filmov
tv
Sulfasalazine Mechanism and Side Effects

Показать описание
Sulfasalazine is a medication that is primarily used to treat inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD), such as ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease. It is an example of a disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drug (DMARD) that is also used to manage certain types of rheumatoid arthritis.
Here are some key points about sulfasalazine:
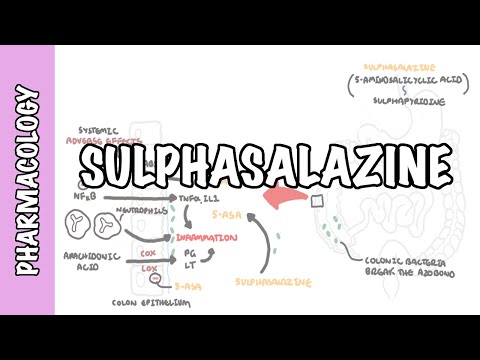
1. Composition: Sulfasalazine is composed of two main components: sulfapyridine and 5-aminosalicylic acid (also known as mesalamine). These components are linked together to form the drug.
2. Mechanism of Action: The exact mechanism of action of sulfasalazine is not fully understood, but it is believed to work through its breakdown products. Sulfapyridine has anti-inflammatory properties, while mesalamine is thought to directly affect inflammation in the intestines. These actions help to reduce the symptoms of inflammatory bowel diseases.
3. Indications: Sulfasalazine is primarily used to treat mild to moderate ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease. It can also be used to manage rheumatoid arthritis, particularly in cases where other treatments have not been effective.
4. Administration: Sulfasalazine is usually taken orally in the form of tablets or capsules. The dosage and frequency of administration can vary depending on the condition being treated and the individual patient's response to the medication.
5. Side Effects: Common side effects of sulfasalazine can include gastrointestinal symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal discomfort. Some individuals may also experience headaches, skin reactions, and decreased appetite. Additionally, a potential side effect is sensitivity to sunlight (photosensitivity).
6. Monitoring: Regular monitoring is important while taking sulfasalazine. This may involve blood tests to check for any adverse effects on the liver or blood cells.
7. Contraindications: Sulfasalazine should be avoided by individuals who are allergic to sulfa drugs or salicylates. It is also contraindicated in certain cases of porphyria and urinary tract obstruction.
8. Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: Sulfasalazine use during pregnancy and breastfeeding should be discussed with a healthcare provider, as there may be potential risks to the fetus or infant.
9. Interactions: Sulfasalazine can interact with other medications, so it's important to inform your healthcare provider about all the medications and supplements you are taking.
10. Long-Term Use: Long-term use of sulfasalazine may require ongoing monitoring for potential side effects and effectiveness in managing the underlying condition.
As with any medication, it's crucial to consult a healthcare professional before starting or stopping sulfasalazine treatment. They can provide personalized guidance based on your medical history, current health status, and specific needs.
Here are some key points about sulfasalazine:
1. Composition: Sulfasalazine is composed of two main components: sulfapyridine and 5-aminosalicylic acid (also known as mesalamine). These components are linked together to form the drug.
2. Mechanism of Action: The exact mechanism of action of sulfasalazine is not fully understood, but it is believed to work through its breakdown products. Sulfapyridine has anti-inflammatory properties, while mesalamine is thought to directly affect inflammation in the intestines. These actions help to reduce the symptoms of inflammatory bowel diseases.
3. Indications: Sulfasalazine is primarily used to treat mild to moderate ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease. It can also be used to manage rheumatoid arthritis, particularly in cases where other treatments have not been effective.
4. Administration: Sulfasalazine is usually taken orally in the form of tablets or capsules. The dosage and frequency of administration can vary depending on the condition being treated and the individual patient's response to the medication.
5. Side Effects: Common side effects of sulfasalazine can include gastrointestinal symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal discomfort. Some individuals may also experience headaches, skin reactions, and decreased appetite. Additionally, a potential side effect is sensitivity to sunlight (photosensitivity).
6. Monitoring: Regular monitoring is important while taking sulfasalazine. This may involve blood tests to check for any adverse effects on the liver or blood cells.
7. Contraindications: Sulfasalazine should be avoided by individuals who are allergic to sulfa drugs or salicylates. It is also contraindicated in certain cases of porphyria and urinary tract obstruction.
8. Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: Sulfasalazine use during pregnancy and breastfeeding should be discussed with a healthcare provider, as there may be potential risks to the fetus or infant.
9. Interactions: Sulfasalazine can interact with other medications, so it's important to inform your healthcare provider about all the medications and supplements you are taking.
10. Long-Term Use: Long-term use of sulfasalazine may require ongoing monitoring for potential side effects and effectiveness in managing the underlying condition.
As with any medication, it's crucial to consult a healthcare professional before starting or stopping sulfasalazine treatment. They can provide personalized guidance based on your medical history, current health status, and specific needs.
Комментарии
 0:04:06
0:04:06
 0:01:48
0:01:48
 0:03:33
0:03:33
 0:05:37
0:05:37
 0:01:49
0:01:49
 0:03:05
0:03:05
 0:10:23
0:10:23
 0:01:27
0:01:27
 0:05:05
0:05:05
 0:05:42
0:05:42
 0:12:59
0:12:59
 0:01:59
0:01:59
 0:07:51
0:07:51
 0:05:33
0:05:33
 0:02:25
0:02:25
 0:03:37
0:03:37
 0:00:42
0:00:42
 0:06:37
0:06:37
 0:04:17
0:04:17
 0:03:18
0:03:18
 0:10:58
0:10:58
 0:08:45
0:08:45
 0:04:31
0:04:31
 0:01:32
0:01:32