filmov
tv
Classical physics derived from quantum mechanics: Feynman Path Integral

Показать описание
Classical Mechanics and Relativity: Lecture 5
0:00 Introduction
2:35 Fermat's Principle
9:57 Variational principles
17:16 Double slit experiment
21:38 Quantum interference
25:08 Feynman Path Integral
31:12 Quantum trajectories
38:26 Classical Action of quantum paths
42:36 Path integral representation of wavefunction
44:17 Classical path from quantum interference
Theoretical physicist Dr Andrew Mitchell presents an undergraduate lecture course on Classical Mechanics and Relativity at University College Dublin. This is a complete and self-contained course in which everything is derived from scratch.
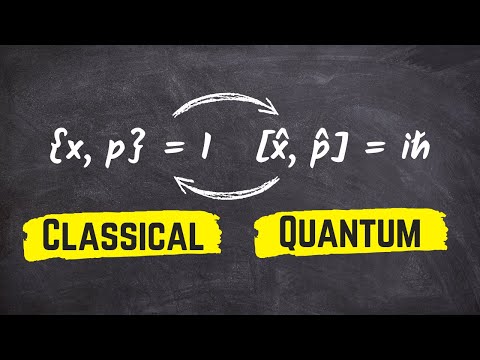
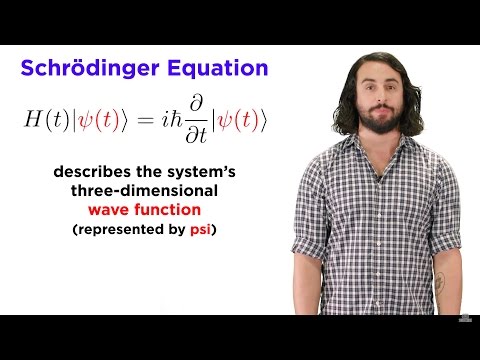
In this lecture I make the connection between classical mechanics and quantum mechanics. By analogy to Fermat's principle of least time in the theory of optics, and by considering a generalization of the double slit experiment, I introduce Feynman's Path Integral formulation of quantum mechanics. From it, I derive the principle of least action, and hence all of classical mechanics.
Course textbooks:
"Classical Mechanics" by Goldstein, Safko, and Poole
"Classical Mechanics" by Morin
"Relativity" by Rindler
0:00 Introduction
2:35 Fermat's Principle
9:57 Variational principles
17:16 Double slit experiment
21:38 Quantum interference
25:08 Feynman Path Integral
31:12 Quantum trajectories
38:26 Classical Action of quantum paths
42:36 Path integral representation of wavefunction
44:17 Classical path from quantum interference
Theoretical physicist Dr Andrew Mitchell presents an undergraduate lecture course on Classical Mechanics and Relativity at University College Dublin. This is a complete and self-contained course in which everything is derived from scratch.
In this lecture I make the connection between classical mechanics and quantum mechanics. By analogy to Fermat's principle of least time in the theory of optics, and by considering a generalization of the double slit experiment, I introduce Feynman's Path Integral formulation of quantum mechanics. From it, I derive the principle of least action, and hence all of classical mechanics.
Course textbooks:
"Classical Mechanics" by Goldstein, Safko, and Poole
"Classical Mechanics" by Morin
"Relativity" by Rindler
Комментарии
 0:52:29
0:52:29
 0:16:20
0:16:20
 0:01:22
0:01:22
 0:29:23
0:29:23
 0:11:05
0:11:05
 0:08:21
0:08:21
 0:04:20
0:04:20
 0:06:28
0:06:28
 0:00:49
0:00:49
 0:14:17
0:14:17
 0:08:32
0:08:32
 0:07:47
0:07:47
 0:02:07
0:02:07
 0:06:34
0:06:34
 0:56:11
0:56:11
 0:14:31
0:14:31
 0:10:24
0:10:24
 0:03:32
0:03:32
 0:00:59
0:00:59
 0:01:01
0:01:01
 0:01:00
0:01:00
 0:16:43
0:16:43
 0:12:45
0:12:45
 0:21:18
0:21:18