilian and military casualties. It has also triggered widespread condemnation and unprecedented economic sanctions on Russia.
Ukraine, with substantial Western military and financial aid, has mounted a robust resistance. The conflict has seen intense battles, including Ukraine's successful counteroffensives to reclaim occupied territories. The war has also underscored the resilience of Ukrainian society and governance under extreme pressure, with President Volodymyr Zelenskyy emerging as a symbol of defiance against aggression.
The war has profoundly impacted global geopolitics, energy markets, and food security. Europe's reliance on Russian energy has decreased, prompting a pivot to alternative sources, while Ukraine's role as a major grain exporter has made the conflict a significant factor in global food inflation. The Western alliance, particularly NATO, has been strengthened, as countries like Finland and Sweden have moved closer to the bloc.
Despite numerous attempts at diplomacy, including negotiations facilitated by Turkey and international organizations, a resolution remains elusive. Both sides hold firm to their objectives, with Ukraine seeking to restore its territorial integrity and Russia demanding recognition of its annexations. The conflict continues to evolve, leaving a lasting mark on the regional and global order.
The full-scale invasion of Ukraine by Russia in February 2022 marked a dramatic escalation. Moscow justified the invasion with claims of protecting ethnic Russians and countering NATO's expansion, while Kyiv and the West denounced it as a blatant violation of international law. The conflict has devastated Ukrainian cities, displaced millions, and resulted in significant civilian and military casualties. It has also triggered widespread condemnation and unprecedented economic sanctions on Russia.
Ukraine, with substantial Western military and financial aid, has mounted a robust resistance. The conflict has seen intense battles, including Ukraine's successful counteroffensives to reclaim occupied territories. The war has also underscored the resilience of Ukrainian society and governance under extreme pressure, with President Volodymyr Zelenskyy emerging as a symbol of defiance against aggression.
The war has profoundly impacted global geopolitics, energy markets, and food security. Europe's reliance on Russian energy has decreased, prompting a pivot to alternative sources, while Ukraine's role as a major grain exporter has made the conflict a significant factor in global food inflation. The Western alliance, particularly NATO, has been strengthened, as countries like Finland and Sweden have moved closer to the bloc.
Despite numerous attempts at diplomacy, including negotiations facilitated by Turkey and international organizations, a resolution remains elusive. Both sides hold firm to their objectives, with Ukraine seeking to restore its territorial integrity and Russia demanding recognition of its annexations. The conflict continues to evolve, leaving a lasting mark on the regional and global order.
Комментарии
 0:17:50
0:17:50
 0:03:53
0:03:53
 0:31:23
0:31:23
 0:04:09
0:04:09
 0:00:34
0:00:34
 0:17:14
0:17:14
 0:00:46
0:00:46
 0:00:13
0:00:13
 0:08:55
0:08:55
 0:19:47
0:19:47
 0:01:01
0:01:01
 0:00:46
0:00:46
 0:03:20
0:03:20
 0:04:51
0:04:51
 0:14:22
0:14:22
 0:01:56
0:01:56
 0:01:04
0:01:04
 0:03:20
0:03:20
 0:16:36
0:16:36
 0:16:22
0:16:22
 0:00:41
0:00:41
 0:20:44
0:20:44
 0:00:29
0:00:29
 0:05:04
0:05:04