filmov
tv
FLOW CYTOMETRY EXPLAINED
Показать описание
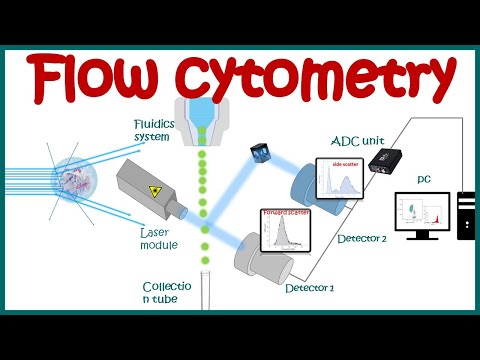
Flow cytometry is used to analyze characteristic such as size and shape of cells or particles. During the process, a sample of cells or particles is suspended in fluid and injected into a flow cytometer machine. The different cells then all pass individually through a laser beam and gets analyzed depending on how they scatter the light from this laser. This in turn is dependent on their size as well as shape and complexity. Approximately 10 000 cells can be analyzed and processed by a computer in less than 1 minute.
The 3 main components of a flow cytometer are the fluidics, optics and electronics.
1. The fluidics system of a flow cytometer is responsible for transporting samples from the sample tube to the flow cell and past the laser.
2. The components of the optical system include excitation light sources, lenses and optical filters used to collect and move wavelengths of light around the instrument and the detection system that generates the photocurrent. The difference in wavelength response in the data helps analyze the cell type.
3. The electronics or flow cytometer instrumentation that outputs the data in a format which can be analyzed.
So how does flow cytometry work?
- The sample consisting of blood, bone marrow or tissue cells is placed in a suspension and injected into the flow cytometer machine. The cells are arranged in a single file line, and then passed in front of a laser beam at the so-called “interrogation point, where each cell in individually analyzed.
- As each cell passes through the laser beam, the laser scatters in several directions and the flow cytometer then detects this scattered light:
- Forward scatter is proportional to the size of the cell, meaning that smaller cells cause less scattering and larger cells cause more scattering
- The side scatter is proportional to the shape and complexity of the cell, where more complexity results in more light scattering.
- Both the forward and side scatter gets detected and converted into an electric pulse, which is directly proportional to the amount of scattered light.
By analyzing the combination of the forward and side scatter, multiple populations of cells may be divided into groups based on size, shape and complexity. This is one if not the greatest strength of the flow cytometry technique.
The 3 main components of a flow cytometer are the fluidics, optics and electronics.
1. The fluidics system of a flow cytometer is responsible for transporting samples from the sample tube to the flow cell and past the laser.
2. The components of the optical system include excitation light sources, lenses and optical filters used to collect and move wavelengths of light around the instrument and the detection system that generates the photocurrent. The difference in wavelength response in the data helps analyze the cell type.
3. The electronics or flow cytometer instrumentation that outputs the data in a format which can be analyzed.
So how does flow cytometry work?
- The sample consisting of blood, bone marrow or tissue cells is placed in a suspension and injected into the flow cytometer machine. The cells are arranged in a single file line, and then passed in front of a laser beam at the so-called “interrogation point, where each cell in individually analyzed.
- As each cell passes through the laser beam, the laser scatters in several directions and the flow cytometer then detects this scattered light:
- Forward scatter is proportional to the size of the cell, meaning that smaller cells cause less scattering and larger cells cause more scattering
- The side scatter is proportional to the shape and complexity of the cell, where more complexity results in more light scattering.
- Both the forward and side scatter gets detected and converted into an electric pulse, which is directly proportional to the amount of scattered light.
By analyzing the combination of the forward and side scatter, multiple populations of cells may be divided into groups based on size, shape and complexity. This is one if not the greatest strength of the flow cytometry technique.
Комментарии
 0:13:24
0:13:24
 0:01:34
0:01:34
 0:08:50
0:08:50
 0:33:55
0:33:55
 0:01:36
0:01:36
 0:56:07
0:56:07
 0:04:42
0:04:42
 0:06:35
0:06:35
 0:11:52
0:11:52
 0:34:10
0:34:10
 0:04:35
0:04:35
 0:42:37
0:42:37
 0:04:00
0:04:00
 0:11:13
0:11:13
 0:01:23
0:01:23
 0:02:50
0:02:50
 0:51:22
0:51:22
 0:03:15
0:03:15
 0:35:58
0:35:58
 0:12:05
0:12:05
 0:03:39
0:03:39
 0:01:48
0:01:48
 0:49:41
0:49:41
 0:03:15
0:03:15