filmov
tv
How to Strengthen Your Calf Muscles and Achilles Tendon

Показать описание
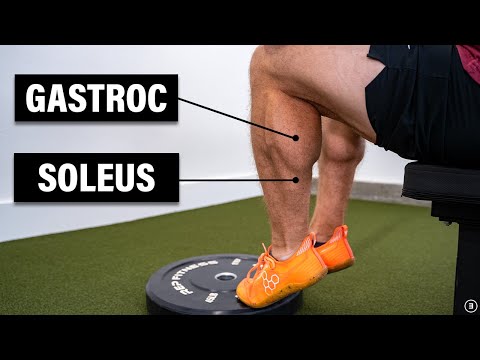
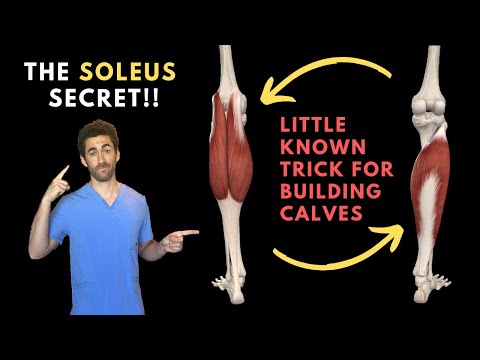
The primary ankle plantarflexors or calf muscles include the gastrocnemius and soleus muscles and contribute to both ankle and knee movement. Other smaller plantarflexors include: plantaris, flexor hallucis longus, flexor digitorum longus, tibialis posterior, peroneus brevis & peroneus longus.
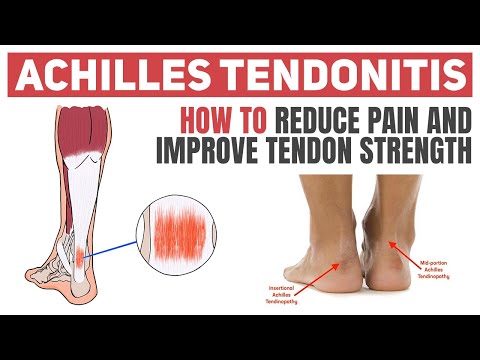
Exercises that train the plantarflexors can help to reduce the likelihood of suffering a foot/ankle injury, such as achilles tendon tears, ankle sprains & plantar fasciopathy. Calf strengthening can also help protect joints and other tissues farther up the kinetic chain.
If calf strengthening is not a regular component of your resistance training program, then be sure to add the exercise shown in the video and aim for 3 sets of 8-12 slow, controlled repetitions 2-3/week.
If you want to test your calf strength first, here are the maximum number repetitions you should be able to do in one set by age group:
20-29yrs: Males 37, Females 30
30-39yrs: Males 32, Females 27
40-49yrs: Males 28, Females 24
50-59yrs: Males 23, Females 21
60-69yrs: Males 19, Females, 19
70-79yrs: Males 14, Females 16
80-89yrs: Males 10, Females 13
Reference: Hébert-Losier K, et al. Updated reliability and normative values for the standing heel-rise test in healthy adults. Physiotherapy. 2017.
Exercises that train the plantarflexors can help to reduce the likelihood of suffering a foot/ankle injury, such as achilles tendon tears, ankle sprains & plantar fasciopathy. Calf strengthening can also help protect joints and other tissues farther up the kinetic chain.
If calf strengthening is not a regular component of your resistance training program, then be sure to add the exercise shown in the video and aim for 3 sets of 8-12 slow, controlled repetitions 2-3/week.
If you want to test your calf strength first, here are the maximum number repetitions you should be able to do in one set by age group:
20-29yrs: Males 37, Females 30
30-39yrs: Males 32, Females 27
40-49yrs: Males 28, Females 24
50-59yrs: Males 23, Females 21
60-69yrs: Males 19, Females, 19
70-79yrs: Males 14, Females 16
80-89yrs: Males 10, Females 13
Reference: Hébert-Losier K, et al. Updated reliability and normative values for the standing heel-rise test in healthy adults. Physiotherapy. 2017.
Комментарии
 0:01:34
0:01:34
 0:15:32
0:15:32
 0:00:43
0:00:43
 0:00:21
0:00:21
 0:03:10
0:03:10
 0:00:58
0:00:58
 0:02:18
0:02:18
 0:02:22
0:02:22
 0:33:30
0:33:30
 0:07:46
0:07:46
 0:00:53
0:00:53
 0:17:05
0:17:05
 0:01:45
0:01:45
 0:06:17
0:06:17
 0:06:44
0:06:44
 0:01:48
0:01:48
 0:01:53
0:01:53
 0:08:15
0:08:15
 0:12:55
0:12:55
 0:04:19
0:04:19
 0:13:13
0:13:13
 0:08:09
0:08:09
 0:07:40
0:07:40
 0:14:35
0:14:35