filmov
tv
Baby's Feet Development - Podiatrist Georgina Tay, East Coast Podiatry

Показать описание
Common Foot Deformities and Conditions in Children
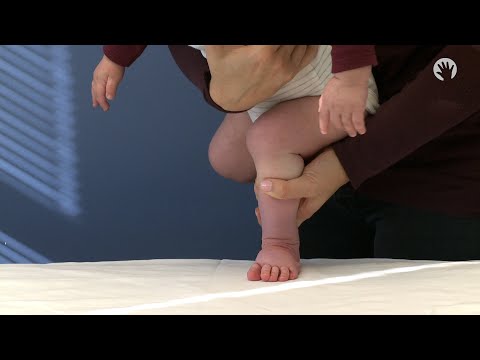
Even at 8 months old, because both of her parents have high arch feet, this little baby is already developing a higher arch. Like adults, children can develop foot deformities and conditions, so it is important for parents to educate themselves and check their children's feet to see if this is happening. While some of these conditions will resolve over time, others may continue into adulthood. Some older children may complain to their parents about the pain while others may think that their condition is normal or may not speak up when experiencing discomfort, so parents need to be proactive and vigilant about their child’s health.
Here are some common lower limb and gait abnormalities Podiatrists often see in children:
- Children In-toeing
In-toeing, or “pigeon-toed”, is often noticed by parents when the toddler starts walking in earnest. The feet appear to turn inward, instead of pointing out or straight ahead. In-toeing can be due to abnormal bone alignment in the legs and feet, or due to soft tissue contractures in the hips, or a combination of both. A lower extremity examination is necessary to pinpoint the site of rotational deformity.
- Children Toe Walking
Parents usually notice toe-walking in a child when he/she first walks independently. The toe-walking may be habitual (voluntary), or it may be due to an underlying neuromuscular or neuropsychiatric disorder (such as autism).
Prolonged toe-walking can lead to a shortening of the calf muscles and Achilles tendon, in which case surgery may be required.
Children Knock Knees
Knock-knees, or genu valgum, is an angular deformity exhibited at the knees when the child is standing at attention: the knees touch, but the feet do not.
While knock-knee development is physiologic and self-correcting for many children, podiatric care is warranted in cases where it is severe or asymmetrical. Surgery may be required.
Where knock-knees are mild and only require monitoring, podiatrists turn their attention to its secondary effects on the feet. The valgus knee angle acts as a pronatory force on the feet, pushing them out and away from under the leg bones. It is important to protect the feet from such abnormal stresses during a child’s development.
Children's Orthotics (shoe insoles)
It is important to assess foot problems in childhood and address them if necessary as some of these issues can have long-lasting effects, affecting the individual’s quality of life as an adult.
Even at 8 months old, because both of her parents have high arch feet, this little baby is already developing a higher arch. Like adults, children can develop foot deformities and conditions, so it is important for parents to educate themselves and check their children's feet to see if this is happening. While some of these conditions will resolve over time, others may continue into adulthood. Some older children may complain to their parents about the pain while others may think that their condition is normal or may not speak up when experiencing discomfort, so parents need to be proactive and vigilant about their child’s health.
Here are some common lower limb and gait abnormalities Podiatrists often see in children:
- Children In-toeing
In-toeing, or “pigeon-toed”, is often noticed by parents when the toddler starts walking in earnest. The feet appear to turn inward, instead of pointing out or straight ahead. In-toeing can be due to abnormal bone alignment in the legs and feet, or due to soft tissue contractures in the hips, or a combination of both. A lower extremity examination is necessary to pinpoint the site of rotational deformity.
- Children Toe Walking
Parents usually notice toe-walking in a child when he/she first walks independently. The toe-walking may be habitual (voluntary), or it may be due to an underlying neuromuscular or neuropsychiatric disorder (such as autism).
Prolonged toe-walking can lead to a shortening of the calf muscles and Achilles tendon, in which case surgery may be required.
Children Knock Knees
Knock-knees, or genu valgum, is an angular deformity exhibited at the knees when the child is standing at attention: the knees touch, but the feet do not.
While knock-knee development is physiologic and self-correcting for many children, podiatric care is warranted in cases where it is severe or asymmetrical. Surgery may be required.
Where knock-knees are mild and only require monitoring, podiatrists turn their attention to its secondary effects on the feet. The valgus knee angle acts as a pronatory force on the feet, pushing them out and away from under the leg bones. It is important to protect the feet from such abnormal stresses during a child’s development.
Children's Orthotics (shoe insoles)
It is important to assess foot problems in childhood and address them if necessary as some of these issues can have long-lasting effects, affecting the individual’s quality of life as an adult.
Комментарии
 0:01:11
0:01:11
 0:02:38
0:02:38
 0:00:40
0:00:40
 0:03:17
0:03:17
 0:01:58
0:01:58
 0:01:51
0:01:51
 0:02:20
0:02:20
 0:02:48
0:02:48
 0:02:30
0:02:30
 0:00:16
0:00:16
 0:02:25
0:02:25
 0:00:31
0:00:31
 0:01:31
0:01:31
 0:02:53
0:02:53
 0:00:57
0:00:57
 0:00:16
0:00:16
 0:01:15
0:01:15
 0:00:16
0:00:16
 0:01:26
0:01:26
 0:00:47
0:00:47
 0:00:16
0:00:16
 0:01:51
0:01:51
 0:00:27
0:00:27
 0:01:20
0:01:20