filmov
tv
How to CURE urinary tract infection? (UTI) - Doctor explains

Показать описание
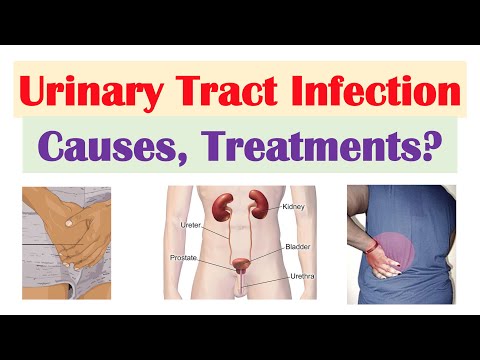
An urinary tract infection typically occurs when bacteria enter the urinary tract through the urethra and begin to multiply in your lower urinary tract, mostly your bladder. This is also called a bladder infection or cystitis. When it affect the upper urinary tract it is called a kidney infection or pyelonephritis.
These infections are in 80-85% of all cases caused by the E. Coli bacteria of your gut. In 5-10% of all cases this can be caused by a staphylococcus saprophyticus. Rarely these infections are caused due to viral or fungal infections.
Risk factors:
First of all intercourse: in young sexually active women it is estimated that about 75-90% of bladder infections are caused by intercourse. This increased risk is not seen in post-menopausal women.
The second risk factor is female anatomy: women have a high risk for developing a UTI. This is caused by their urethra. It is much shorter in women and is closer to the anus.
The next risk factor is menopause: a woman’s estrogen levels decrease overtime. This leads to a loss of protective vaginal flora which makes you more vulnerable for an UTI.
Other risk factors are: obesity, family history, blockages in your urinary tract, an impaired immune system, diabetes, the use of a catheter and/or recent surgery of your urinary tract.
Symptoms:
Lower UTI: discharge, a burning sensation when peeing, frequent peeing, blood in your urine pelvic pressure and pain in your lower belly.
Upper UTI: Upper back and side (flank) pain, high fever, shaking and chills, nausea and vomiting.
Tips:
- Drink plenty of liquids, especially water. It is recommended to drink at least 6-8 glasses per day.
- Drink cranberry juice. Although studies are not conclusive that cranberry juice prevents UTIs, some show it does.
- Wipe from front to back. Doing so prevents bacteria in the anal region from spreading to the vagina and urethra.
- Other common tips are: Pee right after intercourse, avoid using irritating feminine products, take showers instead of baths, wear cotton underwear and change your underwear daily.
Treatment options:
- Get a medical examination.
- A simple UTI can be treated with one of the following antibiotics: Nitrofurantoin, cephalexin, ceftriaxone, trimethoprim or Fosfomycin.
- In addition your doctor might also prescribe you painkillers to relieve abdominal cramps, back pain and any discomfort you might experience.
- If you are frequently dealing with UTIs your doctor might recommend you to take a low-dose of antibiotics for 6 months, use a single dose of antibiotics after sexual intercourse or start with estrogen therapy if you’re postmenopausal.
- Disclaimer: this video and the comments are meant purely informational! This is not medical advice! If you are looking for medical advice always contact your own doctor. -
I want to give special thanks to my sponsors on Patreon:
- Sebastian Houwing: Investor
- Roel: Supporter
Literature:
1: Mayo Clinic. (2020). Urinary tract infection (UTI).
2: WebMD. (2020). Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs).
3: NHS. (2020). Urinary tract infections (UTIs).
Music:
1. Verified Picasso, Fish Room
2. Patrick Patrikos, Good Times
3. Patrick Patrikos, Grut
4: Patrick Patrikios. Rockville
Follow me on instagram: @HOWTOMEDICATE
Follow me on twitter: @HOWTOMEDICATE
Books I used In Medical School:
Gear I use:
Комментарии
 0:00:58
0:00:58
 0:03:52
0:03:52
 0:06:53
0:06:53
 0:01:37
0:01:37
 0:11:44
0:11:44
 0:01:07
0:01:07
 0:06:42
0:06:42
 0:01:14
0:01:14
 0:29:42
0:29:42
 0:01:25
0:01:25
 0:04:30
0:04:30
 0:05:54
0:05:54
 0:02:18
0:02:18
 0:01:24
0:01:24
 0:08:12
0:08:12
 0:04:57
0:04:57
 0:00:35
0:00:35
 0:01:59
0:01:59
 0:04:53
0:04:53
 0:05:17
0:05:17
 0:01:28
0:01:28
 0:03:41
0:03:41
 0:03:42
0:03:42
 0:04:35
0:04:35