filmov
tv
Discrete Random Variables: Distributions 2

Показать описание
We explore the properties of a discrete distribution of a random variable for the number of ice creams sold. This includes finding the expected value, variance and standard deviation for the original distribution, two distributions added together, the distribution times a constant, and the distribution plus a constant.
Note that there is an error at 7:13. It should say Var (aX) = a^2 Var(X). (The constant is squared)
#DrNicStats #Statistics #Probability
Note that there is an error at 7:13. It should say Var (aX) = a^2 Var(X). (The constant is squared)
#DrNicStats #Statistics #Probability
Discrete Random Variables: Distributions 2
02 - Random Variables and Discrete Probability Distributions
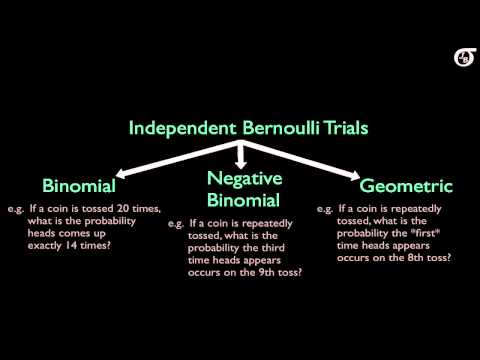
Overview of Some Discrete Probability Distributions (Binomial,Geometric,Hypergeometric,Poisson,NegB)
Discrete Random Variables
L12.2 The Sum of Independent Discrete Random Variables
Probability with discrete random variable example | Random variables | AP Statistics | Khan Academy
Random variables | Probability and Statistics | Khan Academy
Statistical distributions full course
Expected Value and Variance of Discrete Random Variables
Two-dimensional discrete distributions: an introduction
Discrete and continuous random variables | Probability and Statistics | Khan Academy
Probability Distributions and Random Variables | Econometrics 101: Lesson 2.1 | Think Econ
2- Discrete Random Variable & Cumulative distribution function
Joint Probability Distribution Of Discrete Random Variables
Edexcel AS Level Maths: 6.1 Probability Distributions (part 1)
Random Variables and Probability Distributions
Discrete Random Variables and Probability Distribution Functions
Probability Distribution Functions (PMF, PDF, CDF)
An Introduction to Discrete Random Variables and Discrete Probability Distributions
DISCRETE Random Variables: Finite and Infinite Distributions (9-2)
Discrete Random Variables (2 of 3: Notation)
Discrete Random Variables (2 of 3: Considering similar distributions)
Understanding Discrete Random Variables and Probability Distributions
DISCRETE PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTION: FINDING THE UNKNOWN PROBABILITIES.
Комментарии
 0:07:39
0:07:39
 0:29:54
0:29:54
 0:06:21
0:06:21
 0:11:29
0:11:29
 0:07:52
0:07:52
 0:03:50
0:03:50
 0:05:32
0:05:32
 9:59:24
9:59:24
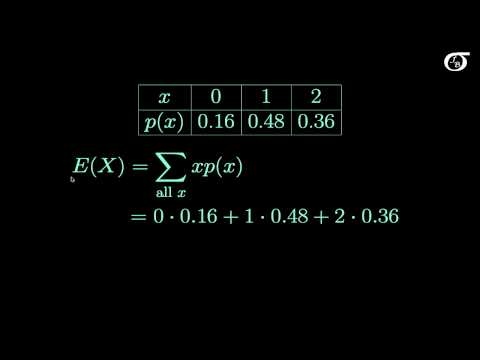 0:07:57
0:07:57
 0:05:10
0:05:10
 0:11:56
0:11:56
 0:10:26
0:10:26
 0:09:19
0:09:19
 0:09:59
0:09:59
 0:04:21
0:04:21
 0:04:39
0:04:39
 0:13:17
0:13:17
 0:16:17
0:16:17
 0:14:11
0:14:11
 0:05:58
0:05:58
 0:08:06
0:08:06
 0:07:25
0:07:25
 0:08:41
0:08:41
 0:05:29
0:05:29