filmov
tv
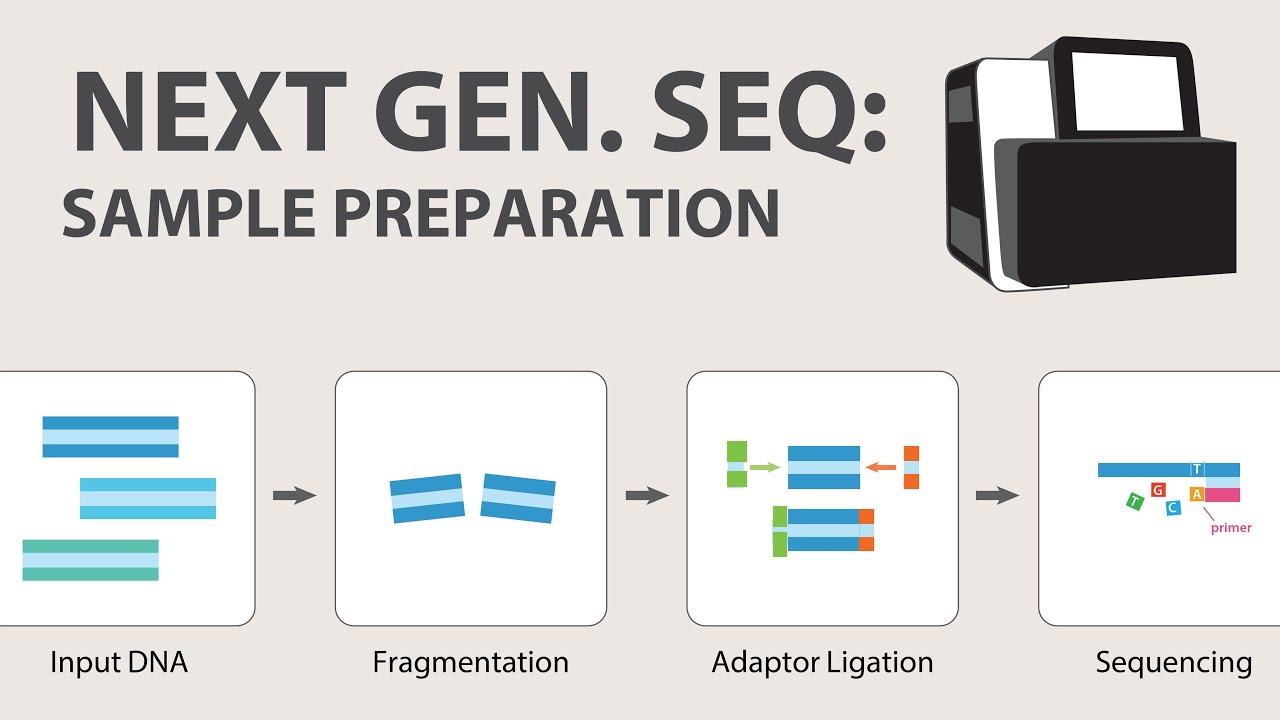
2) Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) - Sample Preparation
Показать описание
What is covered in this video:
For more information on this topic, please visit:
Want to learn about RNA Sequencing? Watch our FREE webinar, "The Beginner's Guide to RNA-Seq"
Watch the other videos in this series on NGS:
Check out our other video series:
Connect with us on our social media pages to stay up to date with the latest scientific discoveries:
For more information on this topic, please visit:
Want to learn about RNA Sequencing? Watch our FREE webinar, "The Beginner's Guide to RNA-Seq"
Watch the other videos in this series on NGS:
Check out our other video series:
Connect with us on our social media pages to stay up to date with the latest scientific discoveries:
2) Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) - Sample Preparation
Overview of Illumina Sequencing by Synthesis Workflow | Standard SBS chemistry
1) Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) - An Introduction
Next Generation Sequencing (Illumina) - An Introduction
Next Generation Sequencing 2: Illumina NGS Sample Preparation - Eric Chow (UCSF)
Overview of Illumina Sequencing by Synthesis Workflow | XLEAP SBS chemistry
When do I use Sanger Sequencing vs. NGS? - Seq It Out #7
Next Generation Sequencing Library Preparation - Seq It Out #10
Introducing Illumina Connected Software
Next Generation Sequencing 1: Overview - Eric Chow (UCSF)
Podcast Episode 2: What is Next Generation Sequencing (NGS)
Ion Torrent Next-generation Sequencing
Learn about Illumina's Next-Generation Sequencing Workflow
Using NGS for Infections | MicroGenDX Minute Ep.2
What Is Sanger Sequencing?
4) Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) - Data Analysis
Next Generation Sequencing (ILLUMINA SEQUENCING)
What is Next-Generation Sequencing?
Bring fast, Automated, End-to-End Next-Generation Sequencing to your Lab
Next-Generation Sequencing for Oncologists
Next-generation sequencing for microbiology | Illumina Video
NGS How does paired end sequencing work?
5) Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) - Applications of Whole Genome Sequencing
Next Generation Sequencing Workflow
Комментарии
 0:12:53
0:12:53
 0:05:13
0:05:13
 0:09:30
0:09:30
 0:04:44
0:04:44
 0:25:05
0:25:05
 0:06:04
0:06:04
 0:03:12
0:03:12
 0:04:49
0:04:49
 0:02:59
0:02:59
 0:31:26
0:31:26
 0:15:31
0:15:31
 0:03:24
0:03:24
 0:41:35
0:41:35
 0:01:35
0:01:35
 0:01:31
0:01:31
 0:07:03
0:07:03
 0:04:41
0:04:41
 0:00:33
0:00:33
 0:01:49
0:01:49
 0:10:20
0:10:20
 0:01:46
0:01:46
 0:02:39
0:02:39
 0:08:08
0:08:08
 0:06:01
0:06:01