filmov
tv
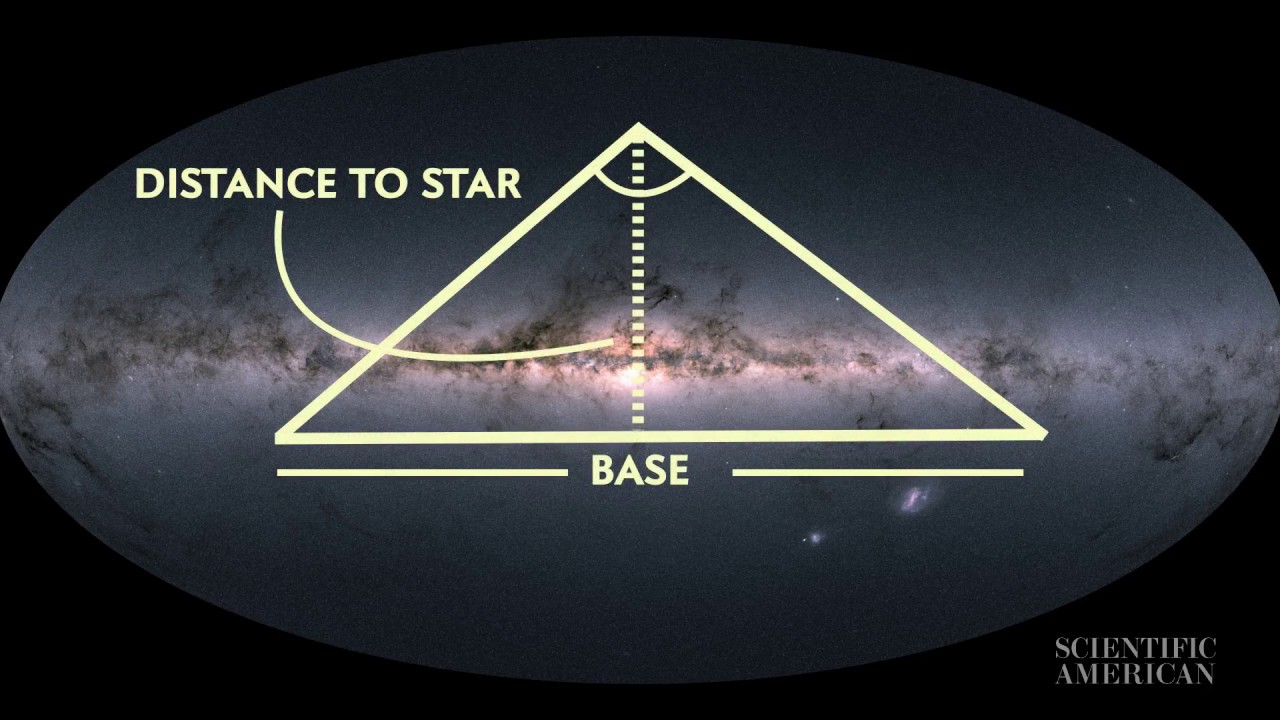
How Do We Measure the Distance to Stars?
Показать описание
The answer lies in the tiny shifts we see in a star's position as Earth revolves around the sun.
How Do We Measure How Big the Universe Is?
How Do We Measure the Distance to Stars?
How Do We Measure The Age of The Universe?
Light seconds, light years, light centuries: How to measure extreme distances - Yuan-Sen Ting
How To Measure The Tiniest Forces In The Universe
How We Measure the World - with Michael de Podesta
How did we measure the fastest speed there is? | The History of the Speed of Light Part I
How Do We Measure the Inter-Pupillary Distance
Laser Distance Meter Review & Test– What Can It Do? Inkerma
How Do You Measure the Size of the Universe?
How to Measure the Stars
Why sailors measure in knots
Measurement/how to measure without a ruler 📏/inches measuring with fingers
How do Scientists Measure a Measuring Tape? #Tapetunnel #accuracy #measurement #tapemeasure #nist
How do you measure the age of a star? | Science News
Beginner's Guide: How to Read a Metric Tape Measure Step-by-Step
How to Read a Tape Measure #measuringtape #tapemeasure #shorts
How Do We Measure the Distance of Stars?
We Can't Measure* Distance In Outer Space!
How can countries measure the well-being of their citizens?
How Will You Measure Your Life? Clay Christensen at TEDxBoston
Your THUMB can measure distance
How to measure your bra size
Finally: How to measure your inseam accurately!
Комментарии
 0:11:14
0:11:14
 0:02:16
0:02:16
 0:01:36
0:01:36
 0:05:29
0:05:29
 0:15:34
0:15:34
 0:34:05
0:34:05
 0:24:26
0:24:26
 0:03:59
0:03:59
 0:03:38
0:03:38
 0:06:37
0:06:37
 0:03:09
0:03:09
 0:00:57
0:00:57
 0:00:31
0:00:31
 0:00:45
0:00:45
 0:06:14
0:06:14
 0:04:34
0:04:34
 0:00:11
0:00:11
 0:09:52
0:09:52
 0:21:25
0:21:25
 0:02:24
0:02:24
 0:19:31
0:19:31
 0:00:39
0:00:39
 0:01:00
0:01:00
 0:00:14
0:00:14