filmov
tv
How Schrodinger Came Up With His Famous Equation (But EASIER)

Показать описание
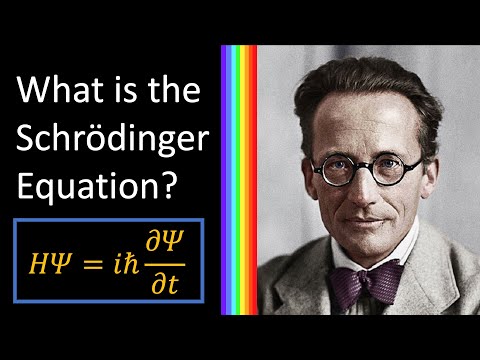
The Schrodinger Equation is one of the most important equations (if not THE most important equation) in the theory of quantum physics. But where does it come from? How did Schrodinger derive it?
Although it's a quantum form of the law of conservation of energy, its derivation isn't discussed anywhere near as much as it should in my opinion. I've even heard some people say that the equation CAN'T be derived, only verified experimentally.
We start with the electromagnetic wave equation - which described electromagnetic waves (as you may have guessed from its name). One of the solutions of this equation is a sinusoidal wave showing the electric field oscillating back and forth between some field value E_0 and its negative, in both space and time.
However this solution is only a solution if a required relationship, or condition, is met. This condition can be boiled down to the idea that any photon corresponding to our wave must have an energy equal to its momentum multiplied by its speed. Luckily, this equation literally defines what a photon is - it's an object whose energy is related to its momentum in that exact way.
Now this relationship (or condition) is actually part of a bigger picture - mass-energy equivalence. For any generic object, we can relate the energy of the object to its momentum and mass through this equivalence relation. For photons, m = 0 so it reduces down to E = pc. However for objects with mass, we get Einstein's famous E = mc^2 equation.
So what if we now go backwards, but starting with the FULL equivalence relation as the condition rather than the reduced one for photons? This way the wave equation we'll end up with SHOULD describe not just photons, but objects with mass (and possibly momentum too). That's exactly what the Schrodinger equation needs to do.
However, when we go backwards like this, the wave equation we end up with is actually the Klein-Gordon equation. This is a relativistic equation, whereas the Schrodinger isn't. So we do need to complete one more step, which is to reduce the Klein-Gordon equation into non-relativistic scenarios. To do this, we see what the equation will look like at low speeds. This is because relativistic effects show up at high speeds, and so if we set the object's speed v to be much less than c, we reduce the Klein-Gordon equation down to the Schrodinger equation!
This derivation is intuitive for those who know the mathematics because we can follow the math through, but it's also intuitive for those who don't know the math because the logical steps can be easily followed.
Thanks for watching, please do check out my links:
INSTAGRAM - @parthvlogs
MUSIC CHANNEL - Parth G Music
Here are some affiliate links for things I use!
Timestamps:
0:00 - The Schrodinger Equation
1:25 - The Electromagnetic Wave Equation and Its Solutions
5:31 - Mass Energy Equivalence - Let's Go Backwards!
7:05 - The Klein-Gordon Equation and Relativity
8:23 - Finally, The Schrodinger Equation (Again)
Videos in Cards:
Although it's a quantum form of the law of conservation of energy, its derivation isn't discussed anywhere near as much as it should in my opinion. I've even heard some people say that the equation CAN'T be derived, only verified experimentally.
We start with the electromagnetic wave equation - which described electromagnetic waves (as you may have guessed from its name). One of the solutions of this equation is a sinusoidal wave showing the electric field oscillating back and forth between some field value E_0 and its negative, in both space and time.
However this solution is only a solution if a required relationship, or condition, is met. This condition can be boiled down to the idea that any photon corresponding to our wave must have an energy equal to its momentum multiplied by its speed. Luckily, this equation literally defines what a photon is - it's an object whose energy is related to its momentum in that exact way.
Now this relationship (or condition) is actually part of a bigger picture - mass-energy equivalence. For any generic object, we can relate the energy of the object to its momentum and mass through this equivalence relation. For photons, m = 0 so it reduces down to E = pc. However for objects with mass, we get Einstein's famous E = mc^2 equation.
So what if we now go backwards, but starting with the FULL equivalence relation as the condition rather than the reduced one for photons? This way the wave equation we'll end up with SHOULD describe not just photons, but objects with mass (and possibly momentum too). That's exactly what the Schrodinger equation needs to do.
However, when we go backwards like this, the wave equation we end up with is actually the Klein-Gordon equation. This is a relativistic equation, whereas the Schrodinger isn't. So we do need to complete one more step, which is to reduce the Klein-Gordon equation into non-relativistic scenarios. To do this, we see what the equation will look like at low speeds. This is because relativistic effects show up at high speeds, and so if we set the object's speed v to be much less than c, we reduce the Klein-Gordon equation down to the Schrodinger equation!
This derivation is intuitive for those who know the mathematics because we can follow the math through, but it's also intuitive for those who don't know the math because the logical steps can be easily followed.
Thanks for watching, please do check out my links:
INSTAGRAM - @parthvlogs
MUSIC CHANNEL - Parth G Music
Here are some affiliate links for things I use!
Timestamps:
0:00 - The Schrodinger Equation
1:25 - The Electromagnetic Wave Equation and Its Solutions
5:31 - Mass Energy Equivalence - Let's Go Backwards!
7:05 - The Klein-Gordon Equation and Relativity
8:23 - Finally, The Schrodinger Equation (Again)
Videos in Cards:
Комментарии
 0:10:35
0:10:35
 0:14:58
0:14:58
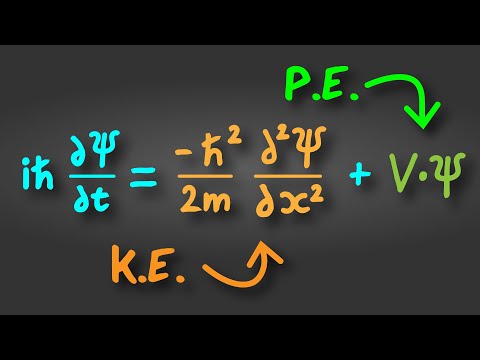 0:01:00
0:01:00
 0:15:53
0:15:53
 0:04:38
0:04:38
 0:12:44
0:12:44
 0:01:00
0:01:00
 0:29:55
0:29:55
 0:18:35
0:18:35
 0:11:09
0:11:09
 0:07:18
0:07:18
 0:08:45
0:08:45
 0:01:00
0:01:00
 0:00:51
0:00:51
 1:27:34
1:27:34
 0:09:28
0:09:28
 0:17:09
0:17:09
 0:00:58
0:00:58
 0:12:19
0:12:19
 0:12:57
0:12:57
 0:01:01
0:01:01
 0:09:13
0:09:13
 0:13:04
0:13:04
 0:13:05
0:13:05