filmov
tv
What is ASCII, Unicode, UTF-8 in simple terms

Показать описание
This video explains how electronic devices store text using ASCII or Unicode encoding and delves into a string representation.
Computers store information in binary format, introducing the need to convert strings into binary. So, a mapping system is required. This is where ASCII comes to solve this challenge.
The limitations of ASCII, including its support for only 128 characters and the English alphabet, are discussed in the context of historical computer storage constraints. The emergence of Unicode in the 1990s as a broader character encoding standard, overcoming ASCII's limitations, is explained.
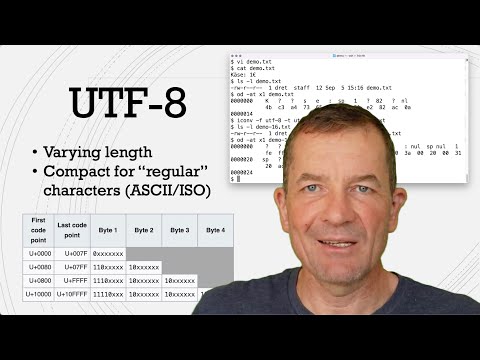
Unicode supports a wider range of characters and uses hexadecimal representation for convenience. It introduces UTF-8, UTF-16, and UTF-32 encoding standards, each with specific use cases. UTF-8, a variable-length encoding, is the most popular, while UTF-16 and UTF-32 are used for specific purposes such as optimizing string operations.
Computers store information in binary format, introducing the need to convert strings into binary. So, a mapping system is required. This is where ASCII comes to solve this challenge.
The limitations of ASCII, including its support for only 128 characters and the English alphabet, are discussed in the context of historical computer storage constraints. The emergence of Unicode in the 1990s as a broader character encoding standard, overcoming ASCII's limitations, is explained.
Unicode supports a wider range of characters and uses hexadecimal representation for convenience. It introduces UTF-8, UTF-16, and UTF-32 encoding standards, each with specific use cases. UTF-8, a variable-length encoding, is the most popular, while UTF-16 and UTF-32 are used for specific purposes such as optimizing string operations.
 0:03:29
0:03:29
 0:10:54
0:10:54
 0:09:37
0:09:37
 0:09:37
0:09:37
 0:05:59
0:05:59
 0:09:24
0:09:24
 0:02:31
0:02:31
 0:10:41
0:10:41
 0:19:07
0:19:07
 0:08:28
0:08:28
 0:17:18
0:17:18
 0:09:11
0:09:11
 0:09:43
0:09:43
 0:24:52
0:24:52
 0:03:16
0:03:16
 0:14:34
0:14:34
 0:29:03
0:29:03
 0:14:36
0:14:36
 0:05:41
0:05:41
 0:09:11
0:09:11
 0:07:56
0:07:56
 0:12:49
0:12:49
 0:01:30
0:01:30
 0:10:32
0:10:32