filmov
tv
What is an unbiased estimator? Proof sample mean is unbiased and why we divide by n-1 for sample var

Показать описание
In this video I discuss the basic idea behind unbiased estimators and provide the proof that the sample mean is an unbiased estimator. Also, I show a proof for a sample standard variance estimator that uses n in the denominator, and show that it is a biased estimator, therefore we use n-1 in the denominator to obtain an unbiased estimator for the population variance.
Unbiased Estimators ... Made Easy!
What is an unbiased estimator? Proof sample mean is unbiased and why we divide by n-1 for sample var
What is an unbiased estimator? (simply explained with biased estimator)
Unbiased Estimators (Why n-1 ???) : Data Science Basics
What is an estimator?
Biased and unbiased estimators from sampling distributions examples
Proof that the Sample Variance is an Unbiased Estimator of the Population Variance
Unbiased estimator
Unbiased Estimator Problem With Solution in 2022
Biased and Unbiased Estimators
Biased v unbiased estimators
How to tell if an estimator is biased or unbiased
what is Unbiased estimate?
Unbiasedness Estimator - For good Point Estimator
Estimation Theory | Unbiased estimator | L17
Traits of an unbiased estimator
Biased and unbiased estimator ch 12 lec 3
Unbiased Estimator
Least Squares Estimators as BLUE
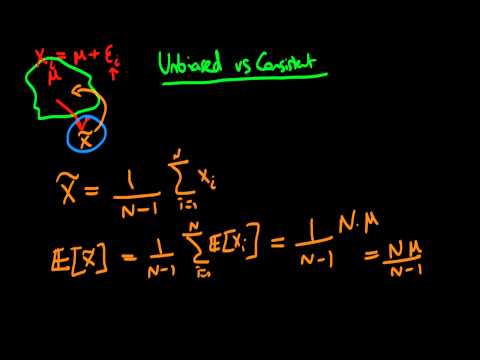
Unbiasedness vs consistency of estimators - an example
BLUE Estimates
6.3.5 Sampling Distributions and Estimators - Biased and Unbiased Estimators
Find an unbiased linear estimator
The Variability (precision) of Unbiased Estimators
Комментарии
 0:06:03
0:06:03
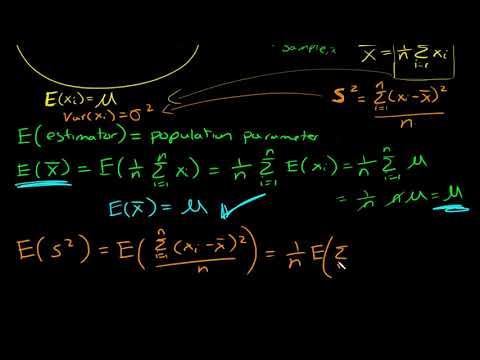 0:17:12
0:17:12
 0:03:02
0:03:02
 0:08:35
0:08:35
 0:02:41
0:02:41
 0:05:56
0:05:56
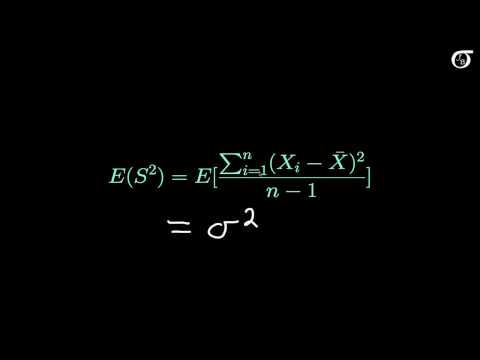 0:06:58
0:06:58
 0:06:25
0:06:25
 0:04:19
0:04:19
 0:03:06
0:03:06
 0:02:20
0:02:20
 0:01:41
0:01:41
 0:09:25
0:09:25
 0:16:02
0:16:02
 0:49:51
0:49:51
 0:01:35
0:01:35
 0:06:24
0:06:24
 0:04:57
0:04:57
 0:07:19
0:07:19
 0:04:09
0:04:09
 0:03:31
0:03:31
 0:12:49
0:12:49
 0:06:00
0:06:00
 0:05:25
0:05:25