filmov
tv
Prostatitis - Symptoms, causes and Treatment
Показать описание
What is the primary function of the prostate gland in the male reproductive system?
What is prostatitis, and what are its most common symptoms?
How common is prostatitis, and which age group does it most frequently affect?
How might prostatitis affect a man's sexual health and overall well-being if left untreated?
What is the relationship between prostatitis, specifically chronic prostatitis, and the risk of prostate cancer?
What are the primary and secondary causes of prostatitis?
What diagnostic methods are used to diagnose prostatitis accurately?
What are the first, second, and third-line treatments for prostatitis, particularly bacterial prostatitis?
Important Highlights from Our Discussion:
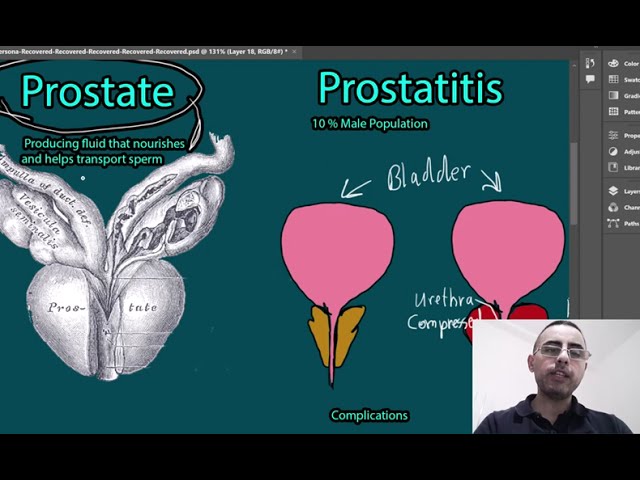
The primary function of the prostate gland is to produce fluid that nourishes and helps transport sperm.
Prostatitis, an inflammation of the prostate, can cause symptoms such as pelvic discomfort, urinary discomfort, and sexual problems.
About 10%-15% of men are affected by prostatitis at some point in their lives, predominantly those under the age of 50.
If left untreated, prostatitis can lead to chronic complications like recurrent urinary tract infections and may slightly increase the risk of prostate cancer.
The primary cause of prostatitis is a bacterial infection, leading to acute bacterial prostatitis, while the second most common cause is non-bacterial, resulting in Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome (CPPS).
Diagnosis of prostatitis involves patient history taking, a Digital Rectal Examination (DRE), and laboratory tests such as urine culture or semen analysis.
First-line treatment for bacterial prostatitis involves antibiotics like fluoroquinolones or trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, with duration depending on whether the condition is acute or chronic.
In cases of resistance or ineffective first-line treatment, other culture-sensitive antibiotics may be employed, and in rare, unresponsive chronic cases, surgical intervention may be considered
What is prostatitis, and what are its most common symptoms?
How common is prostatitis, and which age group does it most frequently affect?
How might prostatitis affect a man's sexual health and overall well-being if left untreated?
What is the relationship between prostatitis, specifically chronic prostatitis, and the risk of prostate cancer?
What are the primary and secondary causes of prostatitis?
What diagnostic methods are used to diagnose prostatitis accurately?
What are the first, second, and third-line treatments for prostatitis, particularly bacterial prostatitis?
Important Highlights from Our Discussion:
The primary function of the prostate gland is to produce fluid that nourishes and helps transport sperm.
Prostatitis, an inflammation of the prostate, can cause symptoms such as pelvic discomfort, urinary discomfort, and sexual problems.
About 10%-15% of men are affected by prostatitis at some point in their lives, predominantly those under the age of 50.
If left untreated, prostatitis can lead to chronic complications like recurrent urinary tract infections and may slightly increase the risk of prostate cancer.
The primary cause of prostatitis is a bacterial infection, leading to acute bacterial prostatitis, while the second most common cause is non-bacterial, resulting in Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome (CPPS).
Diagnosis of prostatitis involves patient history taking, a Digital Rectal Examination (DRE), and laboratory tests such as urine culture or semen analysis.
First-line treatment for bacterial prostatitis involves antibiotics like fluoroquinolones or trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, with duration depending on whether the condition is acute or chronic.
In cases of resistance or ineffective first-line treatment, other culture-sensitive antibiotics may be employed, and in rare, unresponsive chronic cases, surgical intervention may be considered
 0:11:57
0:11:57
 0:03:39
0:03:39
 0:14:32
0:14:32
 0:05:57
0:05:57
 0:06:29
0:06:29
 0:04:43
0:04:43
 0:01:16
0:01:16
 0:02:06
0:02:06
 1:02:05
1:02:05
 0:07:40
0:07:40
 0:02:20
0:02:20
 0:04:16
0:04:16
 0:07:02
0:07:02
 0:00:38
0:00:38
 0:08:37
0:08:37
 0:00:20
0:00:20
 0:06:06
0:06:06
 0:00:44
0:00:44
 0:05:59
0:05:59
 0:04:39
0:04:39
 0:01:13
0:01:13
 0:00:38
0:00:38
 0:06:51
0:06:51
 0:01:38
0:01:38