filmov
tv
Chronic Liver Disease | Surgery Video Lectures | Medical Student Education | V-Learning

Показать описание
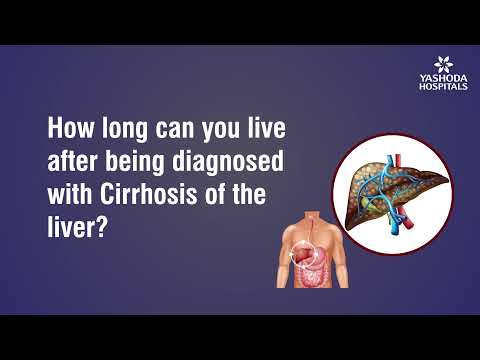
Prime focus of this lecture is on the explanation Chronic liver disease. Stigmata of chronic liver disease, Chronic liver disease pathophysiology, liver disease pathology and chronic liver disease complications are discussed in detail. The liver is the largest organ in the body.
-------------------------------------------------------------
Lecture Duration - 00:52:20
Release Date - January 2020
General Surgery Lectures Collection -
-------------------------------------------------------------
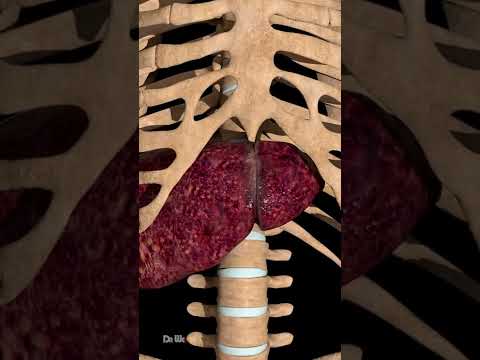
Liver parenchyma is entirely covered by a thin capsule (Glisson’s capsule) and by visceral peritoneum on all but the posterior surface of the liver, termed the ‘bare area’. The liver is divided into a large right lobe, which constitutes three-quarters of the liver volume, and a smaller left lobe.
The liver is fixed in the right upper quadrant by peritoneal reflections that form ligaments. Chronic diseases of liver lasts over a period of six months. It consists of wide range of liver disease pathology. Chronic liver disease pathophysiology is explained here in detail.
Progressive deterioration in liver function is associated with a hyperdynamic circulation involving a high cardiac output, large pulse volume, low blood pressure and flushed warm extremities. Later on, in this lecture radiology is explained that how the imaging of liver is done and what are the standard investigations. CT scan and MRI are used for anatomical planning of liver surgery.
Magnetic resonance (MR) of the liver is superior to CT in characterizing liver lesions and detecting small liver metastases. Furthermore, Imaging of Biliary tract and Percutaneous Transhepatic Cholangiography angiography is explained that what their role in vascular involvement by tumor.
-------------------------------------------------------------
1300+ Medical Courses Lectures.
-------------------------------------------------------------
Positron emission tomography (FDG–PET) depends on the avid uptake of glucose by cancerous tissue in comparison with benign or inflammatory tissue. Laparoscopy is useful for the staging of primary hepatopancreatobiliary cancers.
Later On, in the second half of this lecture chronic liver disease complications are discussed. Portal hypertension along with management of bleeding varices and Oesophageal Balloon Tamponade are well explained. Treatment with a vasoconstrictor combined with endoscopic therapy is the standard medical treatment for acute variceal bleeding.
Surgical Shunts for Variceal Haemorrhage, Variceal Bleeds Secondary to Thrombosis, Ascites and Liver Transplantation for Ascites were point of discussion in the end of this General surgery lecture. Polycystic liver disease and Hepatic cirrhosis pathophysiology will be discussed in the next lecture on Chronic liver conditions.
-------------------------------------------------------------
-------------------------------------------------------------
-------------------------------------------------------------
Lecture Duration - 00:52:20
Release Date - January 2020
General Surgery Lectures Collection -
-------------------------------------------------------------
Liver parenchyma is entirely covered by a thin capsule (Glisson’s capsule) and by visceral peritoneum on all but the posterior surface of the liver, termed the ‘bare area’. The liver is divided into a large right lobe, which constitutes three-quarters of the liver volume, and a smaller left lobe.
The liver is fixed in the right upper quadrant by peritoneal reflections that form ligaments. Chronic diseases of liver lasts over a period of six months. It consists of wide range of liver disease pathology. Chronic liver disease pathophysiology is explained here in detail.
Progressive deterioration in liver function is associated with a hyperdynamic circulation involving a high cardiac output, large pulse volume, low blood pressure and flushed warm extremities. Later on, in this lecture radiology is explained that how the imaging of liver is done and what are the standard investigations. CT scan and MRI are used for anatomical planning of liver surgery.
Magnetic resonance (MR) of the liver is superior to CT in characterizing liver lesions and detecting small liver metastases. Furthermore, Imaging of Biliary tract and Percutaneous Transhepatic Cholangiography angiography is explained that what their role in vascular involvement by tumor.
-------------------------------------------------------------
1300+ Medical Courses Lectures.
-------------------------------------------------------------
Positron emission tomography (FDG–PET) depends on the avid uptake of glucose by cancerous tissue in comparison with benign or inflammatory tissue. Laparoscopy is useful for the staging of primary hepatopancreatobiliary cancers.
Later On, in the second half of this lecture chronic liver disease complications are discussed. Portal hypertension along with management of bleeding varices and Oesophageal Balloon Tamponade are well explained. Treatment with a vasoconstrictor combined with endoscopic therapy is the standard medical treatment for acute variceal bleeding.
Surgical Shunts for Variceal Haemorrhage, Variceal Bleeds Secondary to Thrombosis, Ascites and Liver Transplantation for Ascites were point of discussion in the end of this General surgery lecture. Polycystic liver disease and Hepatic cirrhosis pathophysiology will be discussed in the next lecture on Chronic liver conditions.
-------------------------------------------------------------
-------------------------------------------------------------
 0:03:20
0:03:20
 0:00:45
0:00:45
 0:09:48
0:09:48
 0:01:01
0:01:01
 0:00:53
0:00:53
 0:01:20
0:01:20
 0:03:44
0:03:44
 0:01:28
0:01:28
 0:21:01
0:21:01
 0:01:24
0:01:24
 0:07:44
0:07:44
 0:09:04
0:09:04
 0:29:05
0:29:05
 0:08:12
0:08:12
 0:05:58
0:05:58
 0:03:39
0:03:39
 0:11:20
0:11:20
 0:02:44
0:02:44
 0:26:53
0:26:53
 0:00:31
0:00:31
 0:07:46
0:07:46
 0:03:41
0:03:41
 0:01:51
0:01:51
 0:03:13
0:03:13