filmov
tv
RNA Splicing by the Spliceosome: Supplemental Video 6

Показать описание
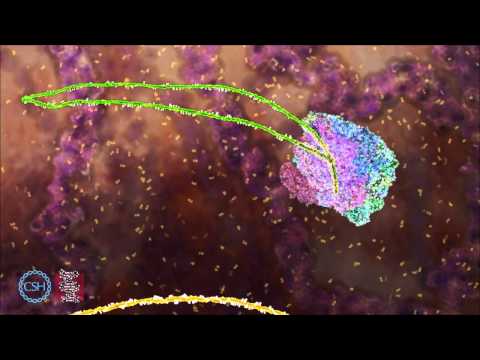
Shown: The exon ligation reaction, showing the transition from C complex to P complex via C* complex. Structures derive from PDB codes 5LJ5 for yeast C complex (29) and 6EXN for yeast P complex (87). Data not shown from other important structures (30, 85, 86, 88, 89). To animate 3′SS docking a hairpin was modelled between the BP and 3′SS as suggested by Liu et al. (88). Transcription of narration: “C complex is formed immediately after the branching reaction. To enable exon ligation, the helicase Prp16 pulls the intron near the 3′SS. This triggers dissociation of the step I factors. The branch helix then undocks, accompanied by a change to the exon ligation conformation, forming C* complex. The step II factors Prp18 and Slu7 then bind along with the helicase Prp22. This promotes docking of the 3′SS into the active site. The 3′SS is recognized by pairing to the 5′SS and branch point adenosine. Upon exon ligation, the 5′ and 3′ exons are connected to form mRNA. The resultant spliceosome after exon ligation is called P complex.” Video used with permission from the MRC Laboratory of Molecular Biology, Cambridge, UK.
 0:01:38
0:01:38
 0:06:53
0:06:53
 0:09:33
0:09:33
 0:01:03
0:01:03
 0:08:05
0:08:05
 0:10:28
0:10:28
 0:02:01
0:02:01
 0:04:55
0:04:55
 0:04:16
0:04:16
 0:01:05
0:01:05
 0:05:33
0:05:33
 0:00:30
0:00:30
 0:01:28
0:01:28
 0:01:13
0:01:13
 0:01:14
0:01:14
 0:23:32
0:23:32
 0:05:21
0:05:21
 0:01:14
0:01:14
 0:02:11
0:02:11
 0:01:28
0:01:28
 0:01:13
0:01:13
 0:00:54
0:00:54
 0:16:49
0:16:49
 0:07:04
0:07:04