filmov
tv
Solving x^3+x^2+4=0 in Two Ways

Показать описание
If you need to post a picture of your solution or idea:
#ChallengingMathProblems #PolynomialEquations
⭐ Similar videos:
PLAYLISTS 🎵 :
#ChallengingMathProblems #PolynomialEquations
⭐ Similar videos:
PLAYLISTS 🎵 :
Solving x^3+x^2+4=0 in Two Ways
Solving a Cubic Equation in Two Ways (x^3-x^2-4=0)
Can You Solve 4x^3-3x-2=0 in Two Ways?
Solving x^3+x^2-x+2=0 in Two Ways
Factorising cubic functions: The kx method
Solve quadratic equation by factorisation
Factoring a polynomial to the fourth power using factoring to second power
Solving a quadratic by completing the square
MATHS PAPER 1 PRELIM REVISION | GAUTENG || GRADE 12
How To Solve Quadratic Equations By Factoring - Quick & Simple! | Algebra Online Course
Solve by completing the square | Step by Step Technique
Solve by Completing the Square: Step-by-Step Technique
solving equations but they get increasingly awesome
How to solve a 5-term 4th degree polynomial equation x^4+x^3+x^2+x+1=0
5 simple unsolvable equations
Solving using the quadratic formula with complex solutions
Solve the Quadratic Equation 3x^2 - 2x = 0 by Factoring
How To Solve Quadratic Equations Using The Quadratic Formula
Solving an equation with variables on both side and one solution
FASTEST way to factor a trinomial! #shorts
Solving Quadratic Equations using Quadratic Formula - Quadratic Equations
How To Solve Quadratic Equations by Extracting the Square Roots by Extracting the Roots?
Solve Quadratic Equations By Factoring - Simple Trick No Fuss!
Solving x^3+x-10=0 in Two Ways
Комментарии
 0:10:27
0:10:27
 0:08:12
0:08:12
 0:12:19
0:12:19
 0:07:48
0:07:48
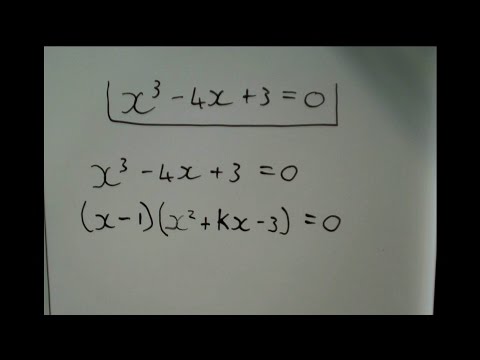 0:10:22
0:10:22
 0:09:05
0:09:05
 0:03:26
0:03:26
 0:10:43
0:10:43
 2:56:13
2:56:13
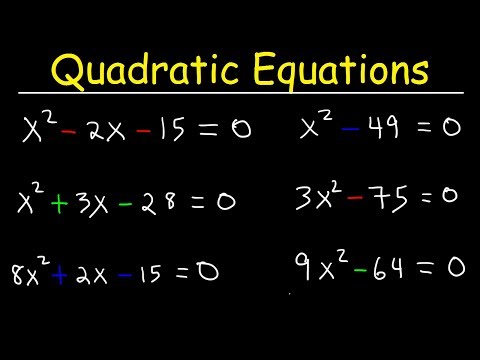 0:12:29
0:12:29
 0:05:20
0:05:20
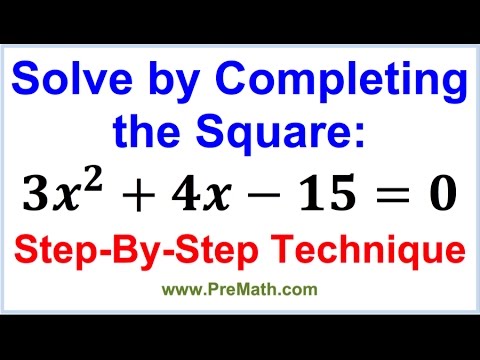 0:07:40
0:07:40
 0:10:44
0:10:44
 0:13:19
0:13:19
 0:00:50
0:00:50
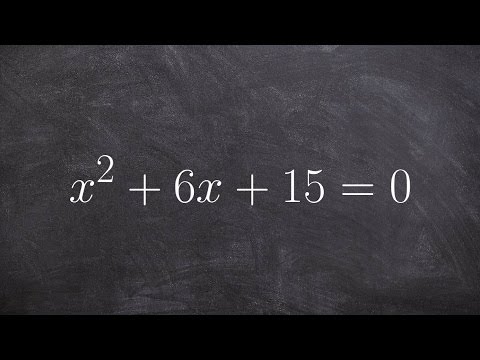 0:05:28
0:05:28
 0:01:13
0:01:13
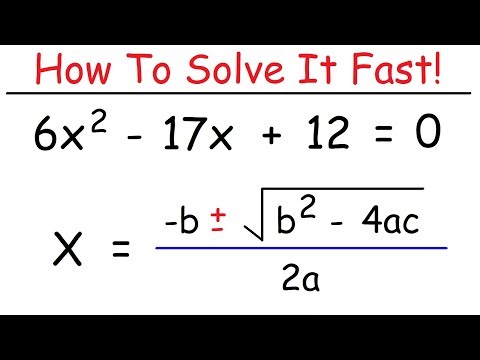 0:05:56
0:05:56
 0:02:36
0:02:36
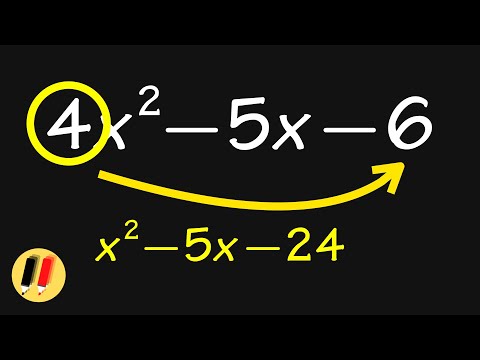 0:00:55
0:00:55
 0:09:06
0:09:06
 0:05:31
0:05:31
 0:06:31
0:06:31
 0:06:33
0:06:33