filmov
tv
Quantitative real time PCR (qPCR)

Показать описание
Download the study materials here-
A quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR), also called real-time polymerase chain reaction, is a laboratory technique of molecular biology based on the polymerase chain reaction (PCR), which is used to amplify and simultaneously quantify a targeted DNA molecule. For one or more specific sequences in a DNA sample, quantitative PCR enables both detection and quantification. The quantity can be either an absolute number of copies or a relative amount when normalized to DNA input or additional normalizing genes.
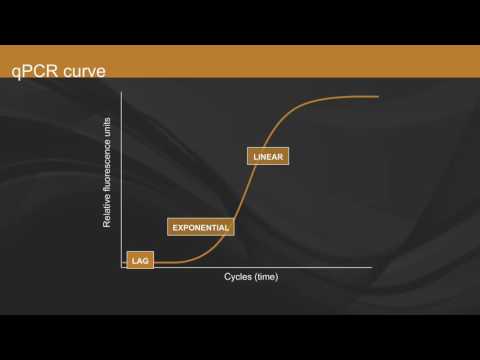
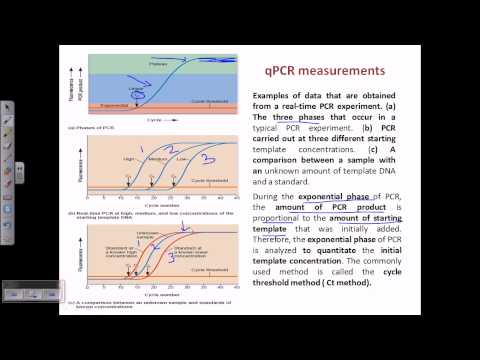
The procedure follows the general principle of polymerase chain reaction; its key feature is that the amplified DNA is detected as the reaction progresses in "real time". This is a new approach compared to standard PCR, where the product of the reaction is detected at its end. Two common methods for the detection of products in quantitative PCR are: (1) non-specific fluorescent dyes that intercalate with any double-stranded DNA, and (2) sequence-specific DNA probes consisting of oligonucleotides that are labelled with a fluorescent reporter which permits detection only after hybridization of the probe with its complementary sequence to quantify messenger RNA (mRNA) and non-coding RNA in cells or tissues.
qPCR is the abbreviation used for quantitative PCR (real-time PCR).[1] Real-time reverse-transcription PCR is often denoted as: qRT-PCR[2][3][4] The acronym "RT-PCR" commonly denotes reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction and not real-time PCR, but not all authors adhere to this convention. Source of the article published in description is Wikipedia. I am sharing their material. Copyright by original content developers of Wikipedia.
A quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR), also called real-time polymerase chain reaction, is a laboratory technique of molecular biology based on the polymerase chain reaction (PCR), which is used to amplify and simultaneously quantify a targeted DNA molecule. For one or more specific sequences in a DNA sample, quantitative PCR enables both detection and quantification. The quantity can be either an absolute number of copies or a relative amount when normalized to DNA input or additional normalizing genes.
The procedure follows the general principle of polymerase chain reaction; its key feature is that the amplified DNA is detected as the reaction progresses in "real time". This is a new approach compared to standard PCR, where the product of the reaction is detected at its end. Two common methods for the detection of products in quantitative PCR are: (1) non-specific fluorescent dyes that intercalate with any double-stranded DNA, and (2) sequence-specific DNA probes consisting of oligonucleotides that are labelled with a fluorescent reporter which permits detection only after hybridization of the probe with its complementary sequence to quantify messenger RNA (mRNA) and non-coding RNA in cells or tissues.
qPCR is the abbreviation used for quantitative PCR (real-time PCR).[1] Real-time reverse-transcription PCR is often denoted as: qRT-PCR[2][3][4] The acronym "RT-PCR" commonly denotes reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction and not real-time PCR, but not all authors adhere to this convention. Source of the article published in description is Wikipedia. I am sharing their material. Copyright by original content developers of Wikipedia.
Комментарии
 0:04:37
0:04:37
 0:08:33
0:08:33
 0:01:39
0:01:39
 0:02:45
0:02:45
 0:14:12
0:14:12
 0:12:36
0:12:36
 0:12:54
0:12:54
 0:03:02
0:03:02
 0:02:24
0:02:24
 0:01:00
0:01:00
 0:58:07
0:58:07
 0:06:10
0:06:10
 0:03:49
0:03:49
 0:03:43
0:03:43
 0:03:28
0:03:28
 0:08:24
0:08:24
 0:02:35
0:02:35
 0:10:44
0:10:44
 0:07:34
0:07:34
 0:05:10
0:05:10
 0:02:10
0:02:10
 0:02:38
0:02:38
 0:03:35
0:03:35
 0:10:03
0:10:03