filmov
tv
DNA and chromatin regulation | Biomolecules | MCAT | Khan Academy

Показать описание
Created by Tracy Kim Kovach.
MCAT on Khan Academy: Go ahead and practice some passage-based questions!
About Khan Academy: Khan Academy offers practice exercises, instructional videos, and a personalized learning dashboard that empower learners to study at their own pace in and outside of the classroom. We tackle math, science, computer programming, history, art history, economics, and more. Our math missions guide learners from kindergarten to calculus using state-of-the-art, adaptive technology that identifies strengths and learning gaps. We've also partnered with institutions like NASA, The Museum of Modern Art, The California Academy of Sciences, and MIT to offer specialized content.
For free. For everyone. Forever. #YouCanLearnAnything
MCAT on Khan Academy: Go ahead and practice some passage-based questions!
About Khan Academy: Khan Academy offers practice exercises, instructional videos, and a personalized learning dashboard that empower learners to study at their own pace in and outside of the classroom. We tackle math, science, computer programming, history, art history, economics, and more. Our math missions guide learners from kindergarten to calculus using state-of-the-art, adaptive technology that identifies strengths and learning gaps. We've also partnered with institutions like NASA, The Museum of Modern Art, The California Academy of Sciences, and MIT to offer specialized content.
For free. For everyone. Forever. #YouCanLearnAnything
DNA and chromatin regulation | Biomolecules | MCAT | Khan Academy
Chromatin Biology: Epigenetics and the Regulation of Gene Activity
Histone acetylation | Chromatin modification | What does histone acetylation do?
DNA and Chromatin Regulation
How DNA methylation works
Epigenetics
EPIGENETICS & CHROMATIN STATES - An introduction to histone modifications & gene transcripti...
Regulation of Gene Expression: Operons, Epigenetics, and Transcription Factors
DNA packaging| Nucleosome| Chromatin| Chromosome| Histone protein| Gene regulation
Introduction to epigenetics - Learn.OmicsLogic.com
Chromosome Structure and Organization
Chuan He - RNA Methylation in Chromatin Regulation
Chromosome structure | Chromatin organization | 3D chromatin | levels of organization in chromosomes
Aufbau & Zustand des Chromatins
Chromatin structure, gene regulation, and epigenomic mapping assays
DNA methylation | What is DNA methylation and why is it important?
Gene Regulation and the Operon
Histone modifications (Introduction)
DNA & CHROMATIN | Introduction to Epigenetics
Regulation of transcription | Biomolecules | MCAT | Khan Academy
Histone acetylation and methylation
Chromatin Remodeling in Eukaryotes
Cell Biology | DNA Structure & Organization 🧬
Nucleosome remodeling complex( introduction)
Комментарии
 0:05:21
0:05:21
 0:02:50
0:02:50
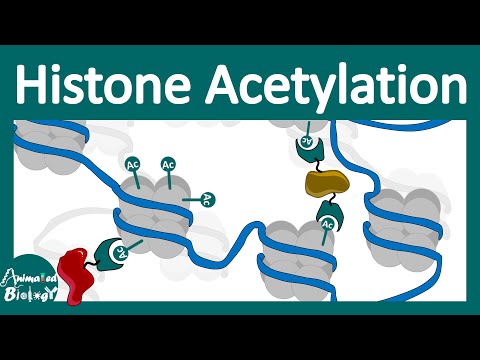 0:06:12
0:06:12
 0:05:21
0:05:21
 0:00:32
0:00:32
 0:08:42
0:08:42
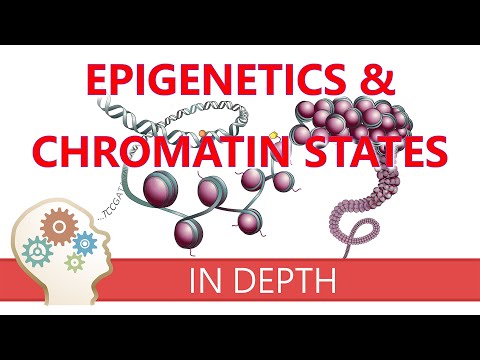 0:39:04
0:39:04
 0:13:07
0:13:07
 0:13:28
0:13:28
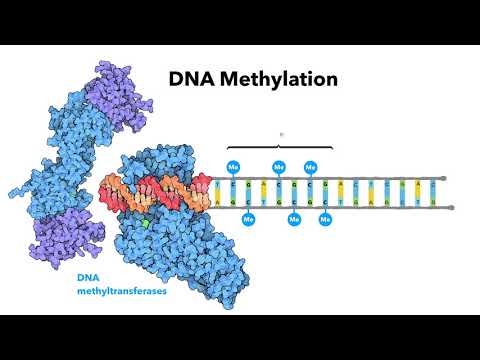 0:12:50
0:12:50
 0:09:30
0:09:30
 0:32:32
0:32:32
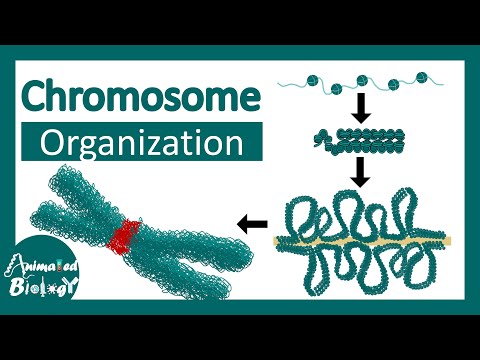 0:18:20
0:18:20
 0:04:56
0:04:56
 0:04:25
0:04:25
 0:04:25
0:04:25
 0:06:16
0:06:16
 0:12:45
0:12:45
 0:21:15
0:21:15
 0:06:47
0:06:47
 0:11:28
0:11:28
 0:04:01
0:04:01
 0:46:23
0:46:23
 0:12:53
0:12:53