filmov
tv
Understanding Ulnar Nerve Facts

Показать описание
"Essential Insights on the Ulnar Nerve: A Comprehensive Guide"
Join this channel to support the channel
Title: Key Facts About the Ulnar Nerve
This is a summary of this long video
Causes of Ulnar Nerve Compression: Dupuytren's contracture can lead to ulnar nerve compression, commonly between the two heads of the flexor carpi ulnaris. Various other causes exist.
Origin and Associated Conditions: The ulnar nerve originates from the C8-T1 nerve roots, also implicated in Horner's syndrome, indicating a poor prognosis for brachial plexus injuries.
Muscle Wasting and Prognosis: Wasting of the first dorsal interosseous muscle indicates ulnar nerve injury, which differs from wasting of the thenar muscles associated with the median nerve.
Anatomical Variations: Martin-Gruber anastomosis is an anomaly between the median and ulnar nerves that can complicate clinical and EMG diagnoses.
Elbow Flexion and Cubital Tunnel Syndrome: Elbow flexion can reduce the cubital tunnel size by 40%, potentially contributing to cubital tunnel syndrome.
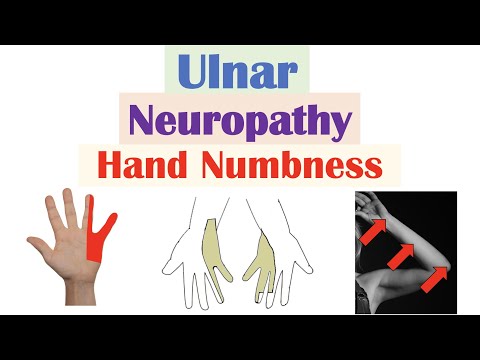
Dorsal Cutaneous Branch Importance: A high ulnar nerve lesion, like at the elbow, results in loss of sensation in the dorsal hand, affecting one and a half fingers.
Hand Clawing: A low ulnar nerve lesion (below the elbow) can cause hand clawing without affecting dorsal hand sensation.
Wartenberg's Sign vs. Syndrome: Wartenberg's sign involves loss of adduction in the fifth finger, while Wartenberg's syndrome is related to superficial radial nerve entrapment.
Pinching and Pronation: Froment's sign demonstrates that a loss of adduction due to ulnar nerve damage affects thumb pinching ability.
Tinel's Sign: Tapping the elbow area can reveal ulnar nerve irritation, which is critical in differential diagnoses, such as between cubital tunnel syndrome and medial epicondylitis.
Differential Diagnosis: Conditions like thoracic outlet syndrome and disc herniation can mimic cubital tunnel symptoms.
Injury and Children: Extension-type injuries can impact the anterior interosseous nerve in children, while flexion-type injuries often affect the ulnar nerve and may require surgical intervention.
Join this channel to support the channel
Title: Key Facts About the Ulnar Nerve
This is a summary of this long video
Causes of Ulnar Nerve Compression: Dupuytren's contracture can lead to ulnar nerve compression, commonly between the two heads of the flexor carpi ulnaris. Various other causes exist.
Origin and Associated Conditions: The ulnar nerve originates from the C8-T1 nerve roots, also implicated in Horner's syndrome, indicating a poor prognosis for brachial plexus injuries.
Muscle Wasting and Prognosis: Wasting of the first dorsal interosseous muscle indicates ulnar nerve injury, which differs from wasting of the thenar muscles associated with the median nerve.
Anatomical Variations: Martin-Gruber anastomosis is an anomaly between the median and ulnar nerves that can complicate clinical and EMG diagnoses.
Elbow Flexion and Cubital Tunnel Syndrome: Elbow flexion can reduce the cubital tunnel size by 40%, potentially contributing to cubital tunnel syndrome.
Dorsal Cutaneous Branch Importance: A high ulnar nerve lesion, like at the elbow, results in loss of sensation in the dorsal hand, affecting one and a half fingers.
Hand Clawing: A low ulnar nerve lesion (below the elbow) can cause hand clawing without affecting dorsal hand sensation.
Wartenberg's Sign vs. Syndrome: Wartenberg's sign involves loss of adduction in the fifth finger, while Wartenberg's syndrome is related to superficial radial nerve entrapment.
Pinching and Pronation: Froment's sign demonstrates that a loss of adduction due to ulnar nerve damage affects thumb pinching ability.
Tinel's Sign: Tapping the elbow area can reveal ulnar nerve irritation, which is critical in differential diagnoses, such as between cubital tunnel syndrome and medial epicondylitis.
Differential Diagnosis: Conditions like thoracic outlet syndrome and disc herniation can mimic cubital tunnel symptoms.
Injury and Children: Extension-type injuries can impact the anterior interosseous nerve in children, while flexion-type injuries often affect the ulnar nerve and may require surgical intervention.
Комментарии
 0:14:51
0:14:51
 0:15:11
0:15:11
 0:05:43
0:05:43
 0:05:26
0:05:26
 0:04:19
0:04:19
 0:00:45
0:00:45
 0:10:59
0:10:59
 0:00:17
0:00:17
 0:00:23
0:00:23
 0:00:19
0:00:19
 0:02:26
0:02:26
 0:00:31
0:00:31
 0:00:29
0:00:29
 0:08:57
0:08:57
 0:01:39
0:01:39
 0:01:00
0:01:00
 0:00:50
0:00:50
 0:00:31
0:00:31
 0:00:50
0:00:50
 0:00:52
0:00:52
 0:00:25
0:00:25
 0:00:50
0:00:50
 0:00:58
0:00:58
 0:02:20
0:02:20