filmov
tv
Introduction to Embryology - Fertilisation to Gastrulation (Easy to Understand)

Показать описание
If you find embryology difficult to understand, then this should be the first video you watch. This video covers the basic concepts from ovulation to the formation of the trilaminar germ disc (which will turn into YOU!).
Post any questions you have about the video below, I read all the comments:
--------------------------------
Recommended Text
--------------------------------
----------------------------------------
Interact With Dr. Minass!
----------------------------------------
Post - Address to:
Minass
Parcel Locker 10106 04448
59 Penshurst Street
Willoughby, NSW
Australia 2068
SUMMARY OF VIDEO:
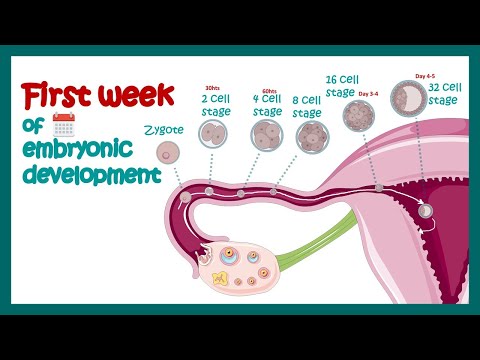
First week of development: Ovulation to Implantation
1. After ovulation the oocyte is transported through the uterine tube.
2. Fertilisation (fusion of a sperm with the oocyte) occurs in the ampulla of the oviduct. For fertilisation to occur, both capacitation and acrosome reaction occur (not explained in video but important to know).
3. Cleavage and blastocyst formation occur.
4. Implantation into the uterine wall.
Second week of development: Bilaminar Germ Disc
1. Trophoblast differentiates into the cytotrophoblast and the syncytiotrophoblast.
2. Epiblast and hypoblast layers develop.
3. Small cavities form the amniotic cavity and yolk sac.
4. Blastocyst completely embedded in the uterus, but it produces a slight protrusion into the lumen of the uterus.
5. Syncytiotrophoblast penetrates deeper and erode the endothelial lining of the maternal capillaries. These capillaries are congested and dilated (sinusoids).
6. Uteroplacental circulation is established.
Third week of development: Trilaminar Germ Disc
1. Gastrulation occurs, beginning with the appearance of the primitive streak.
2. Epiblast cells move inward (invaginate) to form new cell layers, the endoderm and the mesoderm.
3. Cells that do not migrate through the streak but remain in the epiblast form ectoderm.
Note: the epiblast gives rise to all three germ layers, and these layers form all of the tissues and organs.
MORE EMBRYOLOGY:
Embryology of the Heart:
Embryology of the CNS:
Embryology of the Kidney:
Post any questions you have about the video below, I read all the comments:
--------------------------------
Recommended Text
--------------------------------
----------------------------------------
Interact With Dr. Minass!
----------------------------------------
Post - Address to:
Minass
Parcel Locker 10106 04448
59 Penshurst Street
Willoughby, NSW
Australia 2068
SUMMARY OF VIDEO:
First week of development: Ovulation to Implantation
1. After ovulation the oocyte is transported through the uterine tube.
2. Fertilisation (fusion of a sperm with the oocyte) occurs in the ampulla of the oviduct. For fertilisation to occur, both capacitation and acrosome reaction occur (not explained in video but important to know).
3. Cleavage and blastocyst formation occur.
4. Implantation into the uterine wall.
Second week of development: Bilaminar Germ Disc
1. Trophoblast differentiates into the cytotrophoblast and the syncytiotrophoblast.
2. Epiblast and hypoblast layers develop.
3. Small cavities form the amniotic cavity and yolk sac.
4. Blastocyst completely embedded in the uterus, but it produces a slight protrusion into the lumen of the uterus.
5. Syncytiotrophoblast penetrates deeper and erode the endothelial lining of the maternal capillaries. These capillaries are congested and dilated (sinusoids).
6. Uteroplacental circulation is established.
Third week of development: Trilaminar Germ Disc
1. Gastrulation occurs, beginning with the appearance of the primitive streak.
2. Epiblast cells move inward (invaginate) to form new cell layers, the endoderm and the mesoderm.
3. Cells that do not migrate through the streak but remain in the epiblast form ectoderm.
Note: the epiblast gives rise to all three germ layers, and these layers form all of the tissues and organs.
MORE EMBRYOLOGY:
Embryology of the Heart:
Embryology of the CNS:
Embryology of the Kidney:
Комментарии
 0:18:42
0:18:42
 0:17:37
0:17:37
 0:04:00
0:04:00
 0:04:53
0:04:53
 0:12:20
0:12:20
 0:23:10
0:23:10
 0:11:37
0:11:37
 1:13:17
1:13:17
 0:10:51
0:10:51
 0:02:03
0:02:03
 0:17:06
0:17:06
 0:03:35
0:03:35
 0:11:49
0:11:49
 0:37:36
0:37:36
 0:07:36
0:07:36
 0:13:29
0:13:29
 0:03:27
0:03:27
 0:06:34
0:06:34
 0:04:34
0:04:34
 0:08:53
0:08:53
 0:35:26
0:35:26
 0:04:21
0:04:21
 0:36:42
0:36:42
 0:04:53
0:04:53