filmov
tv
Parts Of An Atom | Properties of Matter | Chemistry | FuseSchool

Показать описание
Parts Of An Atom | Properties of Matter | Chemistry | FuseSchool
Learn about the parts of an atom, their mass, and their charge, in this video.
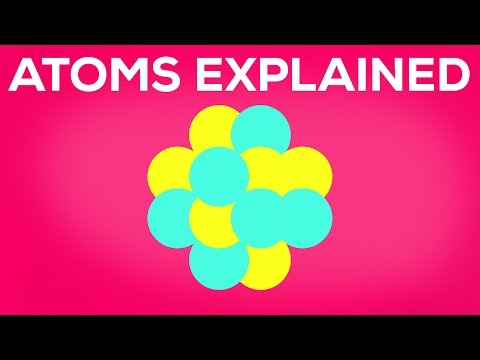
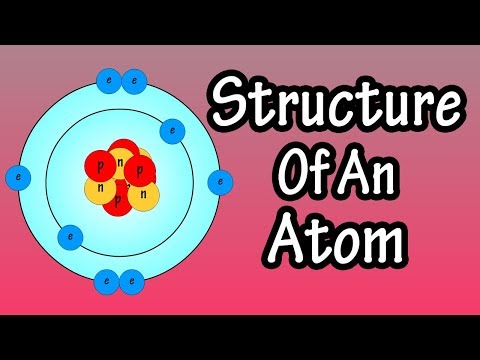
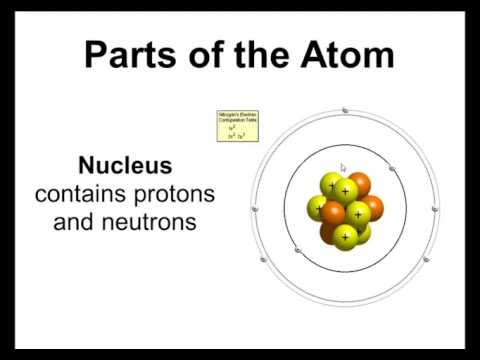
We already know that atoms are really small but we can get smaller. If we zoom into an atom we find that is made up of protons, neutrons and electrons and a lot of empty space.
Imagine an Olympic swimming pool: 50 metres wide, this is our atom. At the centre of our atom is the nucleus. The nucleus is made up of protons and neutrons. But if we jumped into the pool to find the nucleus it would be pretty much impossible because it is a size of a grain of sand.
Around the nucleus you find that electrons are randomly whizzing around. The electrons are even smaller than protons and neutrons. So, say we only have two electrons in our atom. These would be randomly moving around our grain of sand in our 50 meter pool, just these two tiny, tiny electrons. So, what does that leave? a lot of empty space!
If we think about the minuscule scale that we're talking about, the constituents of an atom must have a minuscule scale to match. If we were to weigh protons, we would need 600 sextillion to just weigh one gram so one proton would have a very very small mass. The same is true for neutrons and electrons. This is why we weigh them in relation to each other.
We assign the mass of a proton as one. The neutron has a similar mass to protons and is also given the mass of one. The electron, however, is much lighter and has a mass of 1 over 1840. If we think about how heavy the mass of the protons and neutrons are in relation to the electrons it is clear to see that the mass of an atom is concentrated at the nucleus.
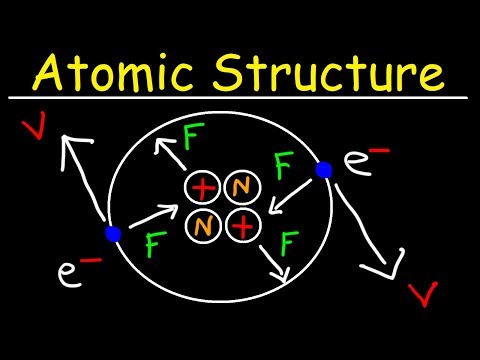
Protons, neutrons and electrons also have a charge associated with them. Protons are positive, neutrons are neutral and electrons are negative. The charge of an atom is always neutral. This means there must be the same amount of protons as there are electrons in an atom. The number of neutrons can vary and they do not affect the charge of the entire atom.
SUPPORT US ON PATREON
SUBSCRIBE to the FuseSchool YouTube channel for many more educational videos. Our teachers and animators come together to make fun & easy-to-understand videos in Chemistry, Biology, Physics, Maths & ICT.
These videos can be used in a flipped classroom model or as a revision aid.
Learn about the parts of an atom, their mass, and their charge, in this video.
We already know that atoms are really small but we can get smaller. If we zoom into an atom we find that is made up of protons, neutrons and electrons and a lot of empty space.
Imagine an Olympic swimming pool: 50 metres wide, this is our atom. At the centre of our atom is the nucleus. The nucleus is made up of protons and neutrons. But if we jumped into the pool to find the nucleus it would be pretty much impossible because it is a size of a grain of sand.
Around the nucleus you find that electrons are randomly whizzing around. The electrons are even smaller than protons and neutrons. So, say we only have two electrons in our atom. These would be randomly moving around our grain of sand in our 50 meter pool, just these two tiny, tiny electrons. So, what does that leave? a lot of empty space!
If we think about the minuscule scale that we're talking about, the constituents of an atom must have a minuscule scale to match. If we were to weigh protons, we would need 600 sextillion to just weigh one gram so one proton would have a very very small mass. The same is true for neutrons and electrons. This is why we weigh them in relation to each other.
We assign the mass of a proton as one. The neutron has a similar mass to protons and is also given the mass of one. The electron, however, is much lighter and has a mass of 1 over 1840. If we think about how heavy the mass of the protons and neutrons are in relation to the electrons it is clear to see that the mass of an atom is concentrated at the nucleus.
Protons, neutrons and electrons also have a charge associated with them. Protons are positive, neutrons are neutral and electrons are negative. The charge of an atom is always neutral. This means there must be the same amount of protons as there are electrons in an atom. The number of neutrons can vary and they do not affect the charge of the entire atom.
SUPPORT US ON PATREON
SUBSCRIBE to the FuseSchool YouTube channel for many more educational videos. Our teachers and animators come together to make fun & easy-to-understand videos in Chemistry, Biology, Physics, Maths & ICT.
These videos can be used in a flipped classroom model or as a revision aid.
Комментарии
 0:02:24
0:02:24
 0:04:06
0:04:06
 0:01:44
0:01:44
 0:06:45
0:06:45
 0:04:00
0:04:00
 0:12:15
0:12:15
 0:04:58
0:04:58
 0:02:20
0:02:20
 0:03:09
0:03:09
 0:07:17
0:07:17
 0:04:14
0:04:14
 0:04:23
0:04:23
 0:09:49
0:09:49
 0:00:48
0:00:48
 0:05:35
0:05:35
 0:04:42
0:04:42
 0:07:44
0:07:44
 0:05:35
0:05:35
 0:01:32
0:01:32
 0:05:22
0:05:22
 0:11:45
0:11:45
 0:30:31
0:30:31
 0:03:36
0:03:36
 0:04:42
0:04:42