filmov
tv
IV Fluids for Beginners - When to Use Each IV Fluid Type??

Показать описание
In this video we talk about the different type of IV fluids and how they relate to the human body. We’ll go over some sample scenarios and what each IV fluid is made of.
Coupon Code: YOUTUBE15
For more educational resources, like our H&P notebooks, ID cards, and reference guides check out our website!
Here at Medical Basics, we hope to make your life as a medical student or nursing student a little easier! After graduating UCSF medical school, we’ve accumulated a lot of knowledge over the years. From things like reading a chest x-ray, to succeeding on your subi, or even how to get into med school, we’ve got you covered.
Prefer podcasting? Listen to this video on the go by subscribing to our podcast!
Coupon Code: YOUTUBE15
For more educational resources, like our H&P notebooks, ID cards, and reference guides check out our website!
Here at Medical Basics, we hope to make your life as a medical student or nursing student a little easier! After graduating UCSF medical school, we’ve accumulated a lot of knowledge over the years. From things like reading a chest x-ray, to succeeding on your subi, or even how to get into med school, we’ve got you covered.
Prefer podcasting? Listen to this video on the go by subscribing to our podcast!
IV Fluids for Beginners - When to Use Each IV Fluid Type??
Types of IV Fluid - Fluid Management
Fluid & Hormones | IV Fluids (Isotonic, Hypotonic, & Hypertonic)
A guide to intravenous fluids (IV) | UKMLA | CPSA
IV Fluid Types & Uses Nursing IV Therapy: Isotonic, Hypertonic, Hypotonic Solutions Tonicity NCL...
IV Fluids Made Easy » hypertonic, isotonic, hypotonic » FREE worksheet
Mastering Tonicity Concepts For IV Fluids - NCLEX Prep
Fundamentals: Intravenous Fluids
How To Insert IV Cannula/IV Cannulation Techniques #nursing #short #trending #vairalshort
Medical School - Intravenous Fluids Made Easy
IV Fluids: Lesson 1 - Basic Principles
IV Therapy, IV Insertion & Cautions Nursing | Intravenous Insertion DEMO
Setting up an intravenous Infusion
How to master IV Fluid Solutions (hyper vs hypo tonic and osmotic pressures)
How to Start an IV | IV Catheter Insertion & Flush Technique in Hand | Nursing Skill
IV Drip Flow Rates Drop Factor gtts/minute Dosage Calculations Nursing | NCLEX Review
IV Fluids: Lesson 2 - Crystalloids and Colloids
Intravenous (IV) cannulation | OSCE Guide | UKMLA | CPSA
IV ACCESS: 3 TOP MISTAKES
Maintenance Fluids & Calculations - Fluid Management
TYPES OF IV FLUIDS (fluids and electrolytes)
IV Angle of Insertion: Clinical Tips | @LevelUpRN
How to Order IV Fluids
IV Fluids
Комментарии
 0:13:30
0:13:30
 0:24:26
0:24:26
 0:02:52
0:02:52
 0:09:46
0:09:46
 0:16:26
0:16:26
 0:04:36
0:04:36
 0:02:33
0:02:33
 0:28:12
0:28:12
 0:00:47
0:00:47
 0:09:45
0:09:45
 0:18:30
0:18:30
 0:03:48
0:03:48
 0:06:17
0:06:17
 0:09:20
0:09:20
 0:07:54
0:07:54
 0:11:08
0:11:08
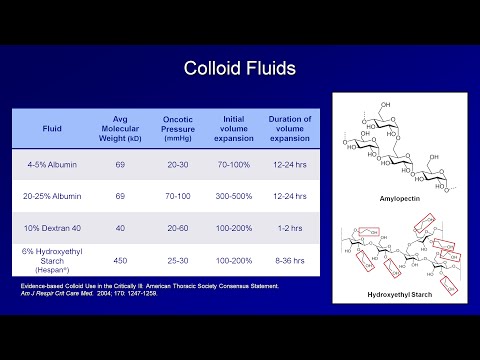 0:20:17
0:20:17
 0:03:46
0:03:46
 0:06:46
0:06:46
 0:14:02
0:14:02
 0:00:41
0:00:41
 0:01:28
0:01:28
 0:02:28
0:02:28
 0:12:13
0:12:13