filmov
tv
Chronic Liver Conditions | Surgery Video Lectures | Medical Education | V-Learning

Показать описание
Primary focus of this General Surgery lecture is to explain the Chronic Liver conditions. There are several chronic liver conditions, which, although rare, are important to recognize because they require a specific plan for investigation and treatment, may present mimicking a more common clinical condition.
-------------------------------------------------------------
Lecture Duration - 00:41:49
Release Date - January 2020
General Surgery Lectures Collection -
-------------------------------------------------------------
Budd–Chiari syndrome (BCS) is a condition principally affecting young females, in which the venous drainage of the Liver is occluded by hepatic venous thrombosis or obstruction from a venous web. Its diagnosis and treatment are discussed in detail.
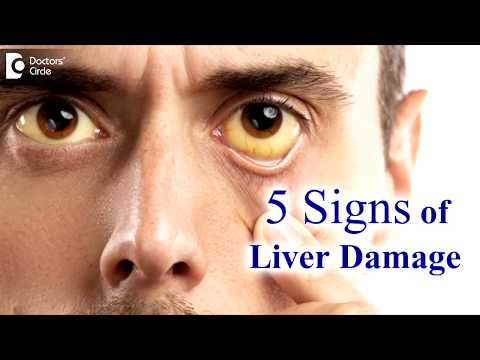
Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis often presents in young adults with mild non-specific symptoms, and biliary disease is suggested by the finding of abnormal liver function tests. Rarely, the first presentation is with jaundice due to biliary obstruction.
Primary biliary cholangitis (PBC), formerly known as primary biliary cirrhosis, is a disease caused by damage to bile ducts in the liver. Primary biliary cholangitis treatment is discussed later. Caroli’s disease is congenital dilatation of the intrahepatic biliary tree, which is often complicated by the presence of intrahepatic stone formation.
-------------------------------------------------------------
1300+ Medical Courses Lectures.
-------------------------------------------------------------
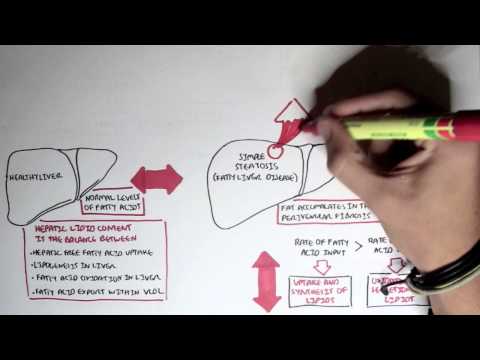
Segmental involvement of the liver by Caroli’s disease may be treated by resection of the affected part, although the ductal dilatation is usually diffuse. Liver transplantation is a radical but definitive treatment. Simple cysts are generally solitary, and occur more frequently in women. Most are incidental findings, and have a characteristic blue hue when seen at laparoscopy. Indications for surgical intervention include symptoms, rupture, haemorrhage, infection or indeterminate diagnosis.
Surgical resection typically involves laparoscopic deroofing, with oversewing of the cyst wall. Polycystic liver disease is less common. It is an autosomal dominant condition, more commonly seen in women, and around half of patients will also have polycystic kidneys. Indications for surgical intervention are broadly similar to those for simple cysts, although the large number of lesions means that deroofing a single cyst is unlikely to relieve symptoms.
-------------------------------------------------------------
-------------------------------------------------------------
-------------------------------------------------------------
Lecture Duration - 00:41:49
Release Date - January 2020
General Surgery Lectures Collection -
-------------------------------------------------------------
Budd–Chiari syndrome (BCS) is a condition principally affecting young females, in which the venous drainage of the Liver is occluded by hepatic venous thrombosis or obstruction from a venous web. Its diagnosis and treatment are discussed in detail.
Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis often presents in young adults with mild non-specific symptoms, and biliary disease is suggested by the finding of abnormal liver function tests. Rarely, the first presentation is with jaundice due to biliary obstruction.
Primary biliary cholangitis (PBC), formerly known as primary biliary cirrhosis, is a disease caused by damage to bile ducts in the liver. Primary biliary cholangitis treatment is discussed later. Caroli’s disease is congenital dilatation of the intrahepatic biliary tree, which is often complicated by the presence of intrahepatic stone formation.
-------------------------------------------------------------
1300+ Medical Courses Lectures.
-------------------------------------------------------------
Segmental involvement of the liver by Caroli’s disease may be treated by resection of the affected part, although the ductal dilatation is usually diffuse. Liver transplantation is a radical but definitive treatment. Simple cysts are generally solitary, and occur more frequently in women. Most are incidental findings, and have a characteristic blue hue when seen at laparoscopy. Indications for surgical intervention include symptoms, rupture, haemorrhage, infection or indeterminate diagnosis.
Surgical resection typically involves laparoscopic deroofing, with oversewing of the cyst wall. Polycystic liver disease is less common. It is an autosomal dominant condition, more commonly seen in women, and around half of patients will also have polycystic kidneys. Indications for surgical intervention are broadly similar to those for simple cysts, although the large number of lesions means that deroofing a single cyst is unlikely to relieve symptoms.
-------------------------------------------------------------
-------------------------------------------------------------
 0:03:20
0:03:20
 0:01:20
0:01:20
 0:03:41
0:03:41
 0:09:48
0:09:48
 0:29:05
0:29:05
 0:01:01
0:01:01
 0:08:12
0:08:12
 0:03:44
0:03:44
 0:05:35
0:05:35
 0:07:46
0:07:46
 0:01:24
0:01:24
 0:02:53
0:02:53
 0:03:39
0:03:39
 0:03:01
0:03:01
 0:02:35
0:02:35
 0:01:20
0:01:20
 0:04:14
0:04:14
 0:00:48
0:00:48
 0:05:40
0:05:40
 0:03:50
0:03:50
 0:03:13
0:03:13
 0:06:29
0:06:29
 0:07:11
0:07:11
 0:00:06
0:00:06