filmov
tv
PCB file importing
Показать описание
SMT50 pick-and-place videos with english translations.
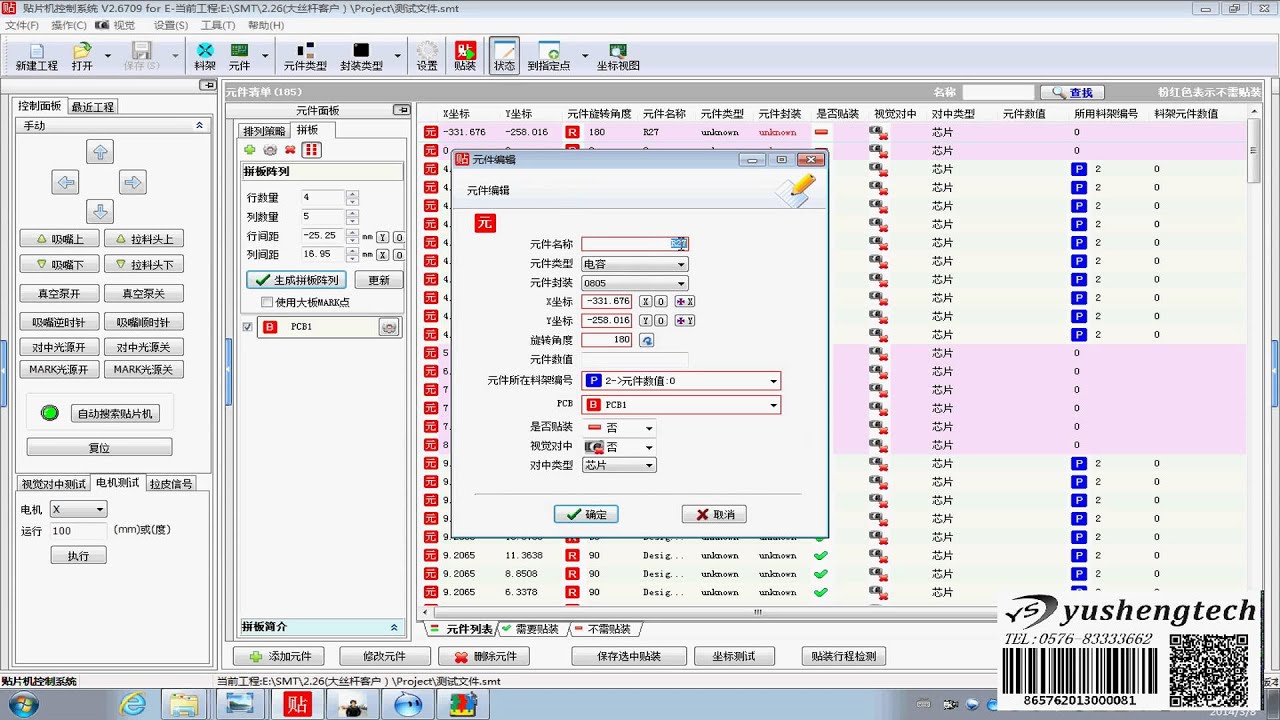
The SMT50 is a cheap, vision enabled pick-and-place machine from China. After buying this machine I had english transcripts created for its instructional videos to help me understand how to use it. Because I like the machine, and because these videos might help others, I’m putting the transcripts and videos here. The transcripts are the first comment with time links into the video for easy reference.
The SMT50 is a cheap, vision enabled pick-and-place machine from China. After buying this machine I had english transcripts created for its instructional videos to help me understand how to use it. Because I like the machine, and because these videos might help others, I’m putting the transcripts and videos here. The transcripts are the first comment with time links into the video for easy reference.
PCB file importing
ALTIUM PCB rules file import
Convert gerber file to pcb file in Altium Designer Software
Importing Altium Designer PCB files to Circuit Studio
Two Ways to Convert Gerber Files to a PCB Layout #pcbdesign #altium #altiumdesigner
Importing Circuit Studio PCB to Altium Designer
Altium intro #21: Importing schematics into PCB
Cadence PCB Import File Manager
How to Convert Gerber to PCB
Import EAGLE design files into SolidWorks PCB - CAD Microsolutions
Video Tech Tip: Importing STEP files in SOLIDWORKS PCB 2016
How to Reverse Engineer a PCB from Gerber Files
Importing Eagle Schematic and PCB projects to DipTrace
Create Board Shape From DXF/DWG | PCB Layout
Altium Designer Tutorial 01 : How to Import 3D PCB Step file in Altium Designer
How to Import Symbol and Footprint Libraries Into Altium (.lia format)
Recreating a PCB From Fab Files: What do you need? #pcbdesign #electronics #altium
How I Reverse-Engineer Simple PCB Boards
How to open EasyEDA Source (.JSON) files and combine PCB and SCH files.
AD Tutorial 12:How to Change in AD PCB board Size,Import 3d Step file ,Configure PCB Mounting Holes.
OrCAD X Quick Tips - Import Altium PCB
Import PCB Footprints Into Cadence Allegro & OrCAD Layout
[Import 06] Allegro PCB Designer
Cadence PCB Allegro Import Boardstation
Комментарии
 0:22:54
0:22:54
 0:01:20
0:01:20
 0:04:25
0:04:25
 0:06:17
0:06:17
 0:00:33
0:00:33
 0:05:05
0:05:05
 0:03:13
0:03:13
 0:03:15
0:03:15
 0:02:32
0:02:32
 0:00:56
0:00:56
 0:01:24
0:01:24
 0:26:36
0:26:36
 0:06:19
0:06:19
 0:02:51
0:02:51
 0:05:36
0:05:36
 0:01:57
0:01:57
 0:00:41
0:00:41
 0:05:14
0:05:14
 0:04:47
0:04:47
 0:21:31
0:21:31
 0:01:01
0:01:01
 0:01:37
0:01:37
![[Import 06] Allegro](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/pEeYjMvwiSQ/hqdefault.jpg) 0:01:44
0:01:44
 0:01:15
0:01:15