filmov
tv
Orthogonal Vectors in R^n | Linear Algebra
Показать описание
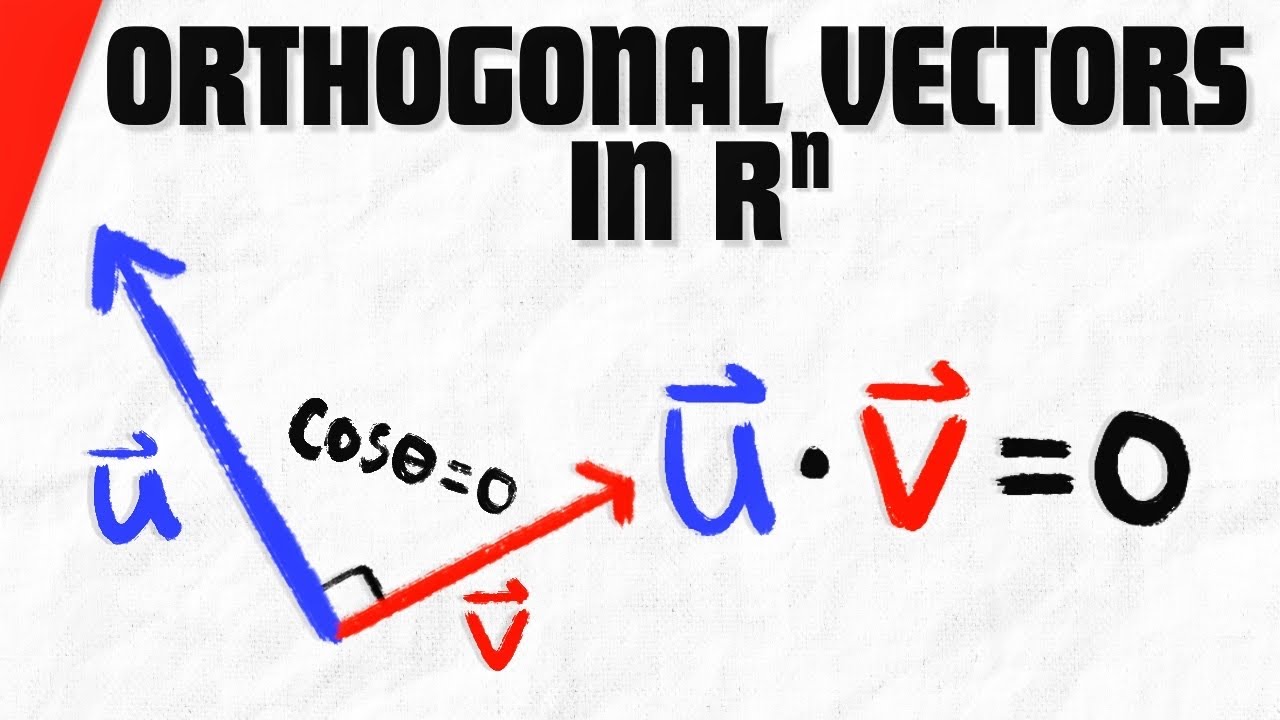
We introduce orthogonal vectors in the vector space R^n. We define two nonzero vectors in R^n to be orthogonal (or perpendicular) if the dot product of u and v is zero. We'll also do some examples showing two vectors are orthogonal by evaluating the dot product. #linearalgebra
Join Wrath of Math to get exclusive videos, music, and more:
◉Textbooks I Like◉
★DONATE★
Thanks to Loke Tan, Raül Beienheimer, Matt Venia, Micheline, Doug Walker, Odd Hultberg, Marc, Shlome Ashkenazi, Barbora Sharrock, Mohamad Nossier, Rolf Waefler, Shadow Master, and James Mead for their generous support on Patreon!
Outro music is mine. You cannot find it anywhere, for now.
Follow Wrath of Math on...
Join Wrath of Math to get exclusive videos, music, and more:
◉Textbooks I Like◉
★DONATE★
Thanks to Loke Tan, Raül Beienheimer, Matt Venia, Micheline, Doug Walker, Odd Hultberg, Marc, Shlome Ashkenazi, Barbora Sharrock, Mohamad Nossier, Rolf Waefler, Shadow Master, and James Mead for their generous support on Patreon!
Outro music is mine. You cannot find it anywhere, for now.
Follow Wrath of Math on...
Orthogonal Vectors in R^n | Linear Algebra
Linear Algebra 6.1.2 Orthogonal Vectors
Introduction to orthonormal bases | Linear Algebra | Khan Academy
What are the Orthogonal and Orthonormal Vectors ?
Orthogonality in Vector Space and Orthogonal Basis
Finding Orthogonal Vectors in R3
Orthogonality in R^n
Orthogonal Vectors and Subspaces
Motion in a Plane | Ch 3 | Analytical Method of Vector Addition | Cbse | NCERT | Class 11th Physics
Orthogonal and Orthonormal Sets of Vectors
Representing vectors in rn using subspace members | Linear Algebra | Khan Academy
How to find many vectors orthogonal to given in vector three space
Definition of Orthogonal Vectors
Orthogonal bases are easy to work with!
Sec 6.3 prep Orthogonal Projections in Rn
Linear Algebra 6.2.2 Orthogonal Projections
Orthogonality & Linear Independence (Theorem)
Sec 4 6: Orthogonal Vectors
Part 3: Orthogonal Vectors
Suppose that U1,U2 are non-zero orthogonal vectors in R^n, then for V ∈ R^n ?
Vector Projections | Vector Calculus #17
Operations on Vectors – Linear Independence, Basis and Orthonormal Vectors
ROB 101: Dot Product & Orthogonal Vectors
Linear Algebra: Length and Dot Product in Rn (Sec. 5.1)
Комментарии
 0:05:27
0:05:27
 0:07:17
0:07:17
 0:11:16
0:11:16
 0:04:45
0:04:45
 0:39:42
0:39:42
 0:06:27
0:06:27
 0:28:25
0:28:25
 0:10:20
0:10:20
 1:08:51
1:08:51
 0:06:52
0:06:52
 0:27:00
0:27:00
 0:06:15
0:06:15
 0:07:23
0:07:23
 0:04:50
0:04:50
 0:08:39
0:08:39
 0:08:45
0:08:45
 0:03:19
0:03:19
 0:27:44
0:27:44
 0:14:09
0:14:09
 0:01:01
0:01:01
 0:05:17
0:05:17
 0:36:22
0:36:22
 0:51:38
0:51:38
 0:25:20
0:25:20