filmov
tv
Diagnosis Of Celiac Disease - Quick Bites Internal medicine (Gastroenterology)

Показать описание
Celiac Disease: Overview
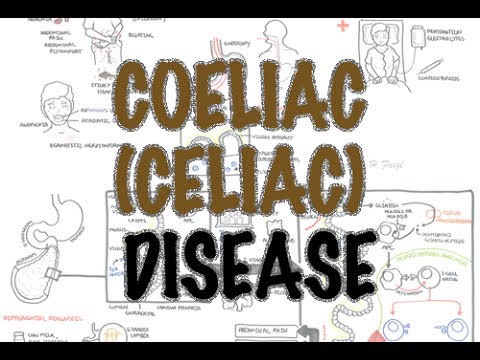
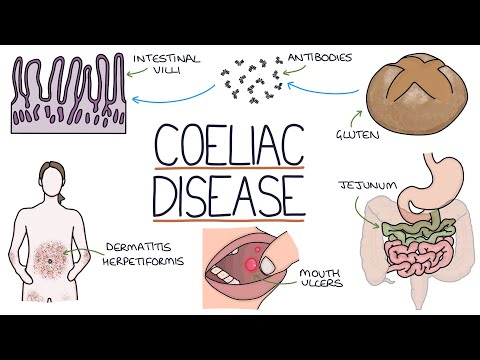
Definition: Celiac disease, also known as celiac sprue or nontropical sprue, is a common autoimmune condition characterized by an inappropriate immune response to gluten, a protein found in various grains, particularly wheat. This immune response leads to damage in the small intestine, resulting in malabsorption of nutrients.
Epidemiology: Celiac disease is relatively common and can affect individuals of all ages. It is associated with specific human leukocyte antigen (HLA) variants that predispose individuals to the condition. It often occurs in individuals with other autoimmune disorders.
Pathophysiology: The underlying pathophysiology involves a combination of gluten intolerance, which triggers an autoimmune reaction, and the production of autoantibodies that target tissue transglutaminase, primarily in the proximal small intestine. This immune response leads to inflammation and damage to the intestinal lining.
Clinical Presentation: Patients with celiac disease may present with a range of symptoms, including changes in bowel habits (such as diarrhea or constipation) and symptoms related to malabsorption, such as fatigue, weight loss, and vitamin deficiencies. The clinical presentation can vary widely among individuals.
Diagnostic Evaluation:
Antibody Testing: Celiac disease can be detected through blood tests that assess the presence of specific antibodies associated with the condition, including anti-tissue transglutaminase antibodies (anti-tTG) and anti-endomysial antibodies (EMA).
Endoscopic Biopsy: To confirm the diagnosis, an endoscopic biopsy of the small intestine is often necessary. Histopathological findings typically include villous atrophy and crypt hyperplasia, which are indicative of damage to the intestinal lining.
Treatment: The primary and most effective treatment for celiac disease is a strict lifelong commitment to a gluten-free diet. Eliminating gluten from the diet helps prevent further immune-mediated damage to the small intestine and alleviates symptoms.
Prognosis: With adherence to a gluten-free diet, the prognosis for individuals with celiac disease is generally very good. This dietary management can lead to the resolution of symptoms and prevent long-term complications. However, ongoing monitoring and dietary compliance are essential to maintaining good health.
Complications: Untreated celiac disease can lead to various complications, including malnutrition, osteoporosis, infertility, and an increased risk of certain malignancies, such as intestinal lymphoma. Early diagnosis and adherence to a gluten-free diet can reduce the risk of these complications.
#fmge #fmgevideos #rapidrevisionfmge #fmgejan2023 #mbbslectures #nationalexitexam #nationalexittest #neetpg #usmlepreparation #usmlestep1 #fmge #usmle #drgbhanuprakash #medicalstudents #medicalstudent #medicalcollege #neetpg2023 #usmleprep #usmlevideos #usmlestep1videos #medicalstudents #neetpgvideos #celiacdisease #internalmedicine #medicine_review #medicinereview #usmlestep2ck
 0:13:59
0:13:59
 0:13:23
0:13:23
 0:15:23
0:15:23
 0:06:23
0:06:23
 0:15:06
0:15:06
 0:03:30
0:03:30
 0:07:52
0:07:52
 0:01:52
0:01:52
 0:02:34
0:02:34
 0:25:58
0:25:58
 0:02:37
0:02:37
 0:14:20
0:14:20
 0:05:10
0:05:10
 0:00:31
0:00:31
 0:08:53
0:08:53
 0:06:26
0:06:26
 0:18:33
0:18:33
 0:55:12
0:55:12
 0:07:32
0:07:32
 0:11:13
0:11:13
 0:15:38
0:15:38
 0:14:31
0:14:31
 0:02:47
0:02:47
 0:07:07
0:07:07