filmov
tv
Absolute Value Theorem For Sequences
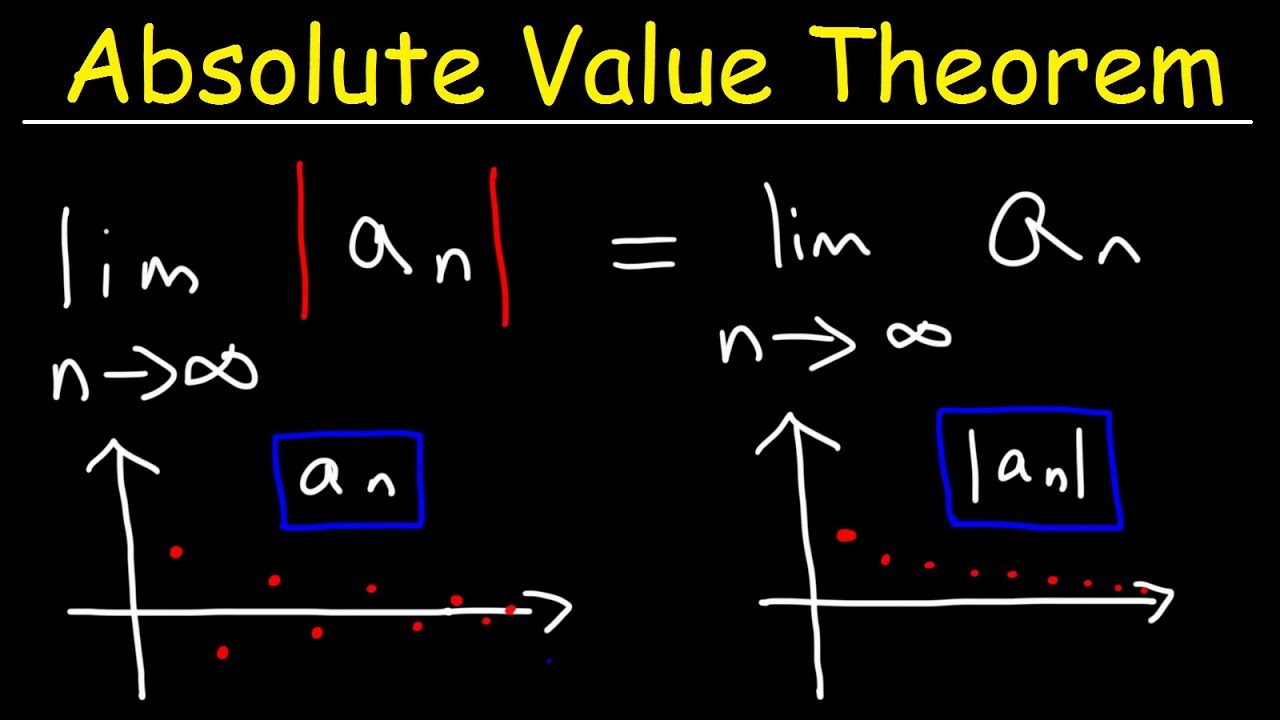
Показать описание
This calculus 2 video provides a basic introduction into the absolute value theorem for sequences. If the absolute value of a sequence converges, then the sequence itself also converges.
Converging & Diverging Sequences:
Monotonic & Bounded Sequences:
Absolute Value Theorem - Sequences:
Squeeze Theorem - Sequences:
________________________________
Geometric Series & Sequences:
Introduction to Series - Convergence:
Divergence Test For Series:
Harmonic Series:
Telescoping Series:
__________________________________
Integral Test For Divergence:
Remainder Estimate - Integral Test:
P-Series:
Direct Comparison Test:
Limit Comparison Test:
___________________________________
Calculus Final Exam and Video Playlists:
Full-Length Videos and Worksheets:
Converging & Diverging Sequences:
Monotonic & Bounded Sequences:
Absolute Value Theorem - Sequences:
Squeeze Theorem - Sequences:
________________________________
Geometric Series & Sequences:
Introduction to Series - Convergence:
Divergence Test For Series:
Harmonic Series:
Telescoping Series:
__________________________________
Integral Test For Divergence:
Remainder Estimate - Integral Test:
P-Series:
Direct Comparison Test:
Limit Comparison Test:
___________________________________
Calculus Final Exam and Video Playlists:
Full-Length Videos and Worksheets:
Absolute Value Theorem For Sequences
MATH 2414 - Sequences (10): Absolute Value Theorem
Proof: Absolute Value Theorem for Sequences | Real Analysis
Absolute Value Convergence of Sequence pg 5
Proof for Absolute Value of a Convergent Sequence | Real Analysis Exercises
Absolute Value (Limit Example 6)
The Squeeze Theorem and Absolute Value Theorem, #1
Absolute Value Theorem and Sandwich Theorem
Squeeze Theorem For Sequences
The Squeeze Theorem and Absolute Value Theorem, #3
65. Convergence and Divergence of Sequences - Part 3 - Squeeze Theorem and Absolute Value Theorem
Limit of Absolute Value Function
Triangle Inequality for Real Numbers Proof
SQUEEZE THEOREM - The Setup
Real Analysis | Cauchy Sequences
Calculus 2: Sequences (Section 11.1) | Math with Professor V
Proof: Product of Absolute Values is the Absolute Value of the Product
Absolute Convergence, Conditional Convergence, and Divergence
Definition of the Limit of a Sequence | Real Analysis
Before JEE vs After JEE 😍 | My Transformation💔 | IIT Motivation|Jee 2023 #transformation #iit #viral...
The Squeeze Theorem and Absolute Value Theorem, #2
9-AP Calculus, Chapter 9, Section 1, Absolute Value Theorem
Calculus 2 Lecture 9.1: Convergence and Divergence of Sequences
The Squeeze Theorem and Absolute Value Theorem, #1 - Calculus
Комментарии
 0:05:47
0:05:47
 0:09:50
0:09:50
 0:07:46
0:07:46
 0:07:16
0:07:16
 0:05:45
0:05:45
 0:03:51
0:03:51
 0:03:04
0:03:04
 0:12:44
0:12:44
 0:06:02
0:06:02
 0:02:36
0:02:36
 0:31:22
0:31:22
 0:07:37
0:07:37
 0:03:08
0:03:08
 0:10:49
0:10:49
 0:19:15
0:19:15
 0:39:19
0:39:19
 0:05:15
0:05:15
 0:13:07
0:13:07
 0:13:59
0:13:59
 0:00:20
0:00:20
 0:03:33
0:03:33
 0:03:30
0:03:30
 2:27:29
2:27:29
 0:02:39
0:02:39