filmov
tv
Proof of the mean of Binomial distribution

Показать описание
If X follows a Binomial distribution with parameters n and p, then the mean/average/expected value is np.
Mathematically,
If X~B(n,p) then E(X)=np
Mathematically,
If X~B(n,p) then E(X)=np
Mean Value Theorem Proof
Proof of the mean of Binomial distribution
Proof of the mean of Poisson distribution
Proof that the Sample Variance is an Unbiased Estimator of the Population Variance
Proof that sample mean is unbiased
What is an unbiased estimator? Proof sample mean is unbiased and why we divide by n-1 for sample var
Mean Value Theorem Proof
Mean Value Theorem - A Simple Proof
Proof 1 - Variance - Doughterty Review Chapter-Econometrics
Mean Value Theorem for Integrals: Proof
What is a POC (Proof Of Concept)? - The Sales Wiki | Michael Humblet
[Proof] MSE = Variance + Bias²
Sampling distribution of the sample means (Normal distribution) proof | ExamSolutions
Real Analysis 56 | Proof of the Fundamental Theorem of Calculus
Mean and variance of Binomial Distribution - A simple proof
Proof by Contradiction: Arithmetic Mean & Geometric Mean
Why the mean of Binomial Distribution is 'np'? Proof of the formula.
Mean and Variance of Poisson Distribution - A simple proof
Arithmetic mean vs Geometric mean | inequality among means | visual proof
Variance Proof 1 - Intro to Statistics
Beta Distribution Mean and Variance Proof
1 + 1 = 3 Proof | Breaking the rules of mathematics
proof of variance of mean both method when sampling is done with replacement and without replacement
What is a Mathematical Proof: Introduction to Mathematical Reasoning #1
Комментарии
 0:02:43
0:02:43
 0:06:40
0:06:40
 0:03:52
0:03:52
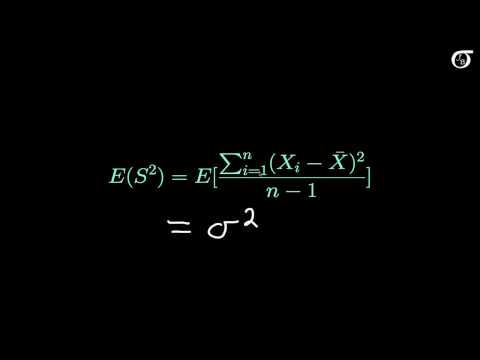 0:06:58
0:06:58
 0:06:32
0:06:32
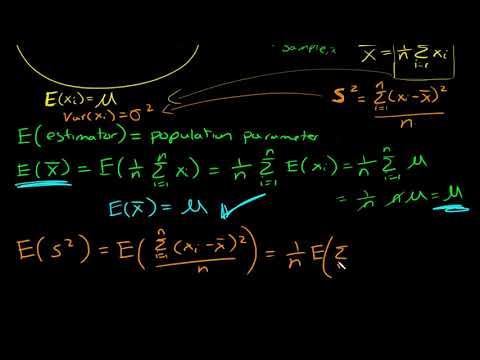 0:17:12
0:17:12
 0:14:54
0:14:54
 0:12:34
0:12:34
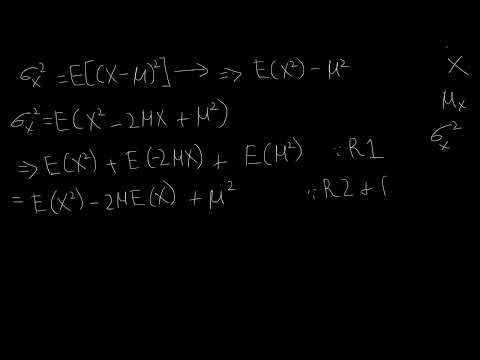 0:04:26
0:04:26
 0:07:20
0:07:20
 0:03:10
0:03:10
![[Proof] MSE =](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/qmVT35gFW-Q/hqdefault.jpg) 0:04:36
0:04:36
 0:08:36
0:08:36
 0:12:18
0:12:18
 0:07:41
0:07:41
 0:12:38
0:12:38
 0:13:01
0:13:01
 0:05:54
0:05:54
 0:01:39
0:01:39
 0:01:06
0:01:06
 0:15:15
0:15:15
 0:08:25
0:08:25
 0:05:42
0:05:42
 0:03:41
0:03:41