filmov
tv
Complex Fourier Series (fourier series engineering mathematics)

Показать описание
We will derive the coefficients formula for the complex Fourier series.
@blackpenredpen
@blackpenredpen
Complex Fourier Series (fourier series engineering mathematics)
Complex Fourier Series
MM41: Complex Fourier series
Complex Exponential Fourier Series
How To Find The Complex Fourier Series of a function
Complex Fourier Series
Fourier series
But what is a Fourier series? From heat flow to drawing with circles | DE4
# Fourier series #trignometry #mathematics #grade #numbertheory #gradefunction #puremathematics
Deriving Complex Fourier Series
Complex Exponential Fourier Series (Example 1)
Fourier Series
Fourier Transforms || Theoretical Interpretations, Complex Exponentials and Window Effect
Advanced Engineering Mathematics | Complex Fourier Series
Epicycles, complex Fourier series and Homer Simpson's orbit
But what is the Fourier Transform? A visual introduction.
Complex Fourier Series Example Problem! (part 2)
Complex Exponential Fourier Series (Example 3)
Complex Exponential Fourier Series (Example 2)
3.6 Complex Fourier series
What is a Fourier Series? (Explained by drawing circles) - Smarter Every Day 205
how to get the Fourier series coefficients (fourier series engineering mathematics)
Fourier Series: Complex Version! Part 1
Complex Fourier Series fx=x^2
Комментарии
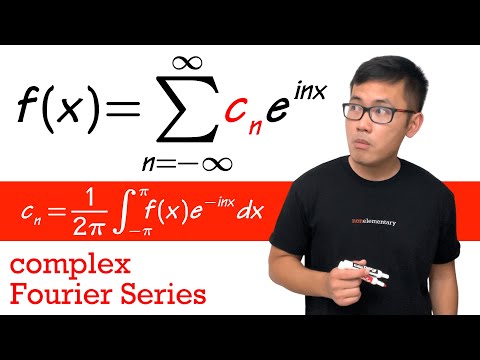 0:12:57
0:12:57
 0:12:25
0:12:25
 0:17:28
0:17:28
 0:10:11
0:10:11
 0:18:35
0:18:35
 0:15:57
0:15:57
 0:01:00
0:01:00
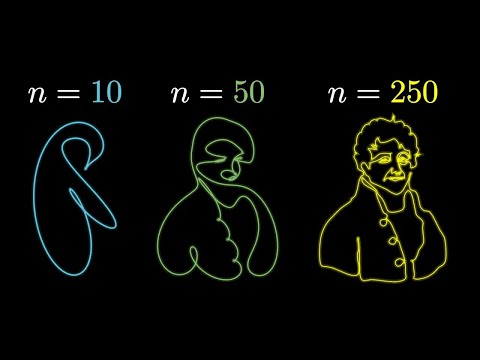 0:24:47
0:24:47
 0:01:01
0:01:01
 0:11:07
0:11:07
 0:13:03
0:13:03
 0:16:36
0:16:36
 0:19:07
0:19:07
 0:30:59
0:30:59
 0:25:35
0:25:35
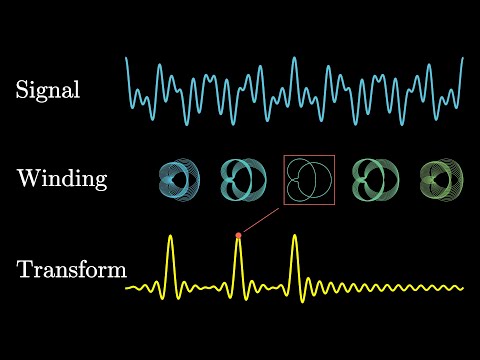 0:20:57
0:20:57
 0:18:59
0:18:59
 0:13:31
0:13:31
 0:08:58
0:08:58
 0:09:13
0:09:13
 0:08:25
0:08:25
 0:20:17
0:20:17
 0:16:49
0:16:49
 0:20:47
0:20:47