filmov
tv
Solving a Homogeneous Differential Equation

Показать описание
If you need to post a picture of your solution or idea:
#CalculusProblems #DifferentialEquations
EXPLORE 😎:
PLAYLISTS 🎵 :
#CalculusProblems #DifferentialEquations
EXPLORE 😎:
PLAYLISTS 🎵 :
Homogeneous Differential Equations
Homogeneous Differential Equations (introduction & example)
How To Solve First Order Homogeneous Differential Equation
How to Solve Constant Coefficient Homogeneous Differential Equations
Solving Homogeneous First Order Differential Equations (Differential Equations 21)
Substitutions for Homogeneous First Order Differential Equations (Differential Equations 20)
How to solve differential equations
Solving a Homogeneous Differential Equation
Homogeneous Second Order Linear Differential Equations
4 Types of ODE's: How to Identify and Solve Them
Class 12th – Homogeneous Differential Equations Problem Example-1 | Tutorials Point
Determine if a First-Order Differential Equation is Homogeneous - Part 1
Solving a Fifth Order Linear Homogeneous Differential Equation
🔵11 - Homogeneous First Order Differential Equations (Solved Examples)
Homogeneous Differential Equation | Problems | Ordinary differential Equations | First ODEs | Maths
Diff Eqn: Solving first order homogeneous equation 1/6
First order, Ordinary Differential Equations.
Homogenous differential equation by substitution
Change of Variables / Homogeneous Differential Equation - Example 1
Differential Equations - Homogeneous DE, Easy Approach Sample Problems Part 1
Homogeneous Differential Equations Problem No 1 - Differential Equations - Diploma Maths II
First Order Homogeneous Differential Equations Lesson 2
🔵18 - Second Order Linear Homogeneous Differential Equations with Constants coefficients
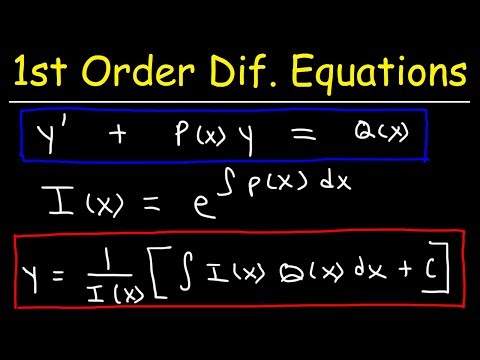
First Order Linear Differential Equations
Комментарии
 0:26:55
0:26:55
 0:07:59
0:07:59
 0:08:33
0:08:33
 0:06:41
0:06:41
 1:55:11
1:55:11
 1:05:45
1:05:45
 0:00:46
0:00:46
 0:08:40
0:08:40
 0:04:35
0:04:35
 0:06:57
0:06:57
 0:06:48
0:06:48
 0:07:47
0:07:47
 0:05:11
0:05:11
 0:42:58
0:42:58
 0:13:34
0:13:34
 0:07:29
0:07:29
 0:48:35
0:48:35
 0:07:21
0:07:21
 0:07:39
0:07:39
 0:25:41
0:25:41
 0:04:55
0:04:55
 0:06:16
0:06:16
 0:26:57
0:26:57
 0:22:28
0:22:28