filmov
tv
Master Solving a quadratic equation using the quadratic formula

Показать описание
So for this example, you can see it's not set equal to 0. So the first thing we want to do is add a 6x onto both sides and add a 1 onto both sides. Therefore I have the equation 9x squared plus 6x plus 1 equals 0. Then the next thing I like to do, is to identify what is your a, b, and your c. Well, remember a is going to be your coefficient of your quadratic term. b is your coefficient of your linear term. And c is your value of your constant. So a in this case is 9. b in this case 6. And c is going to be equal to 1.
Now the next thing I think is very helpful is, rather than plugging in everything into this formula, let's figure out what the discriminant is first. Because the discriminant is all the values that are under the square root. And knowing what type of number that is can be very, very helpful. If that number is 0, then that tells us we're just going to have one solution. If that number is a rational number-- a real rational number-- therefore then we know that there's going to be two possible rational zeros or I'm sorry. If that number is a square number, then we'll have two rational real solutions. If that number is a non-square number-- like a square number would be 9, a non-square number would be 5-- if it's a non square number, then we're going to have two real irrational solutions. And if that number is negative, then we're going to have two imaginary, or complex solutions.
So I always like to go ahead and figure out the discriminant first. And by doing the discriminant-- now that's not part of this problem, but there are questions that ask what are the types of solutions-- So I'm not going to write it down, because that's not really what we're doing. But I will describe what the solution is. OK. So therefore I have 36 minus 4 times 9, which is 36. So that equals the square root of 0, which is equal to 0. So since we have a vector 0, we're going to have one real solution. OK?
Now up here, see what happens. Let's see how that works. Let's just pretend the square root of 0. Let's plug that back in with the rest of the equation. So my solutions are going to be x equals opposite of b. So b in this case is 6, right? It's not negative 6 from up here. But b is actually 6 when I get it set equal to 0. So the opposite of b is negative 6 plus or minus the square root of 0, which we know is 0. But I'll just write it in there. Divided by 2 times a, which in this case is 9. So negative 6 plus or minus the square root of 0. That's just going to equal-- x equals negative 6 plus or minus 0 is just going to be negative 6 over 2 times 9 is going to be 18. And therefore that equals a negative 1/3. So therefore my one solution, the value where the graph crosses the x-axis, is going to be negative 1/3.
In the next example over here. We're going to do the exact same case here. First thing we need do is identify our a, b, and our c. a in this case is 1. b in this case is 4. And c in this case is going to be a negative 3.
Again let's determine the discriminant first. So the discriminant is going to be the square root of b squared minus 4 times a times c. So therefore in this case I'm going to have 16 minus, or negative 4 times negative 3 times 1 is going to be a positive 12. So the discriminant equals the square root 16 plus 12, is going to be 28. We can break apart the square root of 28 into the square root of 4 times 7, which is equal to 2 square root of 7. Now 28 is not a square number, you can see. So therefore our solutions are going to be two real irrational solutions.
Комментарии
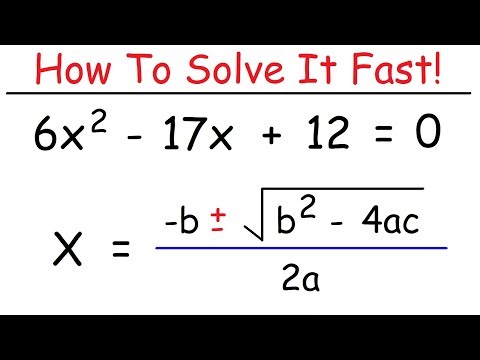 0:05:56
0:05:56
 0:12:29
0:12:29
 0:03:02
0:03:02
 0:11:02
0:11:02
 0:08:20
0:08:20
 0:08:43
0:08:43
 0:14:13
0:14:13
 0:06:20
0:06:20
 0:43:57
0:43:57
 0:02:43
0:02:43
 0:25:59
0:25:59
 0:09:37
0:09:37
 0:09:05
0:09:05
 0:05:00
0:05:00
 0:00:30
0:00:30
 0:00:55
0:00:55
 0:19:55
0:19:55
 0:12:07
0:12:07
 0:07:28
0:07:28
 0:05:20
0:05:20
 0:02:19
0:02:19
 0:12:25
0:12:25
 0:10:04
0:10:04
 0:09:06
0:09:06